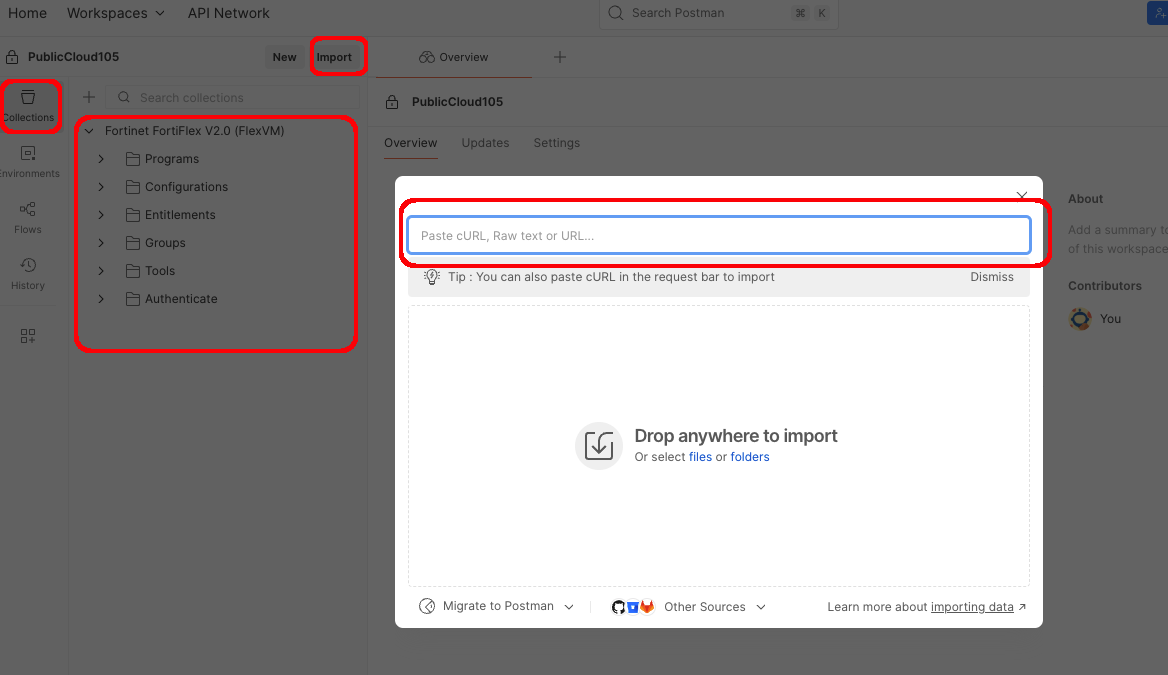
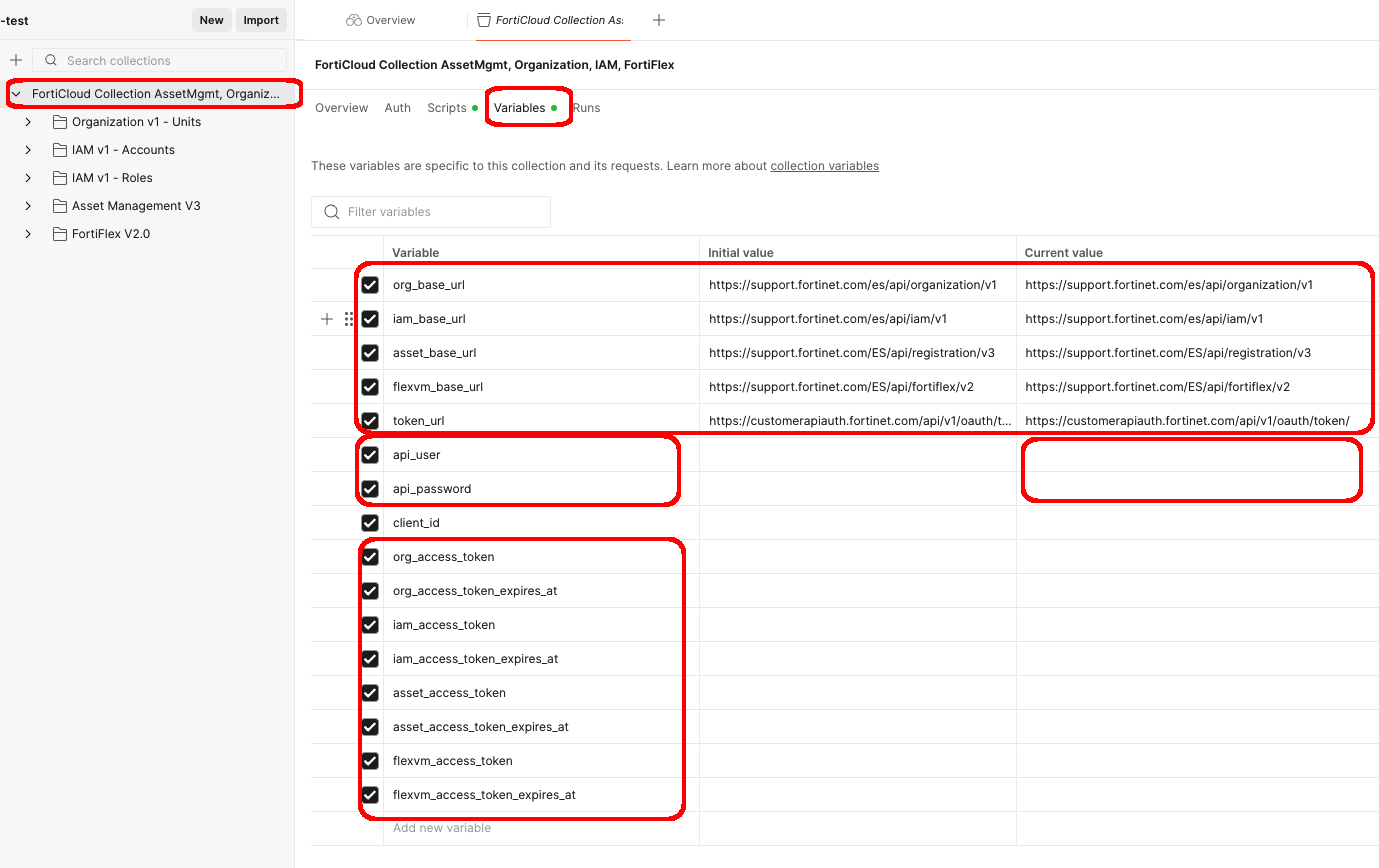
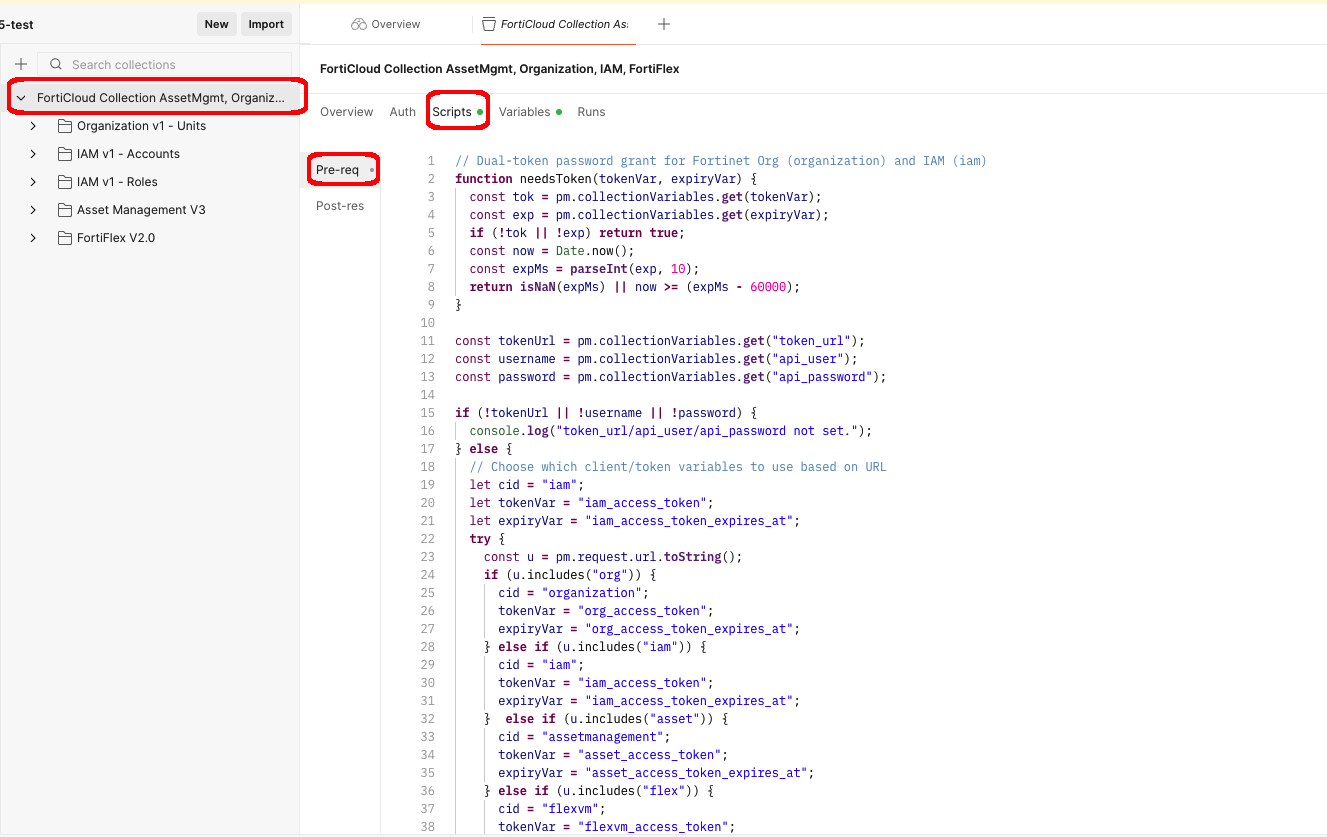
FortiFlex Workshop
Real-World Scenario: CloudSecure Solutions MSSP Challenge
Company: CloudSecure Solutions - A mid-sized MSSP serving 150+ enterprise customers
The Challenge: CloudSecure Solutions was struggling with their traditional Fortinet licensing model. Their customers had varying security needs that changed seasonally - retail customers needed additional protection during holiday seasons, financial services required scaling during quarterly reporting, and manufacturing clients had project-based security requirements.
Pain Points:
- Procurement Delays: Traditional licensing required 2-4 weeks lead time, missing customer opportunities
- Over-provisioning Costs: Customers paid for peak capacity year-round, leading to 40% waste during low-usage periods
- Manual Provisioning: Each new customer deployment required manual license allocation, taking 3-5 business days
- Billing Complexity: Monthly reconciliation across different license types and customer usage patterns consumed 20+ hours of administrative work
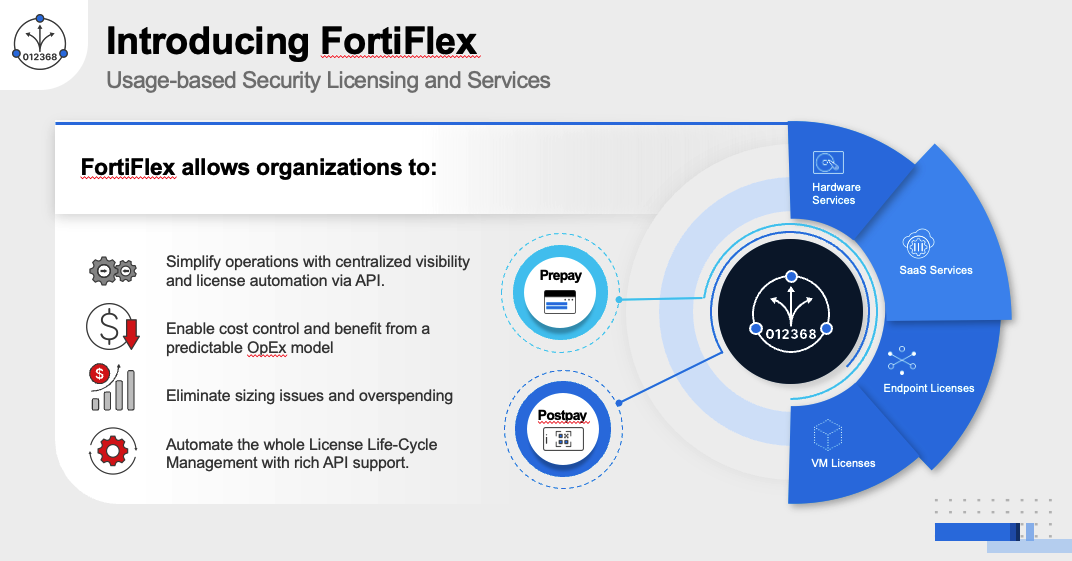
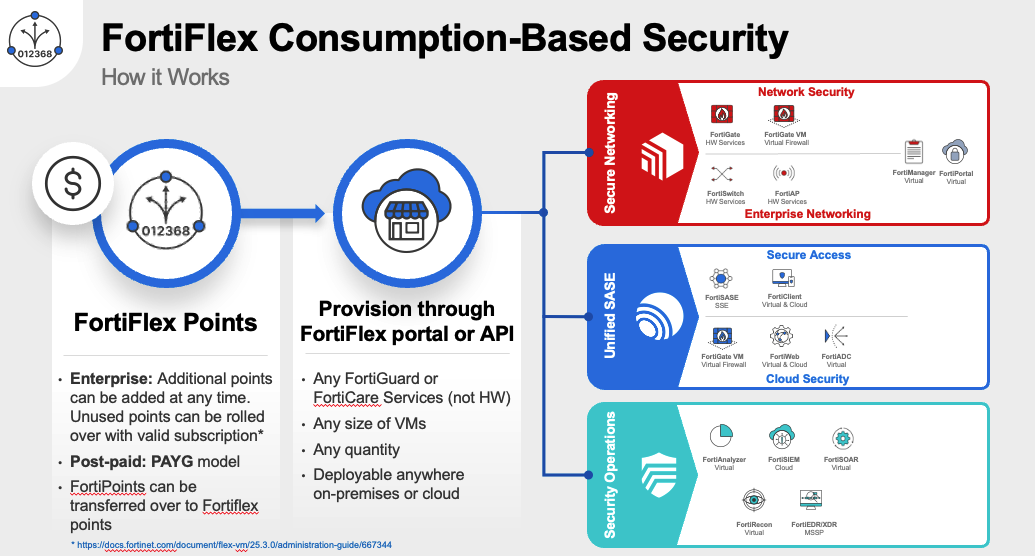
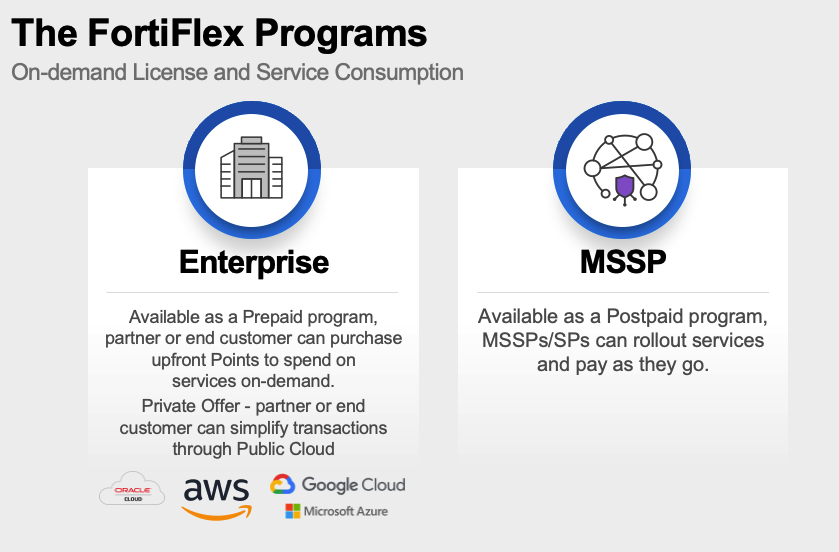
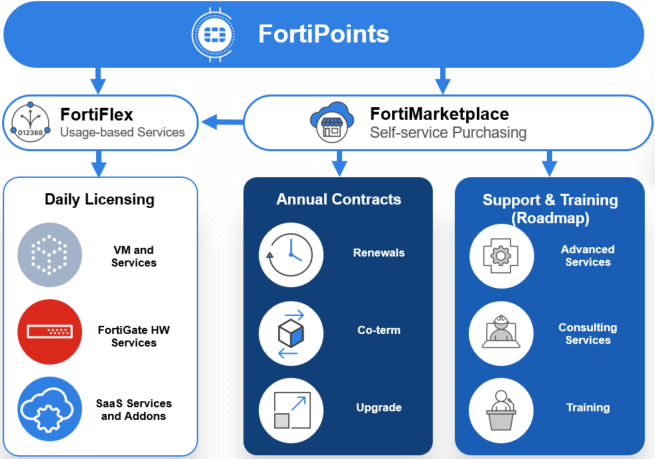
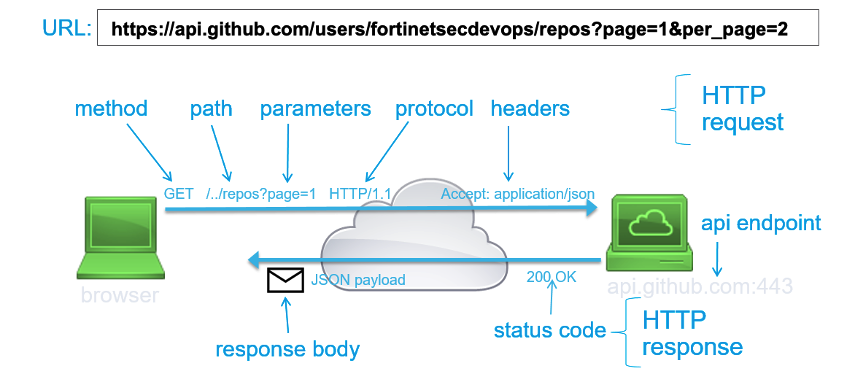
The FortiFlex Solution: With FortiFlex’s usage-based licensing and API-driven automation, CloudSecure Solutions transformed their operations:
- Instant Provisioning: New customer deployments automated down to 15 minutes
- Cost Optimization: Customers now pay only for actual usage, reducing costs by 35%
- Automated Scaling: Seasonal traffic handled automatically without manual intervention
- Streamlined Billing: API integration with their billing system reduced admin overhead by 80%
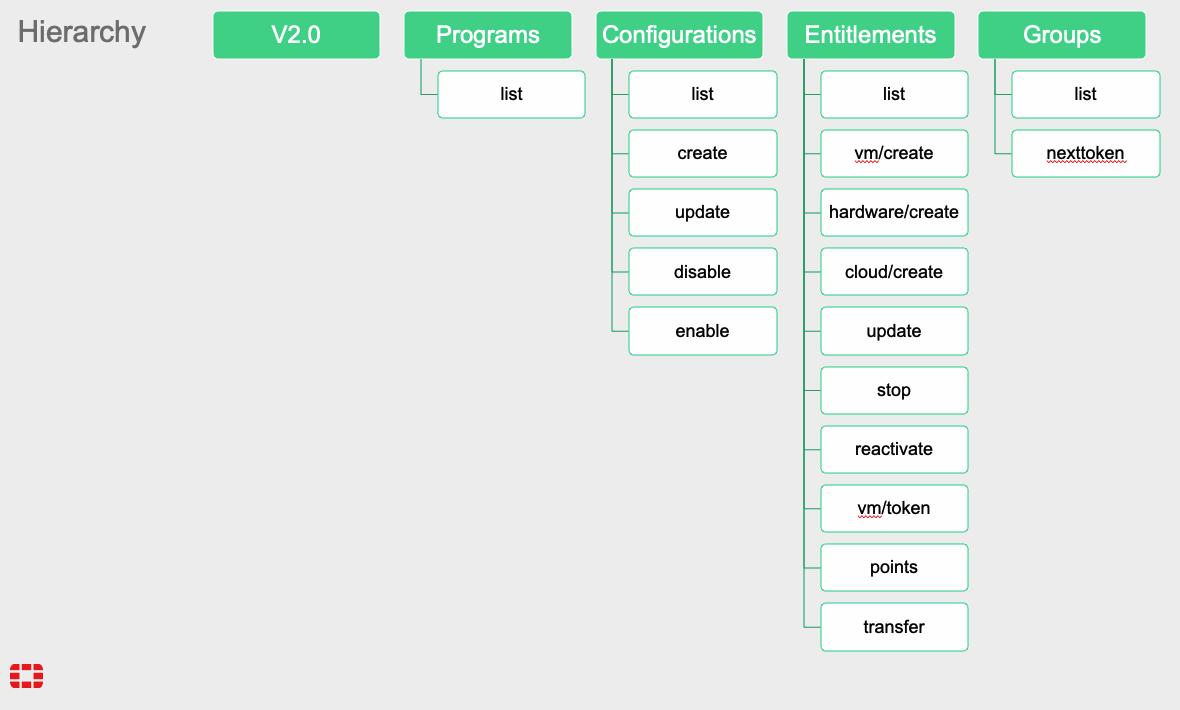
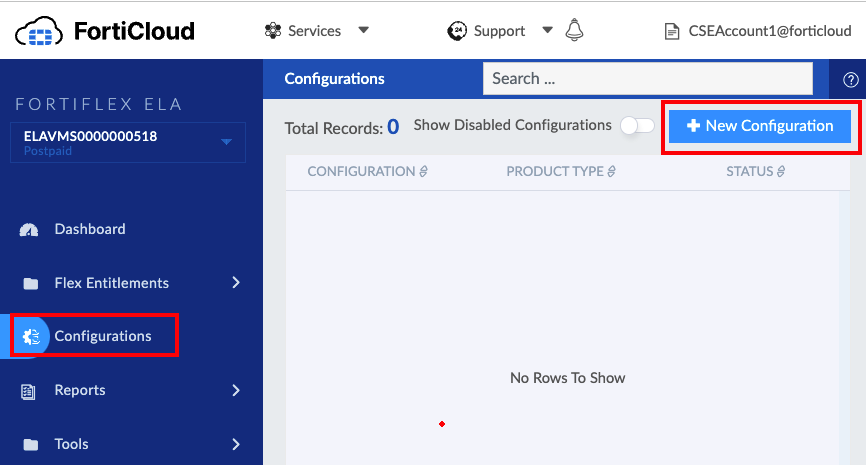
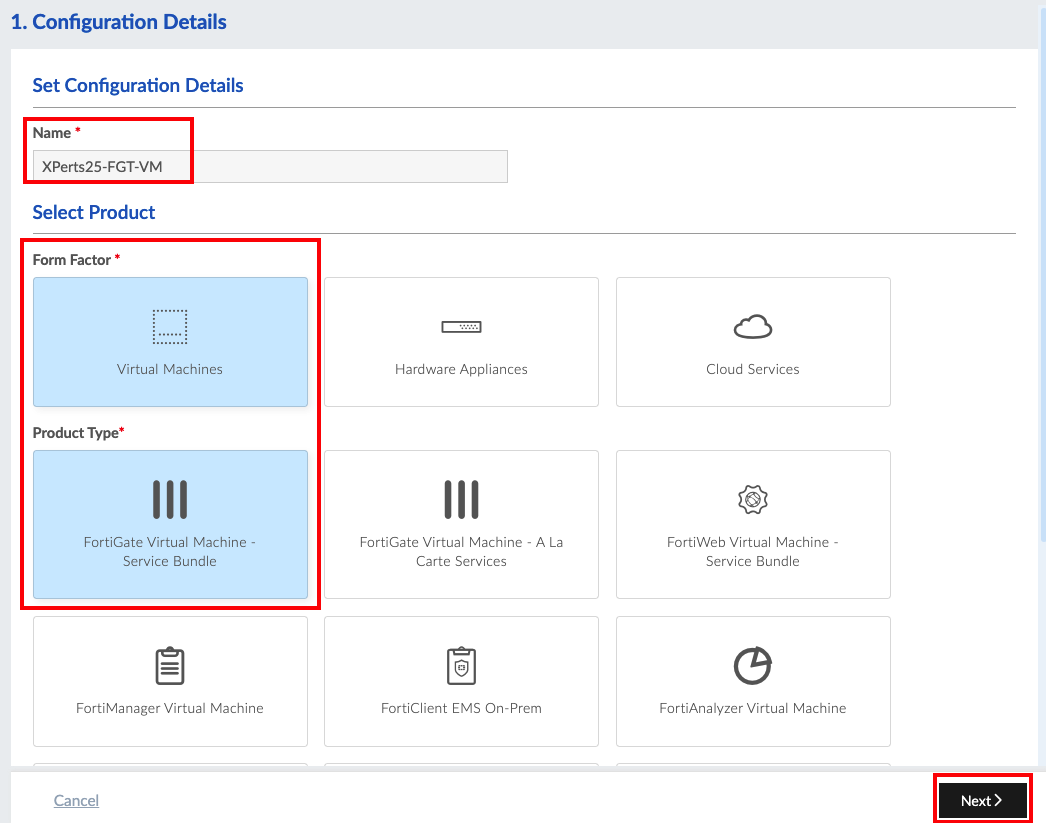
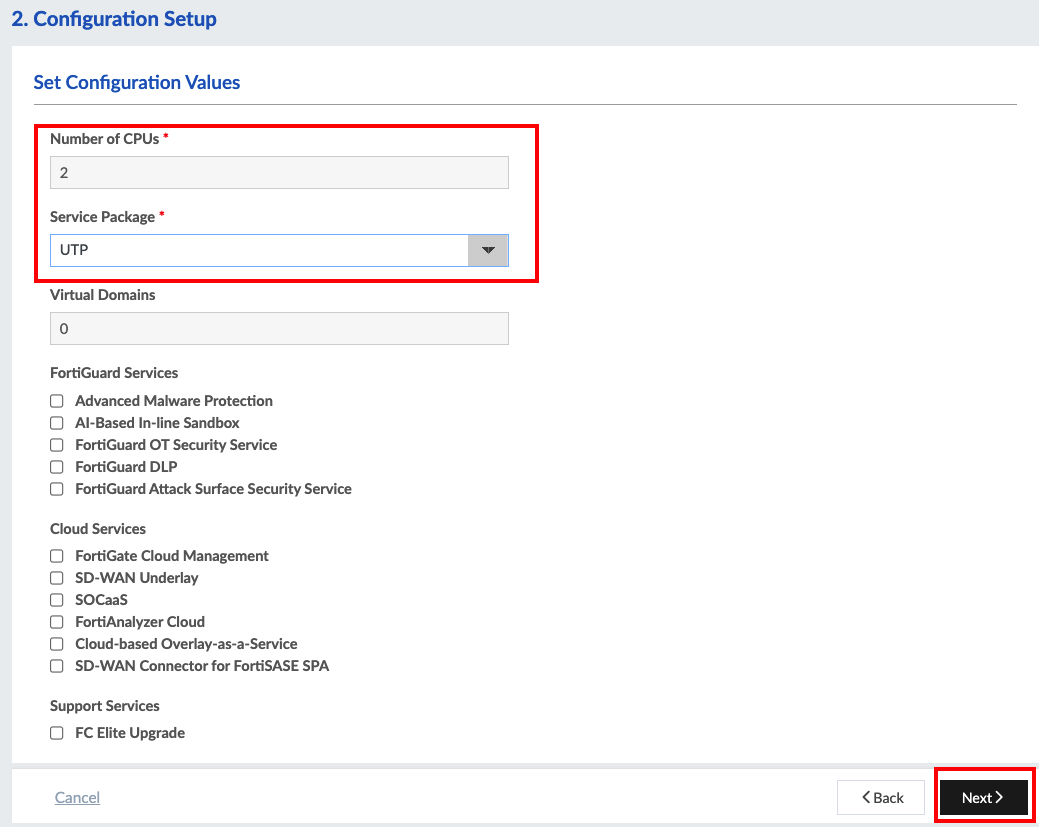
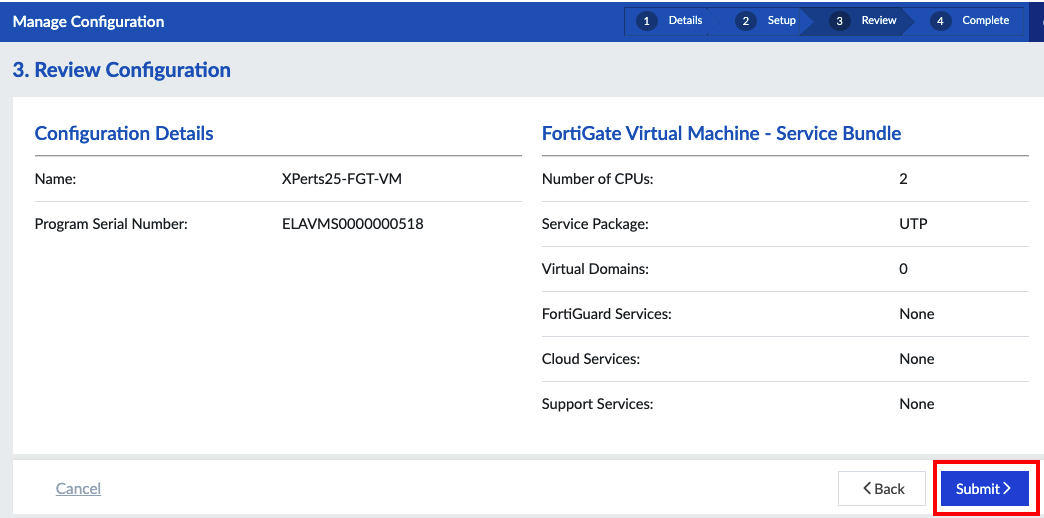
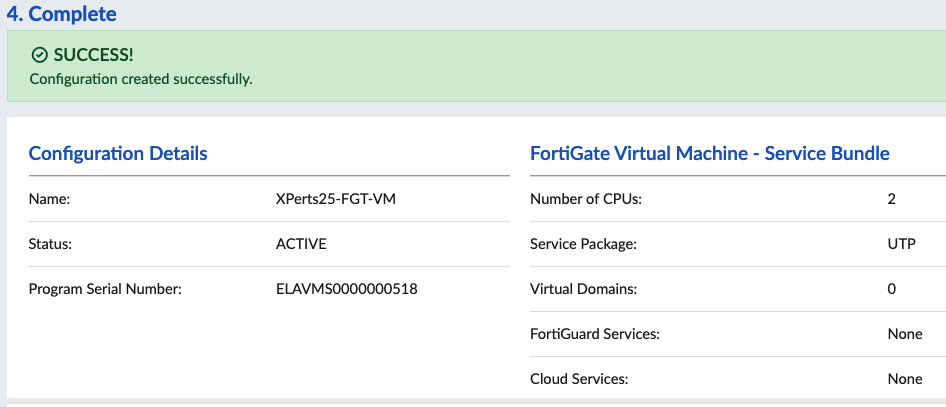
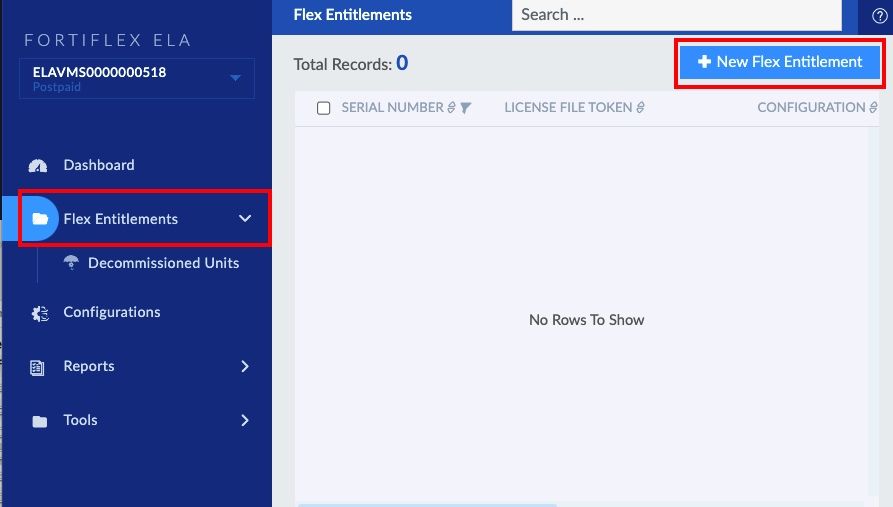
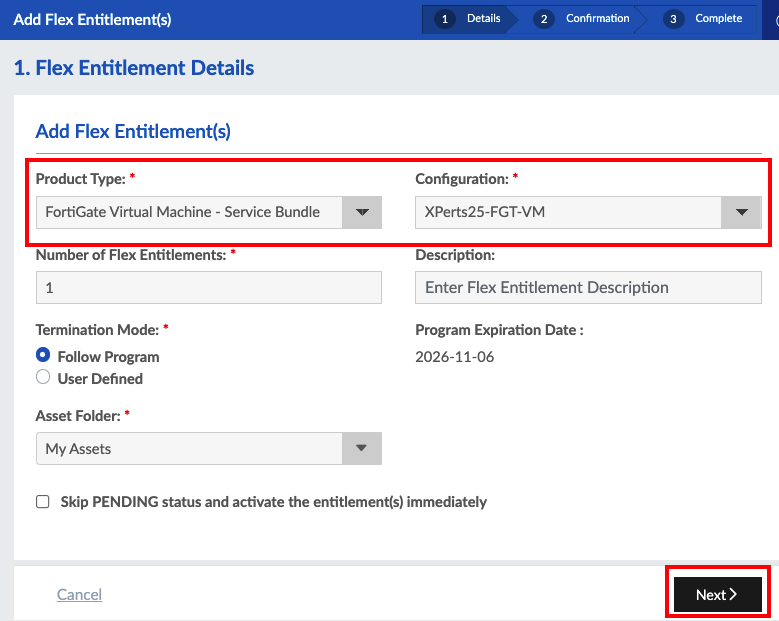
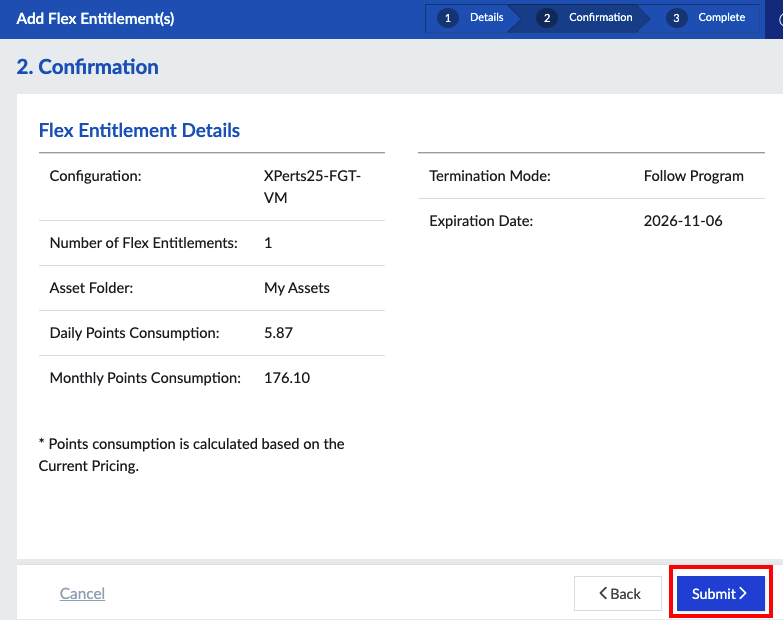
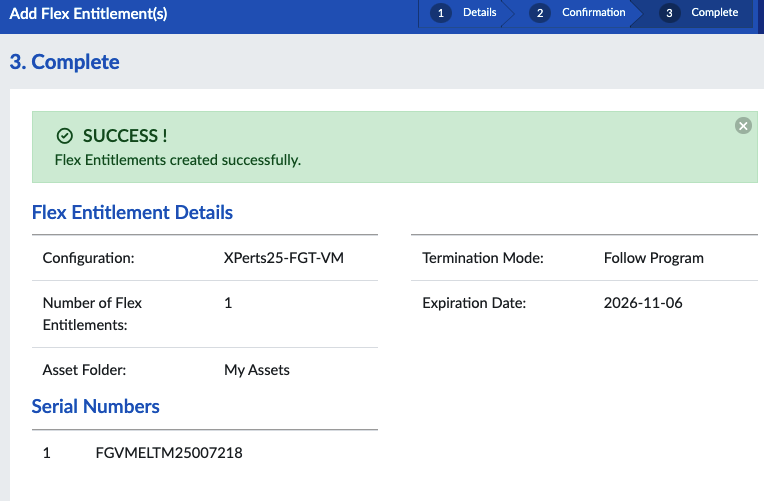
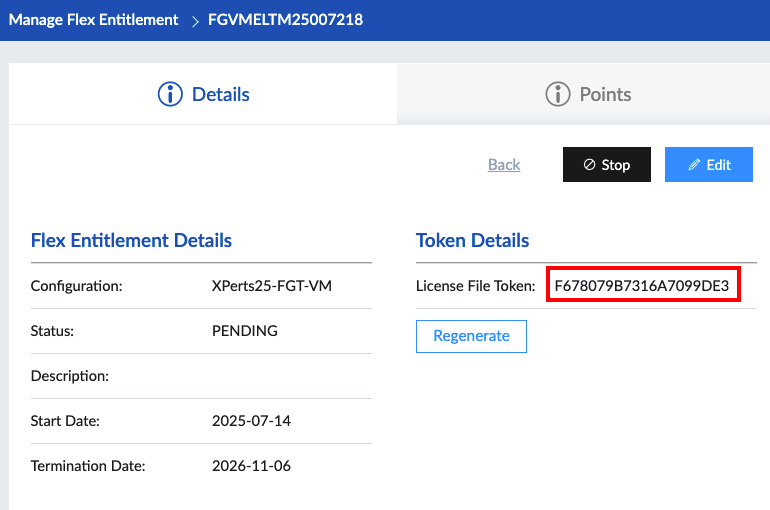
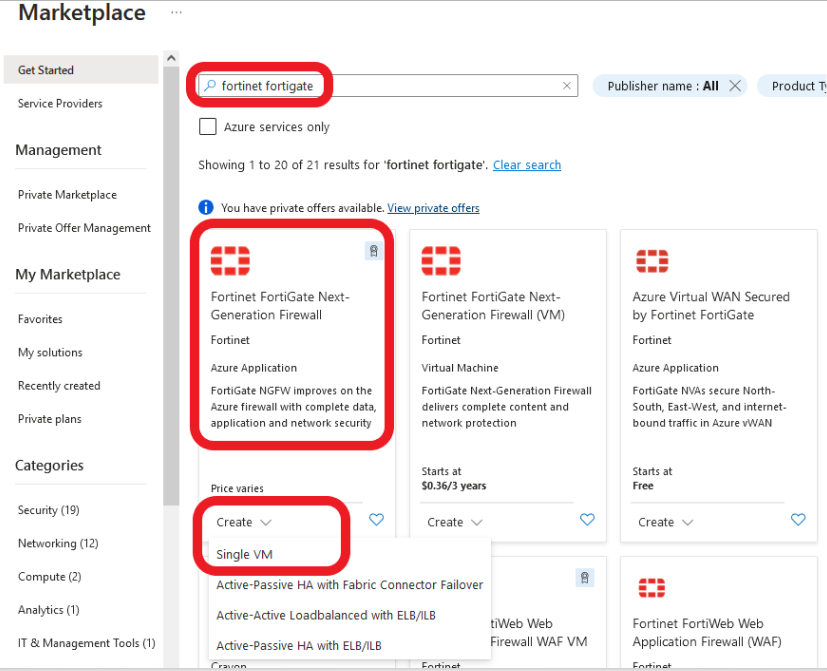
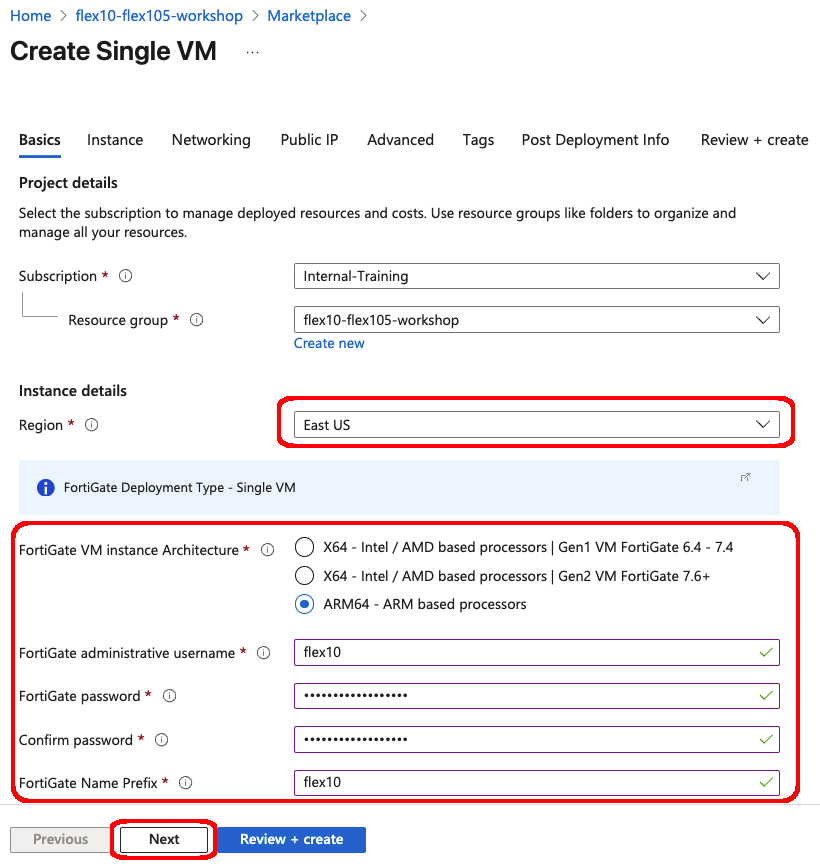
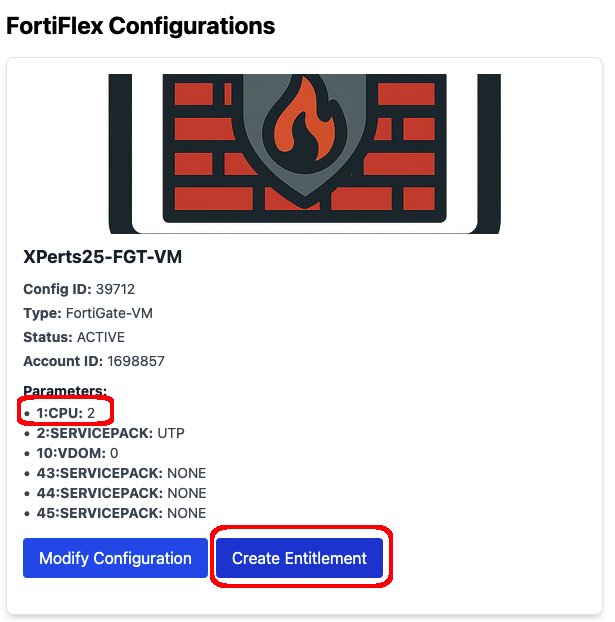
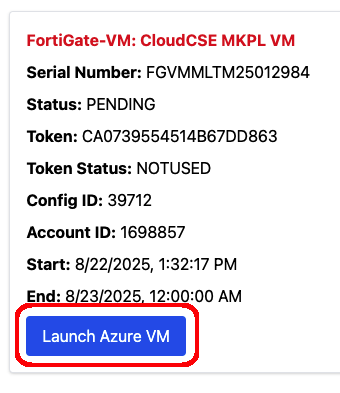
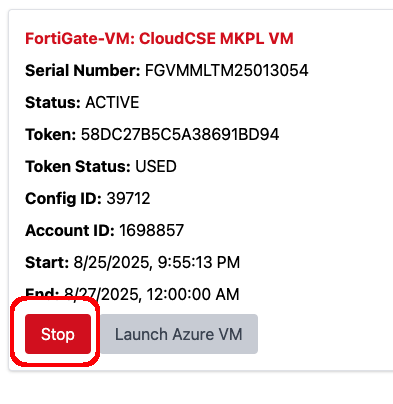
Workshop Goal: Learn how to implement FortiFlex to solve similar challenges in your organization through hands-on experience with both manual operations and API automation.