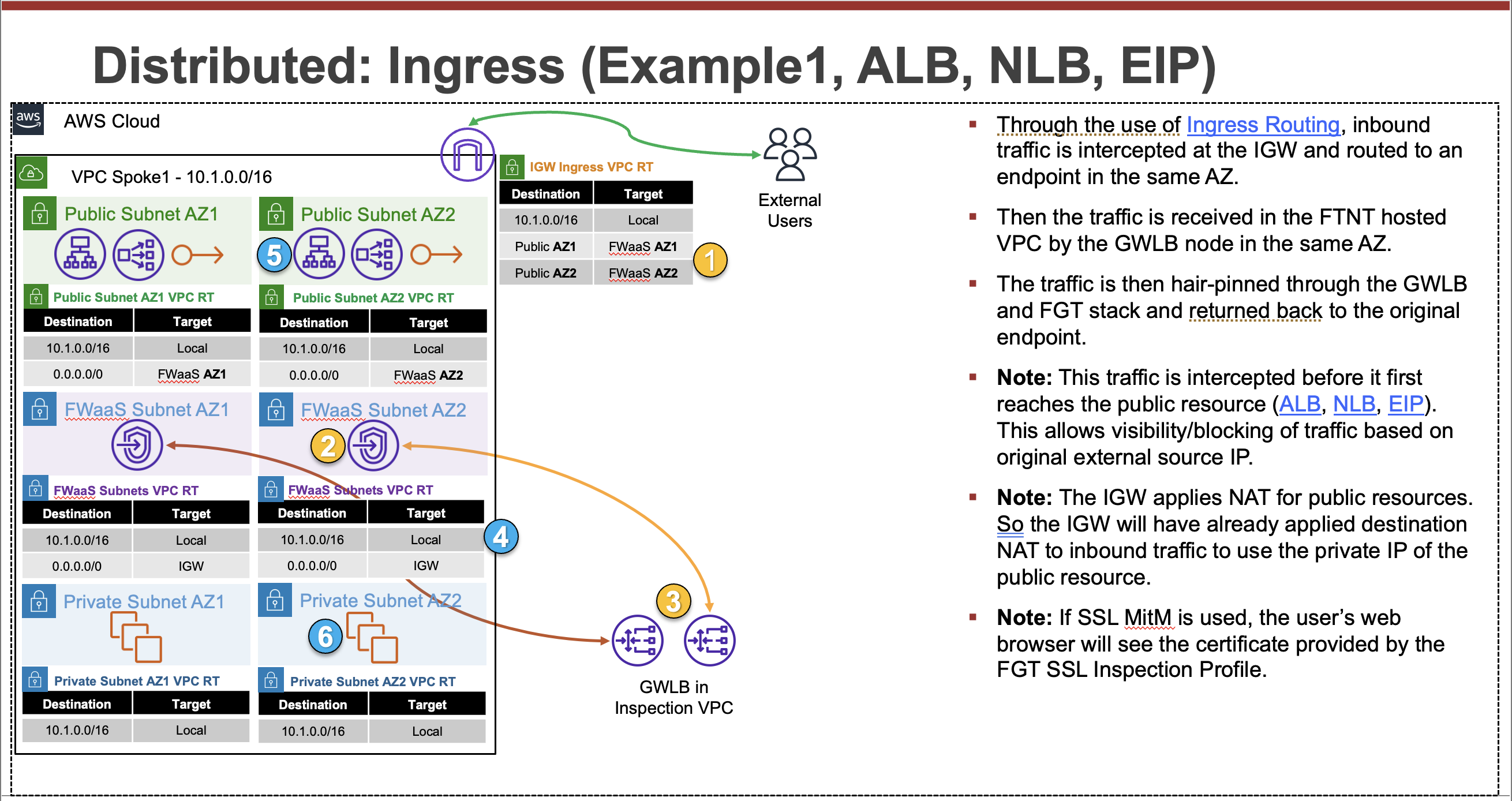
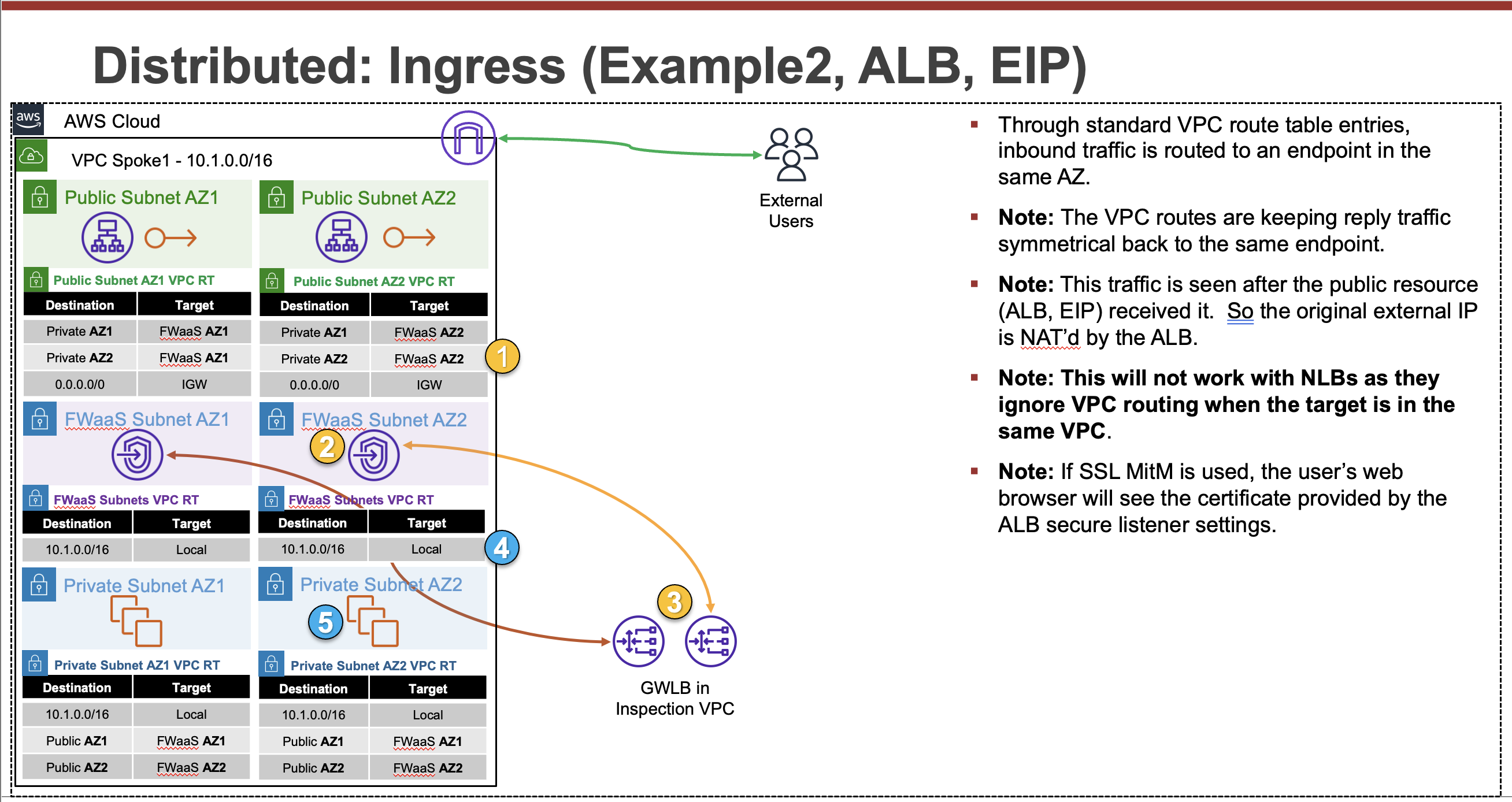
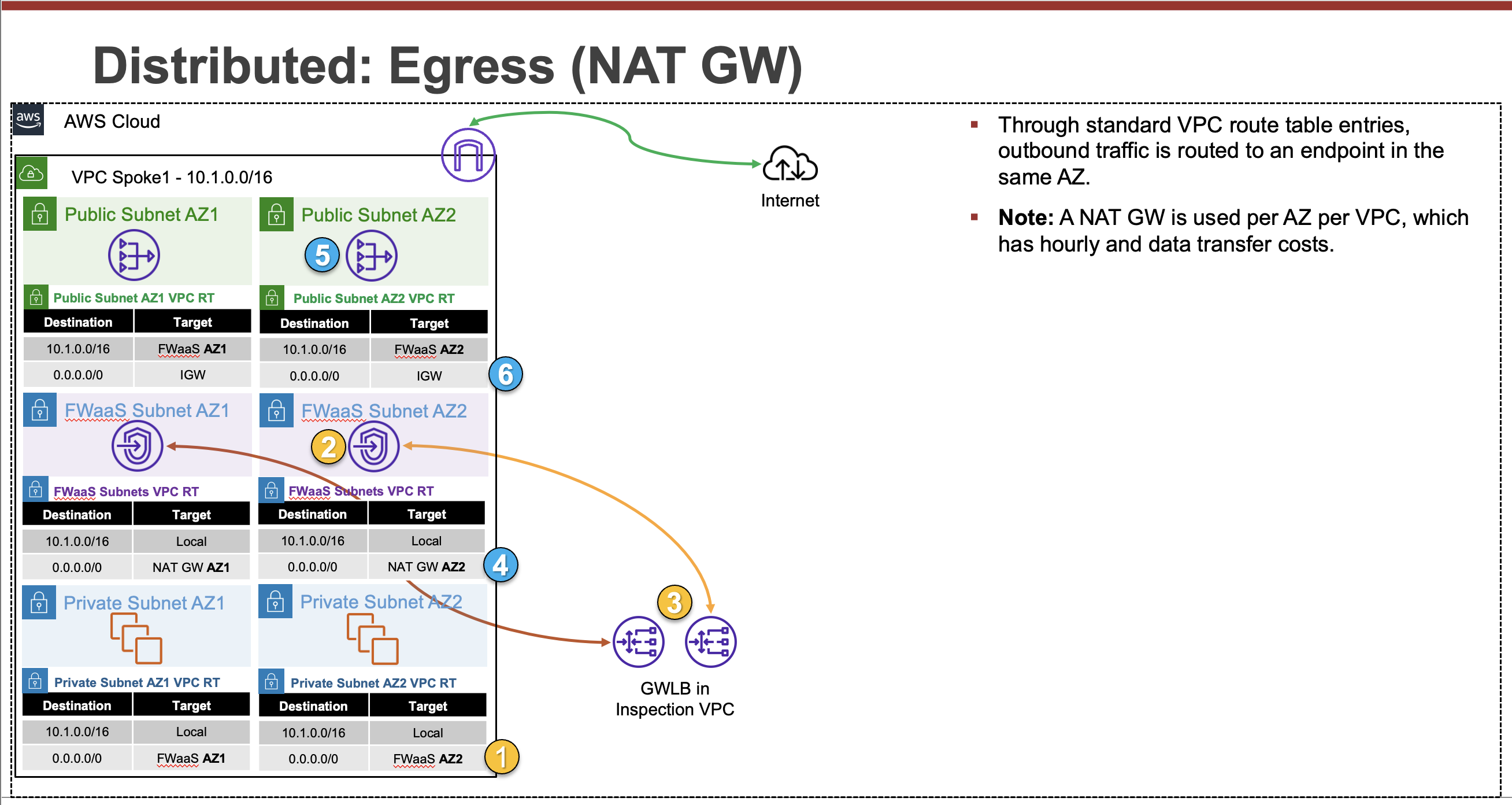
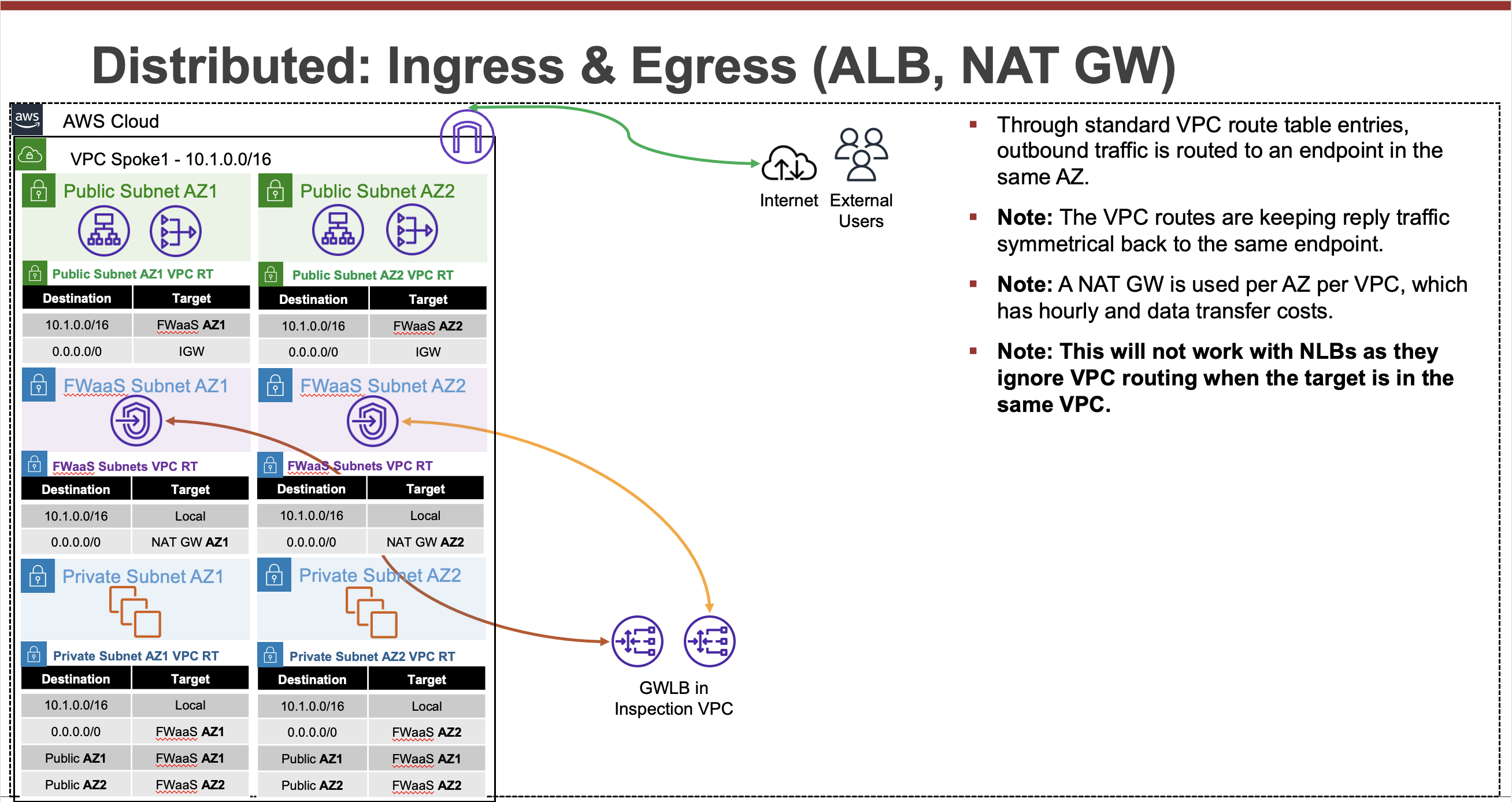
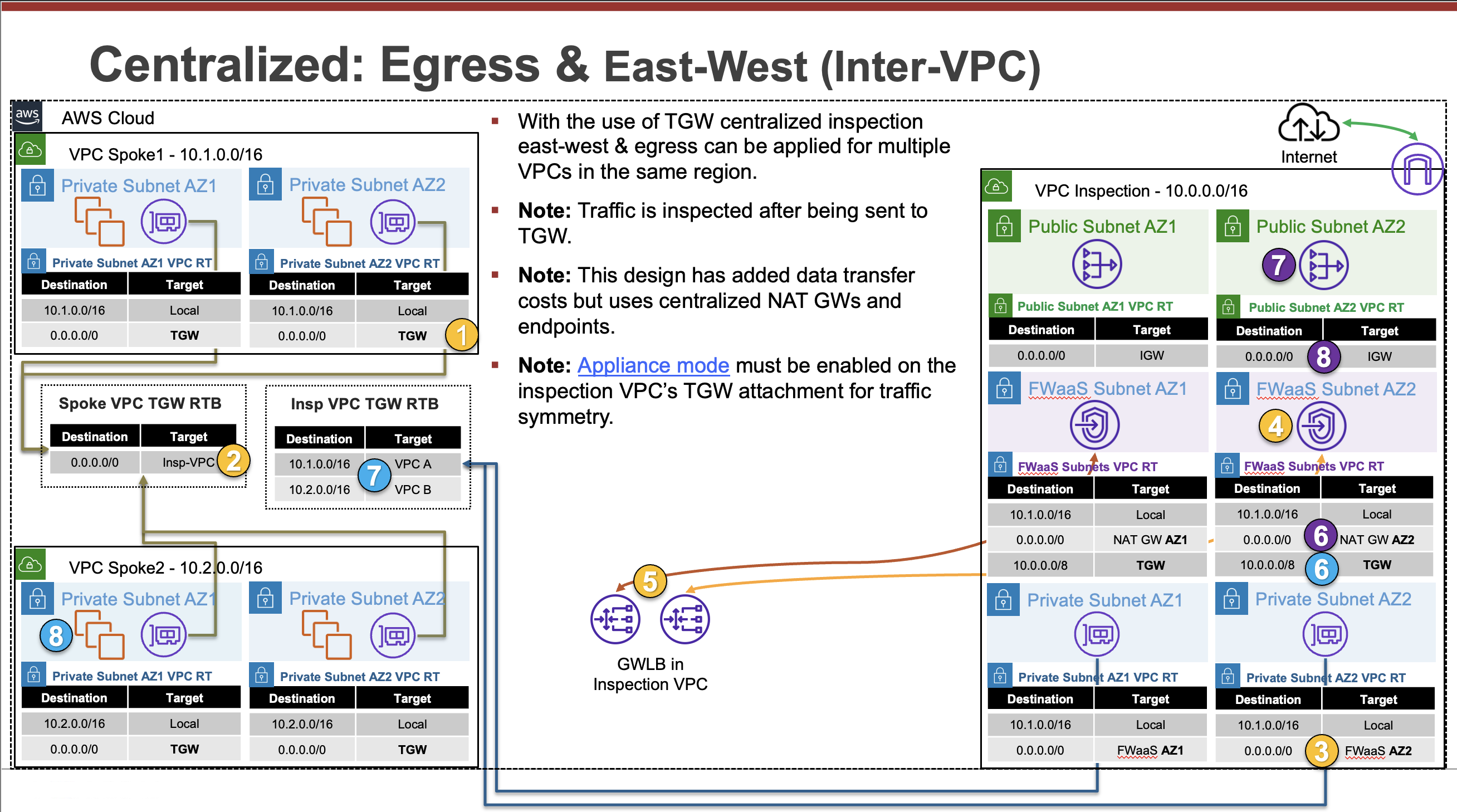
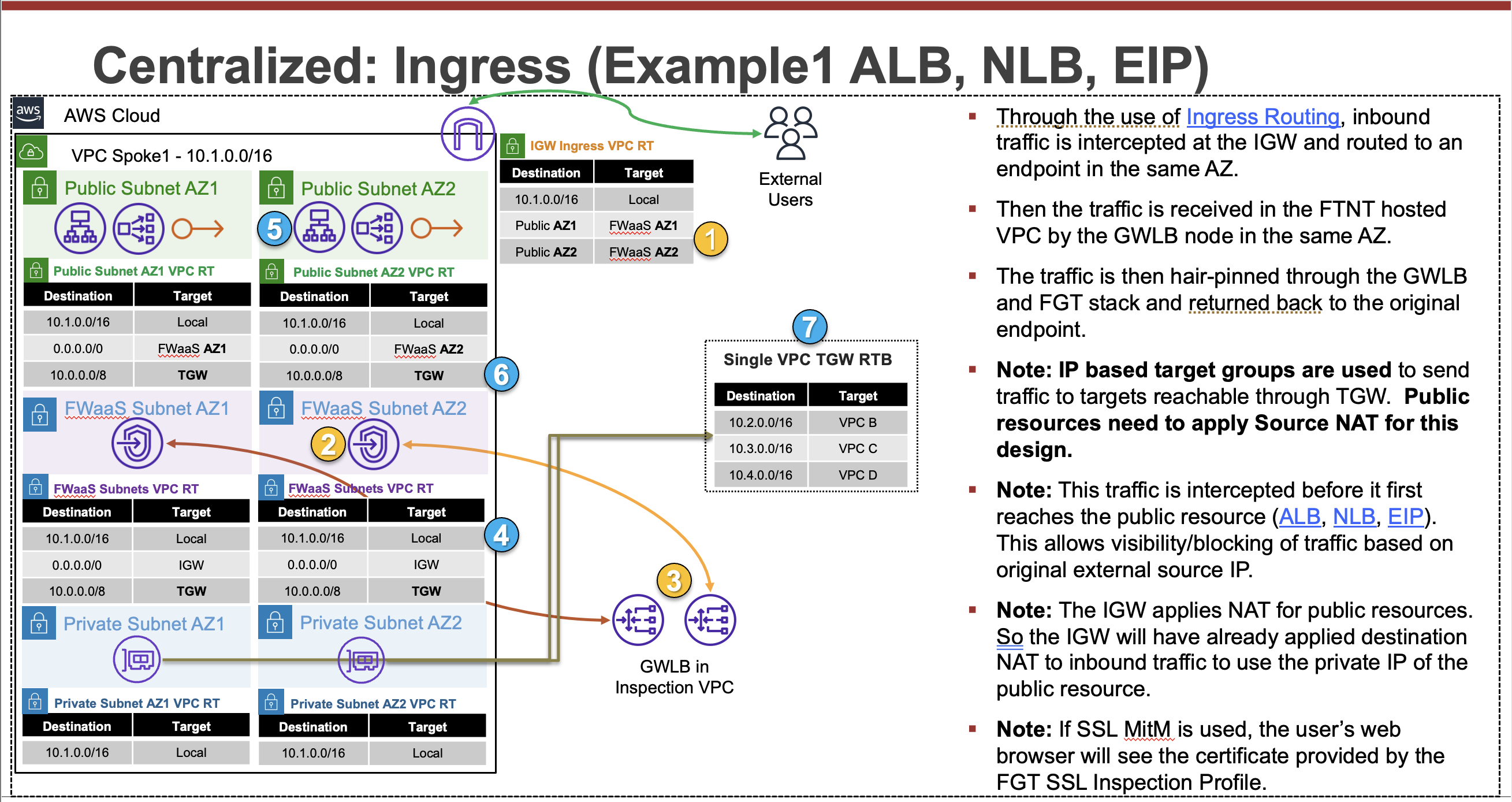
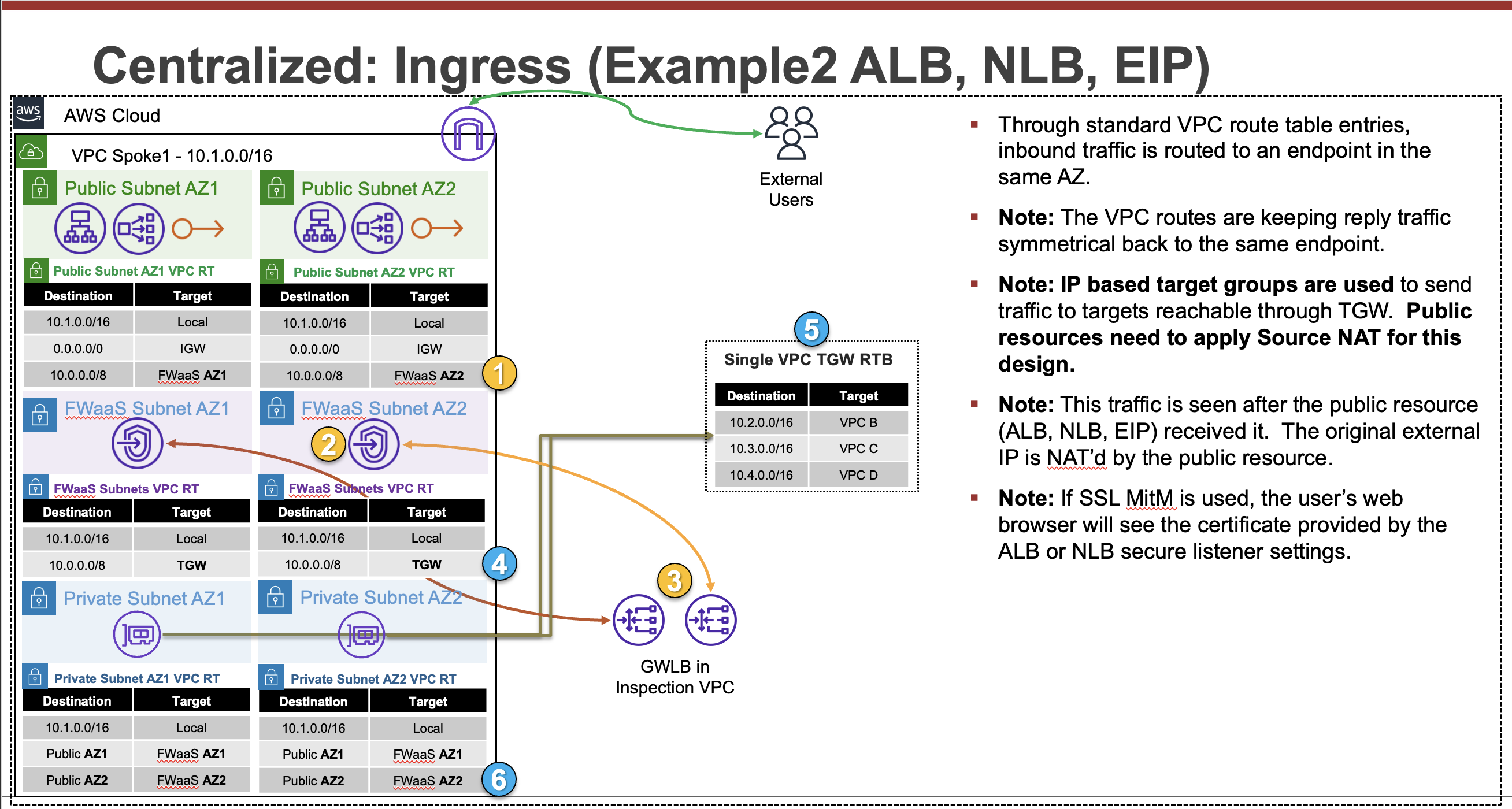
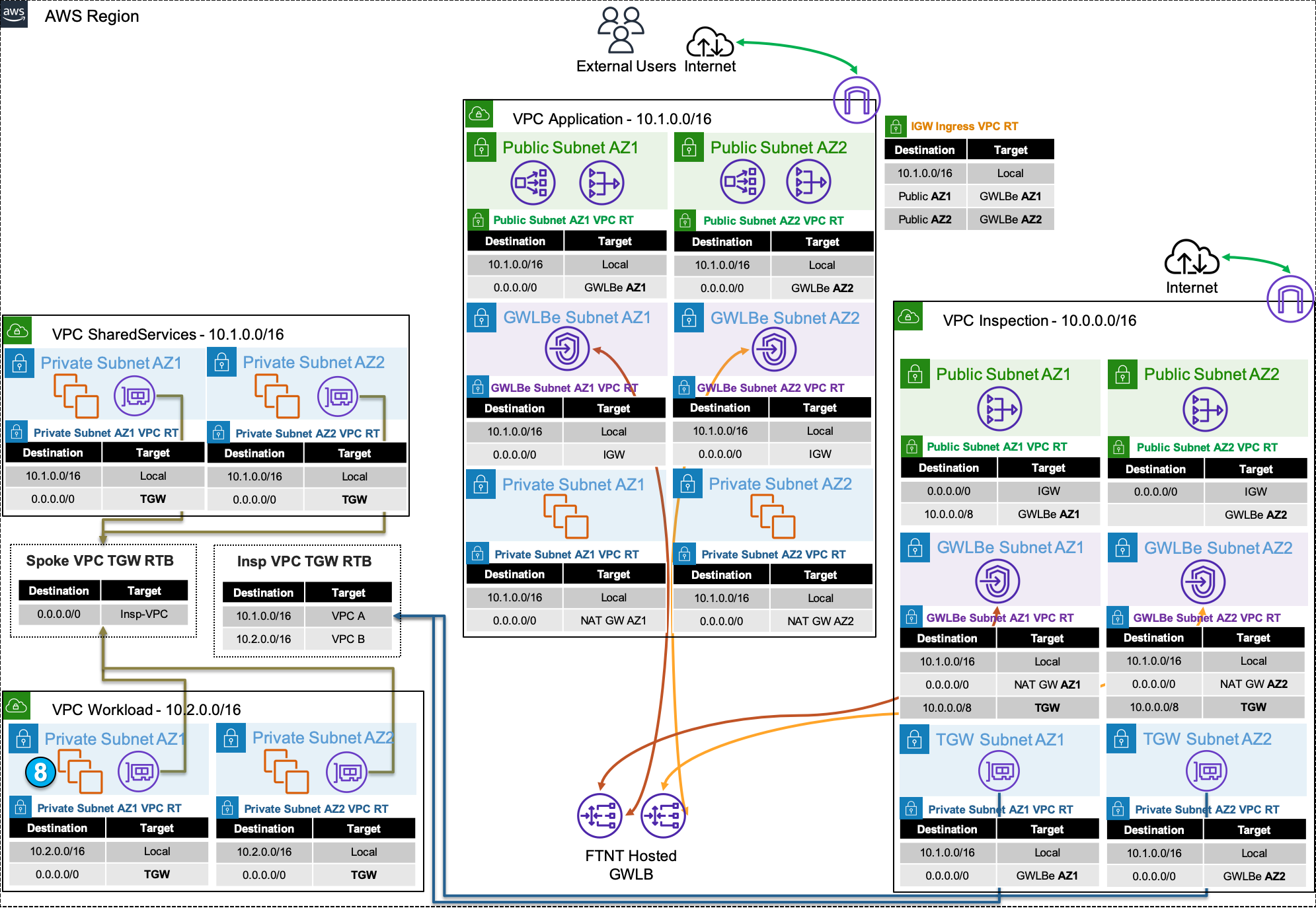
Common Architecture Patterns
While there are many ways to organize your infrastructure there are two main ways to design your networking when using GWLB, centralized and distributed. From the perspective of networking, routing, and GWLBe endpoint placement
Expand each section to see the details.