Terraform Fundamentals
In this lab you will learn the basics of DevOps using Terraform to provision cloud resources. To keep it simple you will access a virtual server running in AWS with the tools and configuration already setup. You will download a Infrastructure as Code (IaC) file that contains IaC code. You will then execute a few commands and two new virtual server, a virtual private network and networking will be setup. Finally you will confirm these resource exist in the AWS EC2 console.
Why use IaC tooling like Terraform
In the previous lab you used the AWS Web Console to deploy a single virtual server. This is often referred to as ClickOps. ClickOps is a great way to create a small set of resource for learning or testing. Click Ops is not a ideal way to create full production environments that may have many many services. Imagine you need to create a hundred virtual server spread out over availability zone and regions. This is where tools like IaC and Terraform come in.
Using Terraform you can define the cloud resources we want as code. Running Terraform will then create all those resources. This could be virtual server, networks, security groups, storage assets, users and much more. If later you need make change to those resources, update your IaC code and rerun Terraform to make those changes. Further if none of those resources are needed anymore you can have Terraform destroy them.
Terraform is part of modern software development movement know as DevOps. DevOps combines two seperate concerns operations and development. It allows these two teams, with different concerns, work together to achieve business objective faster.
Log into AWS Console
The log in details for your lab provided AWS account are on the left hand of the lab. Each field has a copy link you can use.
Click on the Open Console link.
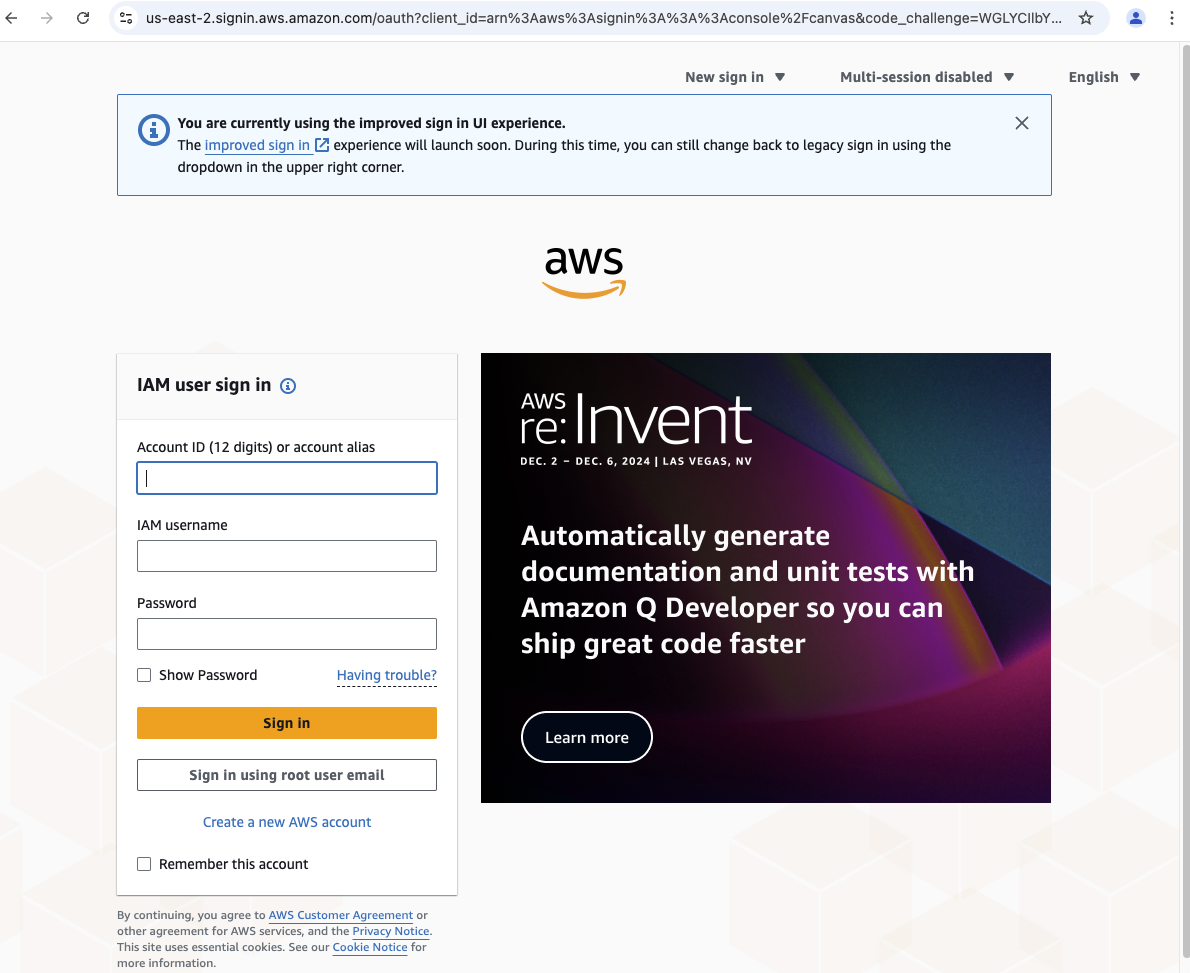
Copy/paste the Username, Password and click Sign In.
Access a Virtual Server running in EC2
EC2 is a AWS service that allows for easily creating virtual servers in the cloud. When moving from an on prem data center to the cloud, EC2 is often part of a ’lift and shift’ project. Each virtual server in EC2 is analogous to a physical server running in your own data center.
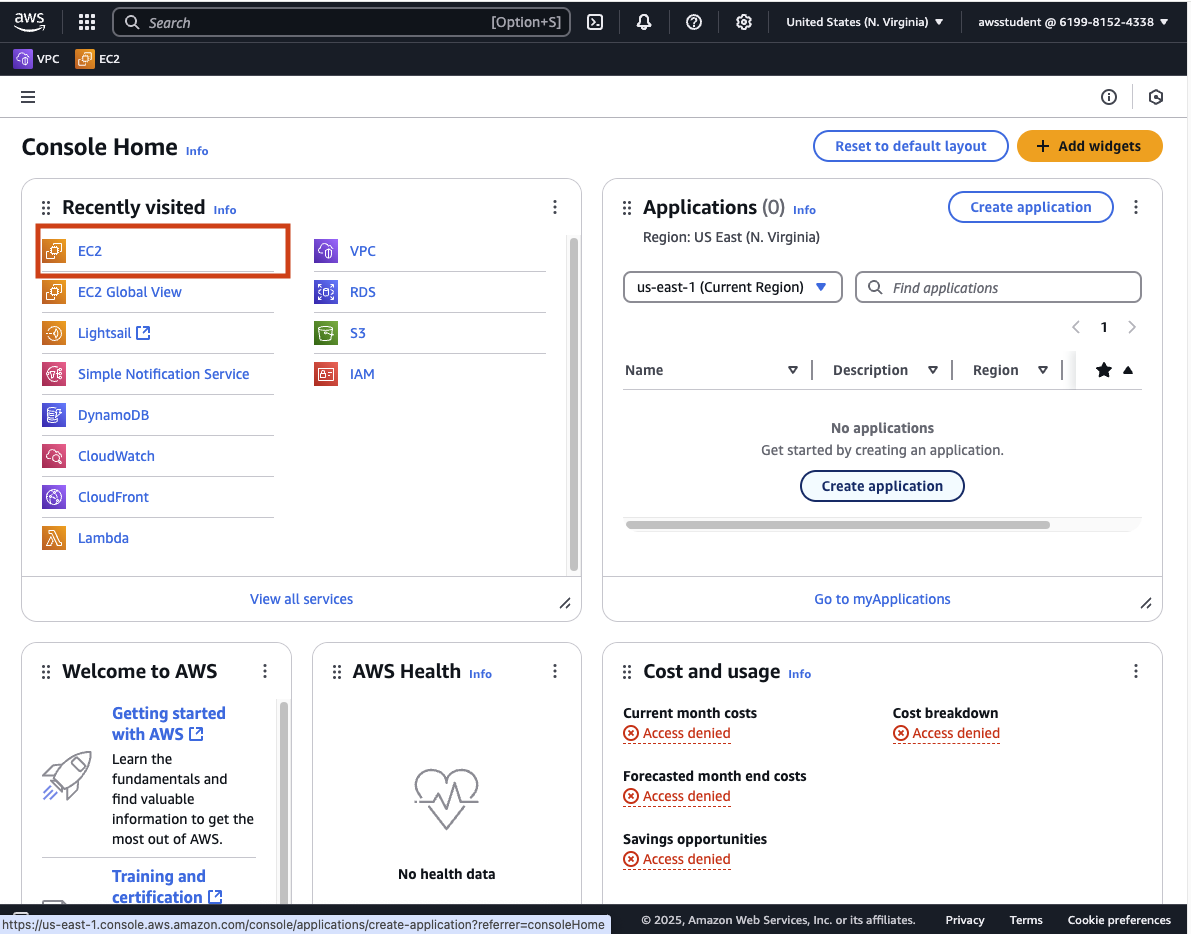
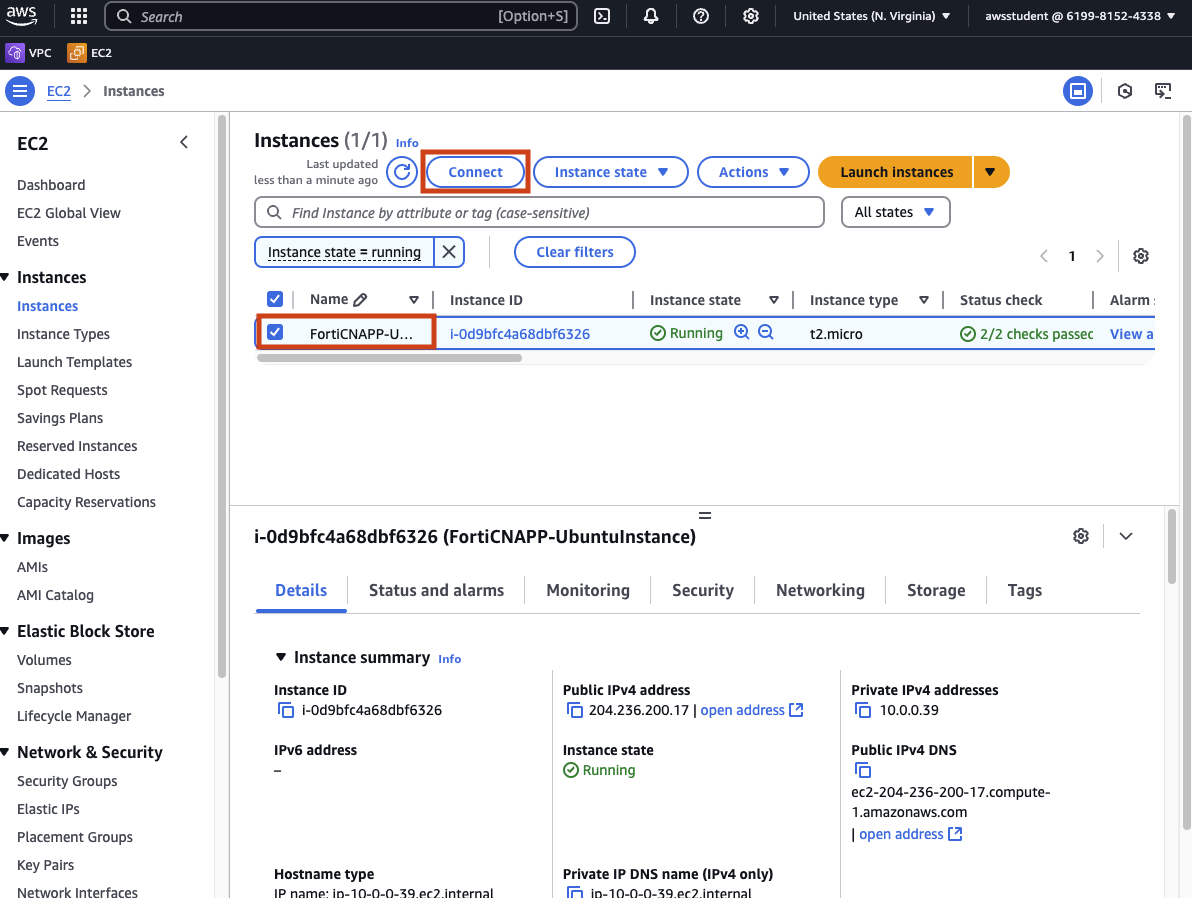
Click on (or search for) EC2.
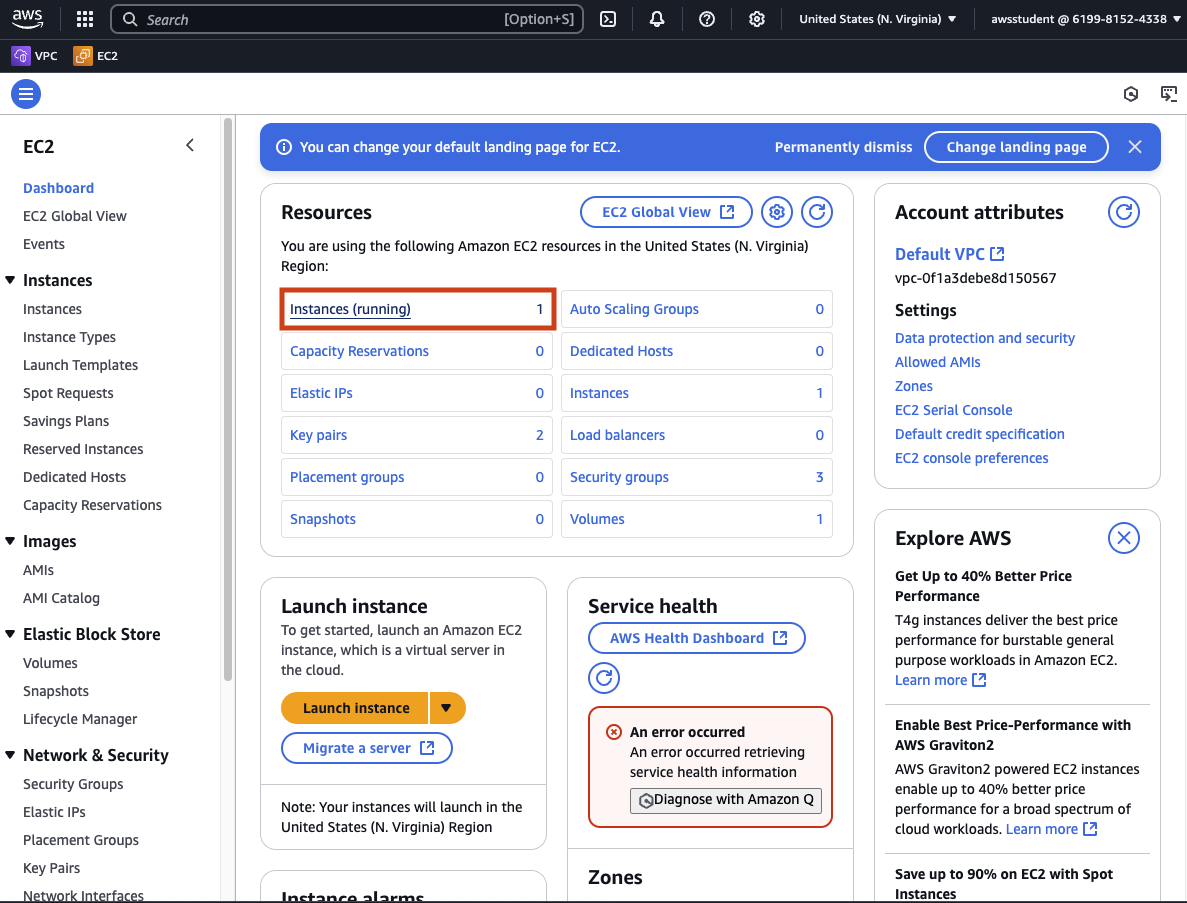
Click on Instance (running) to see a list of the current virtual machine running.
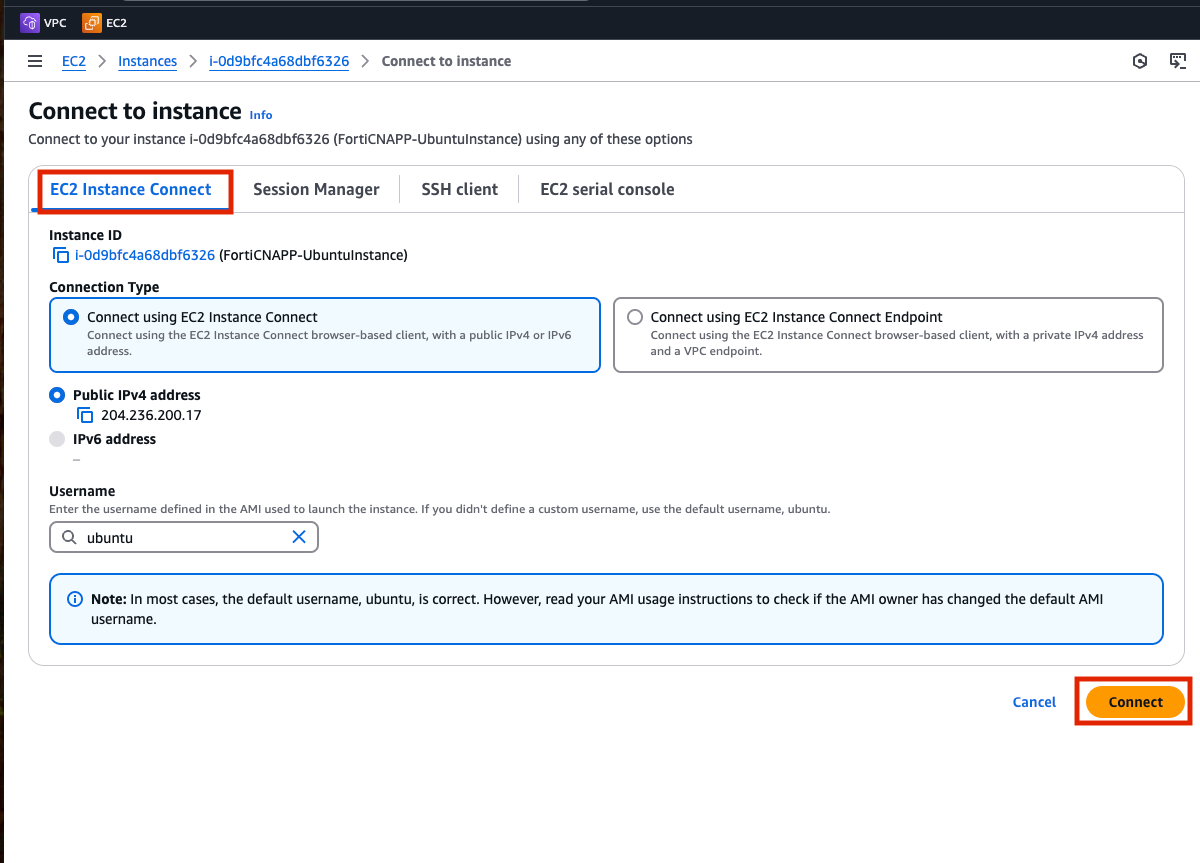
Select the checkbox next to FortiCNAPP-UbuntuInstance and then click on Connect.
Use the EC2 Instance Connect connection type and click Connect.
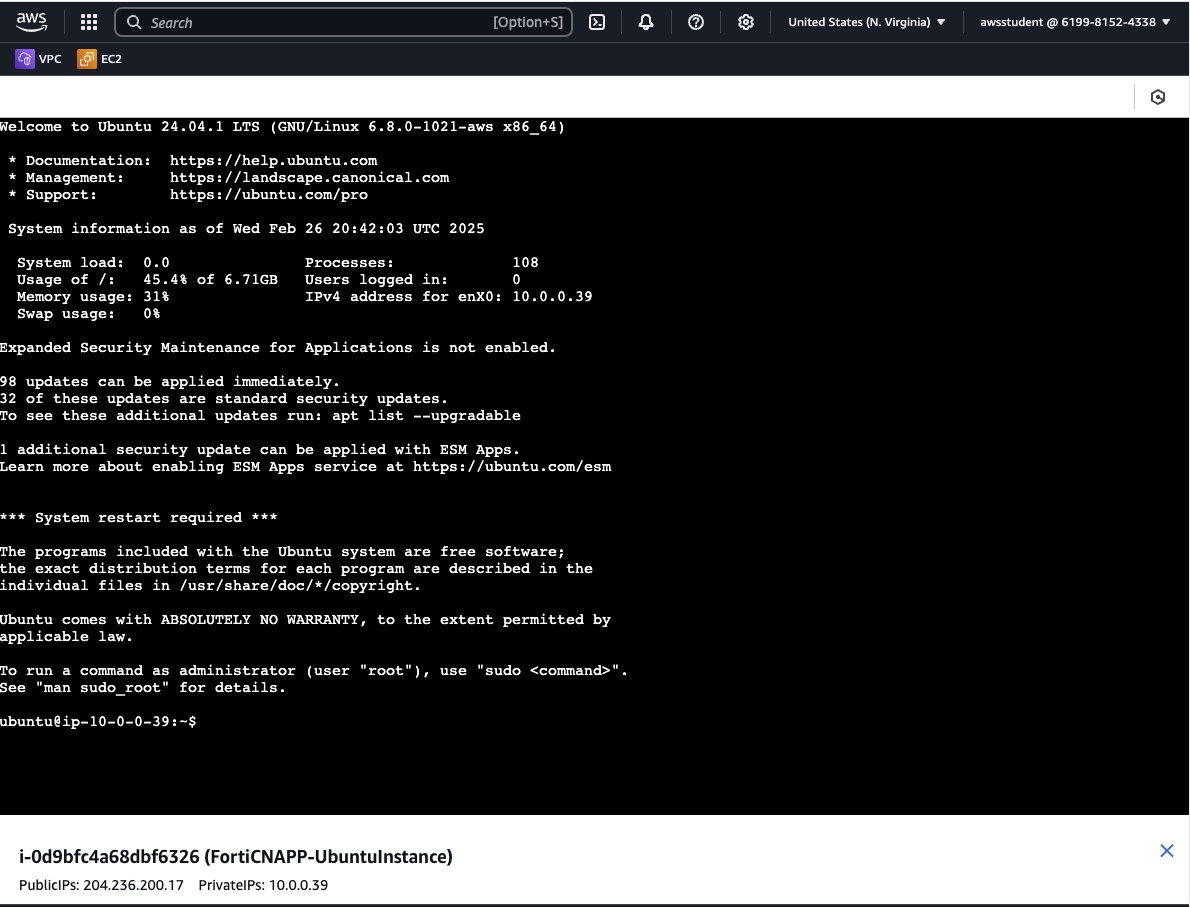
Instance connect will launch and you will be logged into your own virtual server running in AWS. From here you will be able to run commands on the virtual server.
Create Cloud Resources with Terraform
Great, with access to the virtual server let’s run some commands!
Setup a directory for the Terraform Configuration and download the IaC File
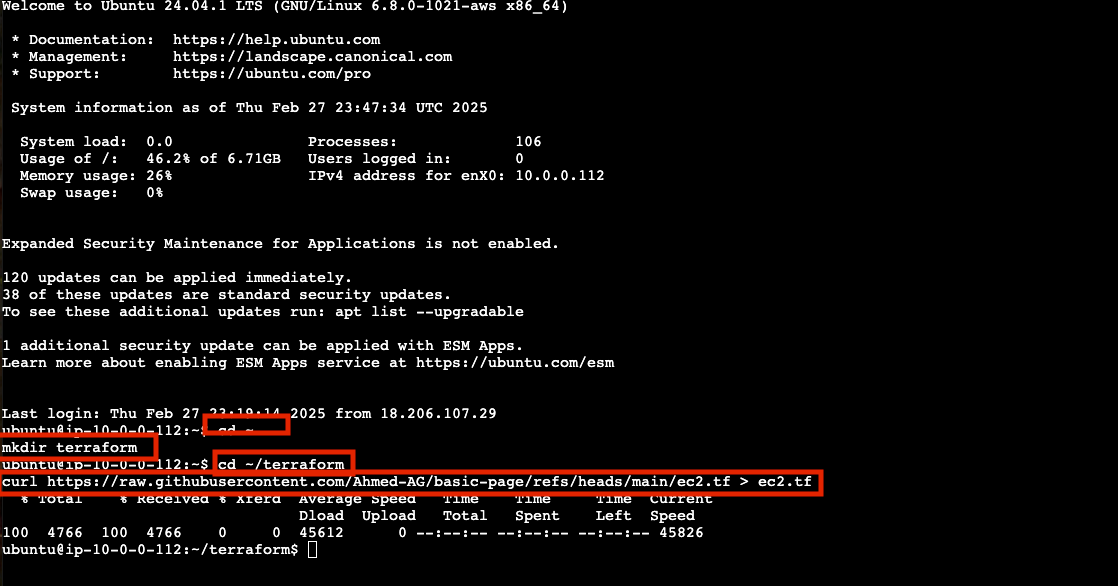
Create a new directory for your Terraform project and navigate and download the file:
cd ~
mkdir terraform
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Ahmed-AG/basic-page/refs/heads/main/ec2.tf > ~/terraform/ec2.tfReview the IaC file
Take a moment to examine the IaC file to see what we are asking Terraform to create. The cat command will output the file so you can read it.
cat ec2.tfHere is a review of the resources we will create:
- VPC
- Subnets
- A group of instances
Installing Terraform
Run terraform --version to verify that you have Terraform installed:
terraform --versionIf Terraform is not installed you can install it by running the following the instructions: [https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/tutorials/aws-get-started/install-cli#install-cli]
Then test again:
terraform --versionInitializing Terraform
This initializes the Terraform project and downloads necessary providers:
cd ~/terraform
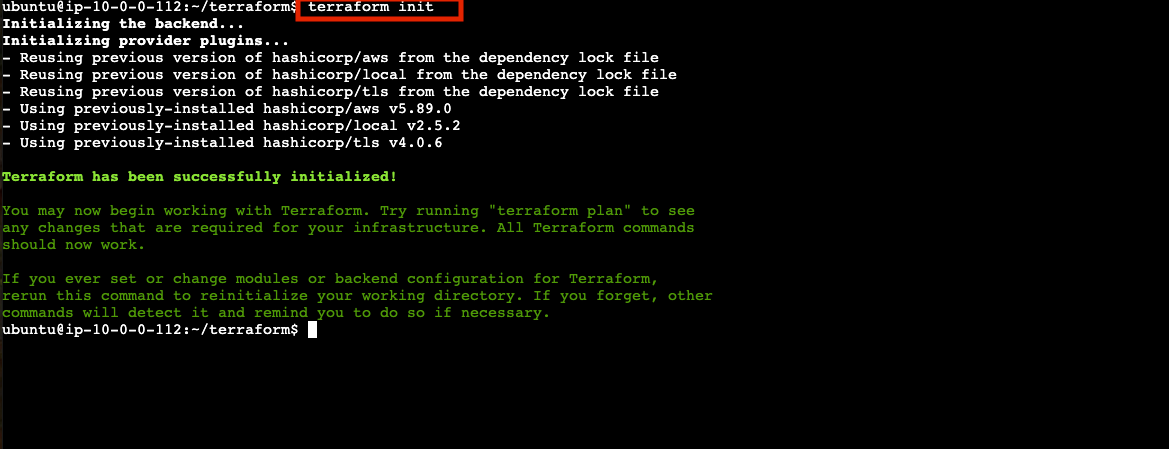
terraform initView the plan Terraform will apply
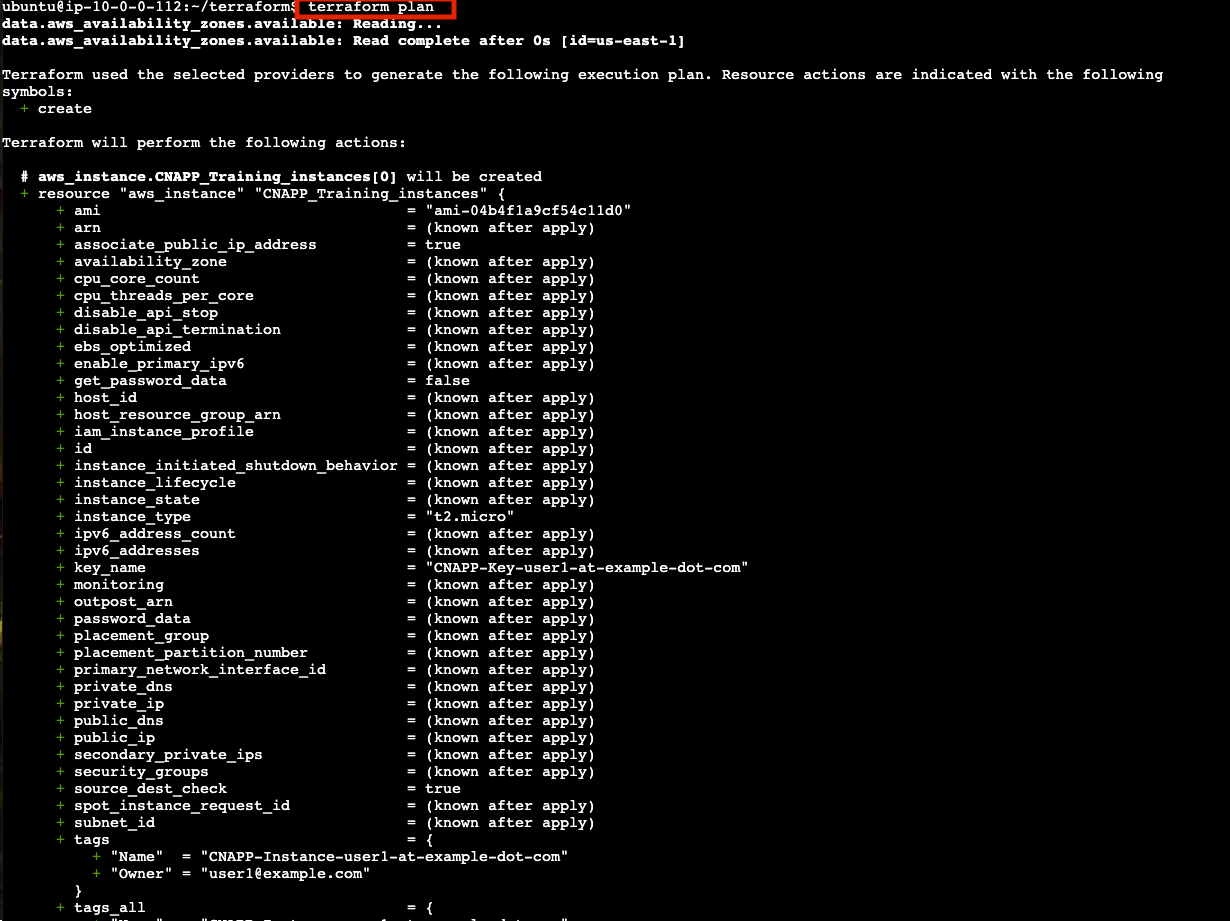
terraform planView the plan Terraform will apply
This previews the changes Terraform will make:
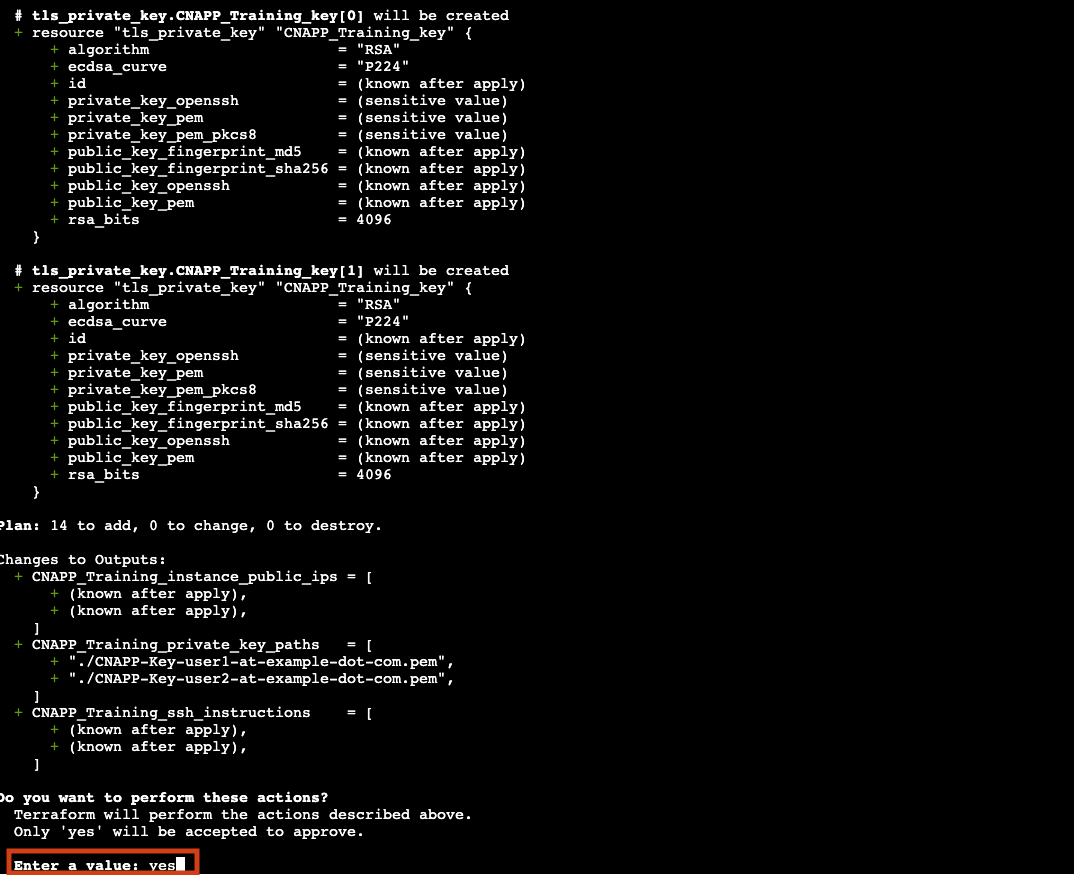
terraform applyConfirm the action when prompted by typing yes.
Verifying the Deployment
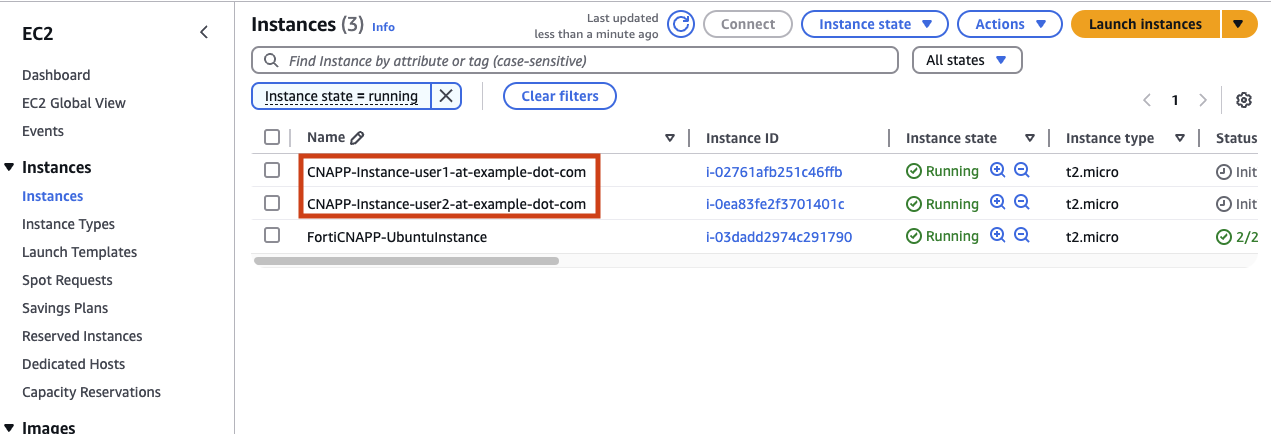
Once applied, you can check the virtual machine in the AWS console and examine the EC2 service. View the instances and the VPCs
Destroying the Infrastructure
To clean up resources, run:
terraform destroyConfirm the action when prompted by typing yes.
Conclusion
You have successfully run Terraform and deployed a AWS VPC and virtual servers using Infrastructure as Code! Next steps would be to learn more about what other resources you can mange with Terraform, how to make change to existing Terraform managed resources and what you can do with other clouds like Google and Azure.