Transit Gateway w/ BGP
| Goal | Utilize dynamic routing with Transit Gateway and FortiGates. |
| Task | Create attachment associations + propagations and configure FortiGate routes and firewall policies to allow secured traffic to pass. |
| Validation | Confirm outbound and east/west connectivity from EC2 Instance-A via Ping, HTTP, HTTPS. |
Introduction
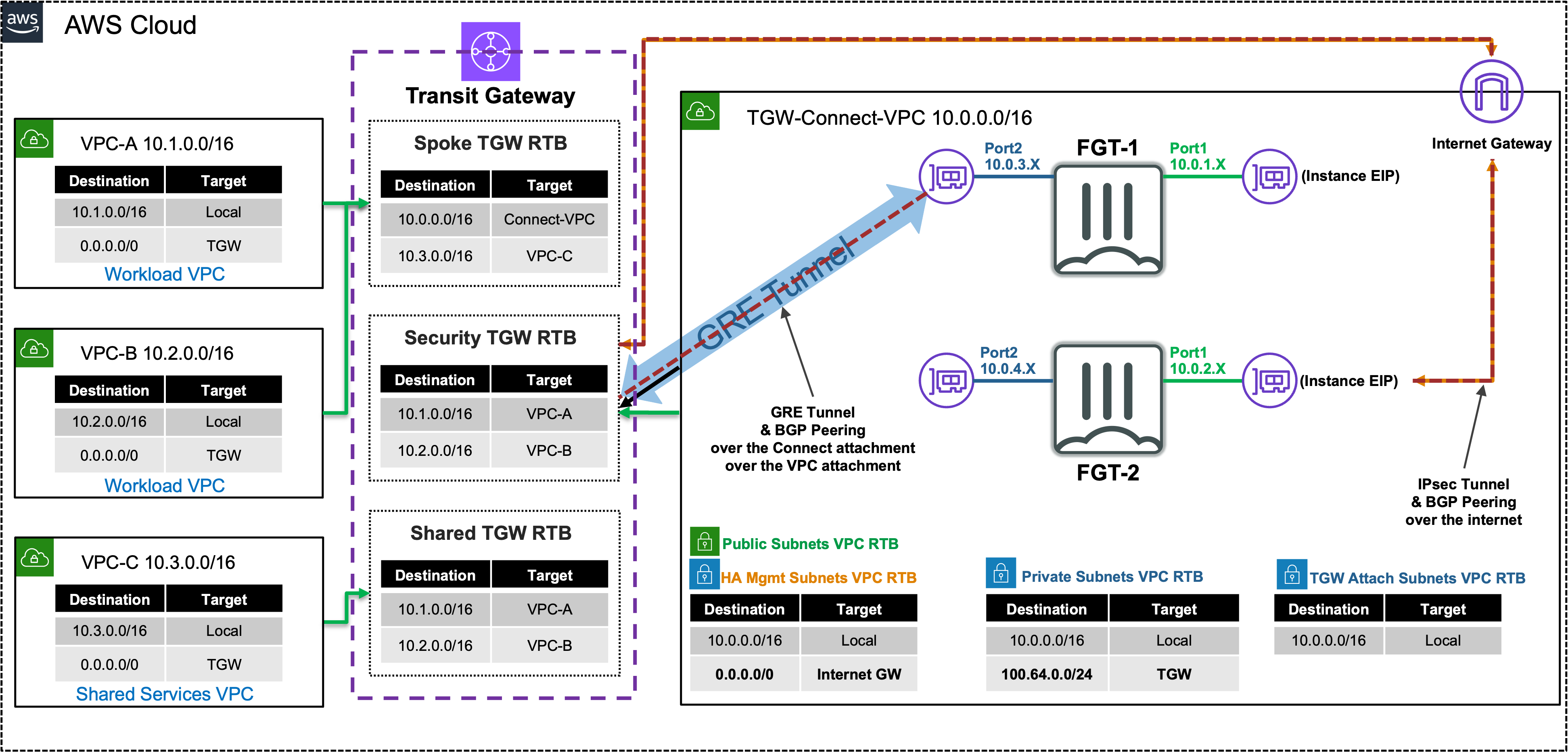
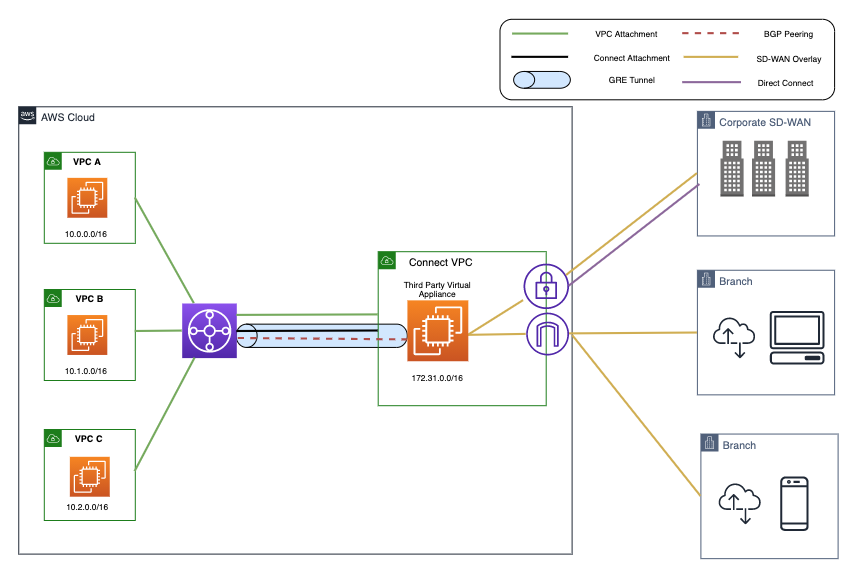
In this task, there are multiple VPCs in the same region that have one instance each. Transit Gateway is configured with multiple Transit Gateway Route Tables. You will need to create the appropriate VPC attachment associations and propagations to the correct TGW Route Tables, FW policy, and update BPG configuration on the independent FortiGates.
In this scenario the FortiGates are completely independent of each other (not clustered, nor sharing config/sessions, etc.) and are showing different connectivity options to attach remote locations to Transit Gateway. VPN attachments can be used to connect to any IPsec capable device located anywhere. TGW Connect attachments require a private path to reach a VM deployed in a VPC or HW/VM deployed on premise and must be reachable over Direct Connect (a dedicated, private circuit).
Summarized Steps (click to expand each for details)
0) Lab environment setup
1) Check the Transit Gateway Route Tables and confirm east/west is not working
2) Review FortiGate1’s GRE + BGP config and advertise a summary route to Transit Gateway
3) Test east/west connectivity from Instance-A to Instance-B and validate there is no internet connectivity
4) Let’s dig deeper to understand how all of this works
5) Review FortiGate2’s VPN and BGP configurations
6) Test secured egress connectivity from Instance-A through FortiGate2
7) Configure FortiGate1 with default-route-originate and a route-map as well
8) Test secured egress connectivity from Instance-A through FortiGate1
9) Lab environment teardown
Discussion Points
- TGW Connect & VPN attachments allow a simple means to connecting remote resources to TGW
- These attachment types are also helpful when dynamic routing is needed for a design
- Connect uses GRE + BGP to privately connect to an appliance reachable via Direct Connect or within a VPC
- VPN uses IPsec + BGP to publicly connect to an appliance reachable over the Internet
- TGW has a route evaluation priority to select the best path when multiple routes have the same CIDR
- TGW supports ECMP routing with routes from the same attachment type
- TGW is a stateless router which will result in asymmetric routing of traffic
- SNAT is required for flow symmetry to the correct FortiGate in Active-Active design
- Simple & scalable Active-Active for Ingress/Egress inspection
- Active-Active for East/West inspection possible with caveats
- Each TGW VPN connection (2x IPsec tunnels per connection) supports up to 2.5 Gbps
- Each TGW Connect peer supports up to 5 Gbps
- TGW supports multiple peers per TGW Connect attachment and multiple attachments to a single VPC
- TGW supports multiple VPN attachments to the same or different customer gateway (remote IPsec appliance)
- Jumbo frames (8500 bytes) are supported for all attachments except VPN (1500 bytes)
This concludes this task