AWS Command Line Basics
Lab Overview
The goal of this lab is to learn the basics of the AWS command line interface (CLI). You have already seen how you can use the AWS Web Console to create and manage cloud resouce. Everything you can do with the Web Console you can do with the CLI. One advantage of thbuild automation around performing tasks like creating users and fetching lists of virtual server.
Log into AWS Console
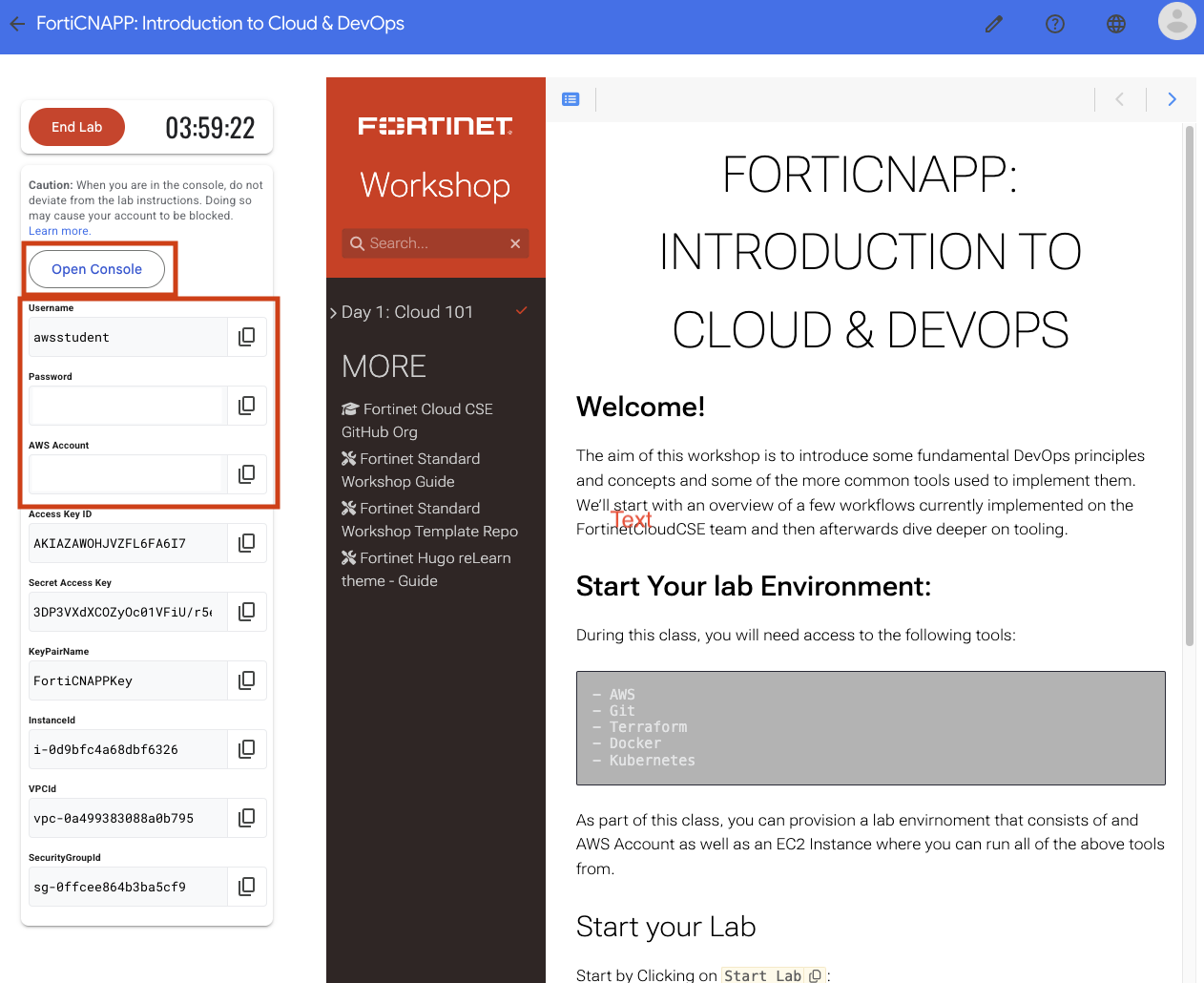
Before we can do anything you will need to get access AWS web console in your browser. The log in details for your lab provided AWS account are on the left hand of the lab. Each field has a copy link you can use.
Click on the Open Console link.
Copy/paste the Username, Password and click Sign In.
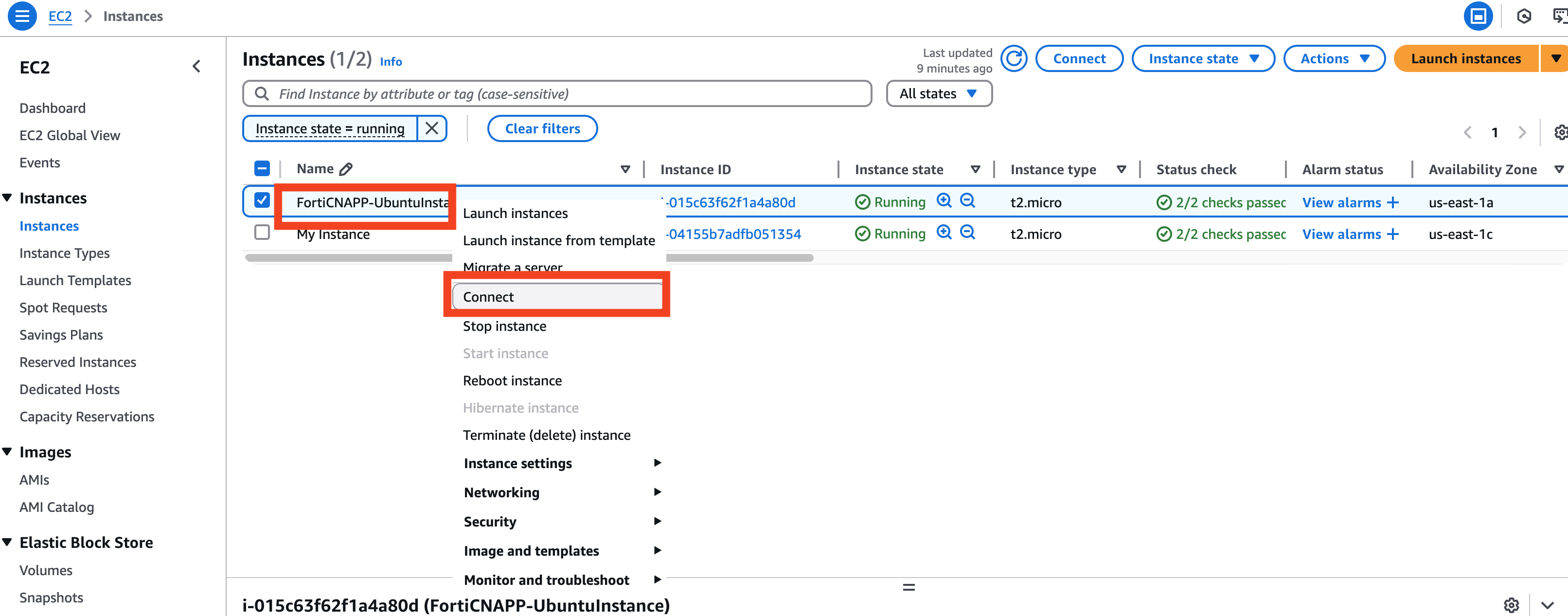
Conenect to FortiCNAPPUbuntu
Connect to the FortiCNAPPUbuntu Instance that was created automatically for you
Use the AWS CLI
The AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) is a tool that enables users to interact with AWS services using command-line commands. It provides a direct way to manage AWS resources without needing to use the AWS Management Console.
Installing AWS CLI
Before using AWS CLI, ensure it is installed on your EC2 instance. You can check if AWS CLI is installed with:
aws --versionIf it is not installed, install it using the following command (for Amazon Linux 2):
sudo apt update
sudo apt install unzip -y
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip -qq awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/installNow run :
aws --versionConfiguring AWS CLI
Once installed, you need to configure AWS CLI with your credentials. Use the following command:
aws configureYou will be prompted to enter:
- AWS Access Key ID
- AWS Secret Access Key
- Default Region Name (e.g.,
us-east-1,us-west-2) - Default Output Format (
json,text, ortable)
Use us-east-1
This stores the credentials in ~/.aws/credentials and the configuration in ~/.aws/config.
Basic AWS CLI Commands
Check Current AWS Identity
To verify the credentials are working, run:
aws sts get-caller-identityCheck Current AWS Identity
aws iam list-attached-role-policies --role-name us-east-1CloudLabRoleThis should return details about your IAM user or role.
List Available Regions
To see all AWS regions:
aws ec2 describe-regions --output tableEC2 Instance Management
List All EC2 Instances
aws ec2 describe-instancesPress q to exit back the terminal
aws ec2 describe-instances | jqaws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].[InstanceId,State.Name,PublicIpAddress]' --output jsonaws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].[InstanceId,State.Name,PublicIpAddress]' --output tableDynamically Extract Instance ID
Instead of manually specifying the instance ID, we can extract it dynamically:
INSTANCE_ID=$(aws ec2 describe-instances --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].InstanceId' --output text)
echo "Your Instance ID is: $INSTANCE_ID"S3 Bucket Operations
We will use a predefined S3 bucket: training-bucket-demo and a sample file: sample.txt
List All S3 Buckets
aws s3 lsIAM User and Role Management
List IAM Users
aws iam list-usersCreate a New IAM User
aws iam create-user --user-name trainee-userYour role does not allow you to create users
Conclusion
These are just a few essential AWS CLI commands to get started. The AWS CLI is powerful and can manage almost all AWS services directly from the terminal. To explore more, refer to the official AWS CLI documentation: