Task 5: VNET Peering and Verifying Routing
In this task setup peering between the spokes/VNETs and the vWAN hub. Then second part of this task it to verify routing by viewing the routing tables on the FortiGate NVAs, the hub, and effective routes on the Linux hosts.
Peer Spoke VNETS to Hub
Peer Spoke1-vHub1_VNET to hub
Navigate to your Virtual Wan - vwanXX-training_VWAN
Click “Virtual network connections” on the left under “Connectivity”.
Click “+ Add connection”
Enter - “Connection name” -
Spoke1Select - “Hubs” - your assigned hub -vwanXX-eastus-vHub1_VHUB
Select - “Resource group” - your resource group - vwanXX-training
Select - “Virtual Network” - Spoke1 VNET - Spoke1-vHub1_VNET
Click - “Create”
Peer Spoke2-vHub1_VNET
Navigate to your Virtual Wan - vwanXX-training_VWAN
Click “Virtual network connections” on the left under “Connectivity”.
Click “+ Add connection”
Enter - “Connection name” -
Spoke2Select - “Hubs” - your assigned hub -vwanXX-eastus-vHub1_VHUB
Select - “Resource group” - your resource group - vwanXX-training
Select - “Virtual Network” - Spoke2 VNET - Spoke2-vHub1_VNET
Click - “Create”
Info
VNET Peering takes a few minutes to complete. The Connectivity Status can be reviewed by Clicking Refresh
Verify Routing
Routes and routing are the key for users to access workloads in an Azure VNET and for those workloads to be able to access resources outside of their VNET. At this point routes and routing should be set within the Azure environment and in the FortiGate NVAs.
From the perspective of the FortiGate, a decision will be made to send traffic to a specific port based on FortiGate policy. Once the traffic leaves the FortiGate’s port, it is up to Azure to forward the traffic.
Where traffic will be sent in Azure can be determined by viewing the effective routes associated to a particular networking service.
- What routes do the FortiGates know about?
- What are the effective routes of the hub?
- What are the effective routes of the Linux VMs in the Spoke VNETs?
View each FortiGate’s route table
Open each FortiGate in a browser tab/window
Open FortiGate CLI
Run CLI command
get router info routing-table all
The output shows that BGP routes have been learned for the two Spoke VNETs that were peered to the Hub
View the hub effective routes in the default route table
Navigate to your vWAN hub - vwanXX-eastus-vHub1_VHUB
On the left side, expand “Routing” and then “Effective Routes”
Select - “Route Tables” under “Choose resource type”
Select - “Default” under “Resource”
All effective routes should have the FortiGate NVA group as next hop.
View the effective routes on the spoke Linux VMs
Navigate to your Linux VM Linux-Spoke1-VM
Click - “Network settings” located under “Networking” on the left side of the page
Click - “Linux-Spoke1-VM_nic1 (primary) / ipconfig (primary)
One the next page, navigate to Help on the bottom left and Click - “Effective Routes”
Repeat for Linux-Spoke2-VM
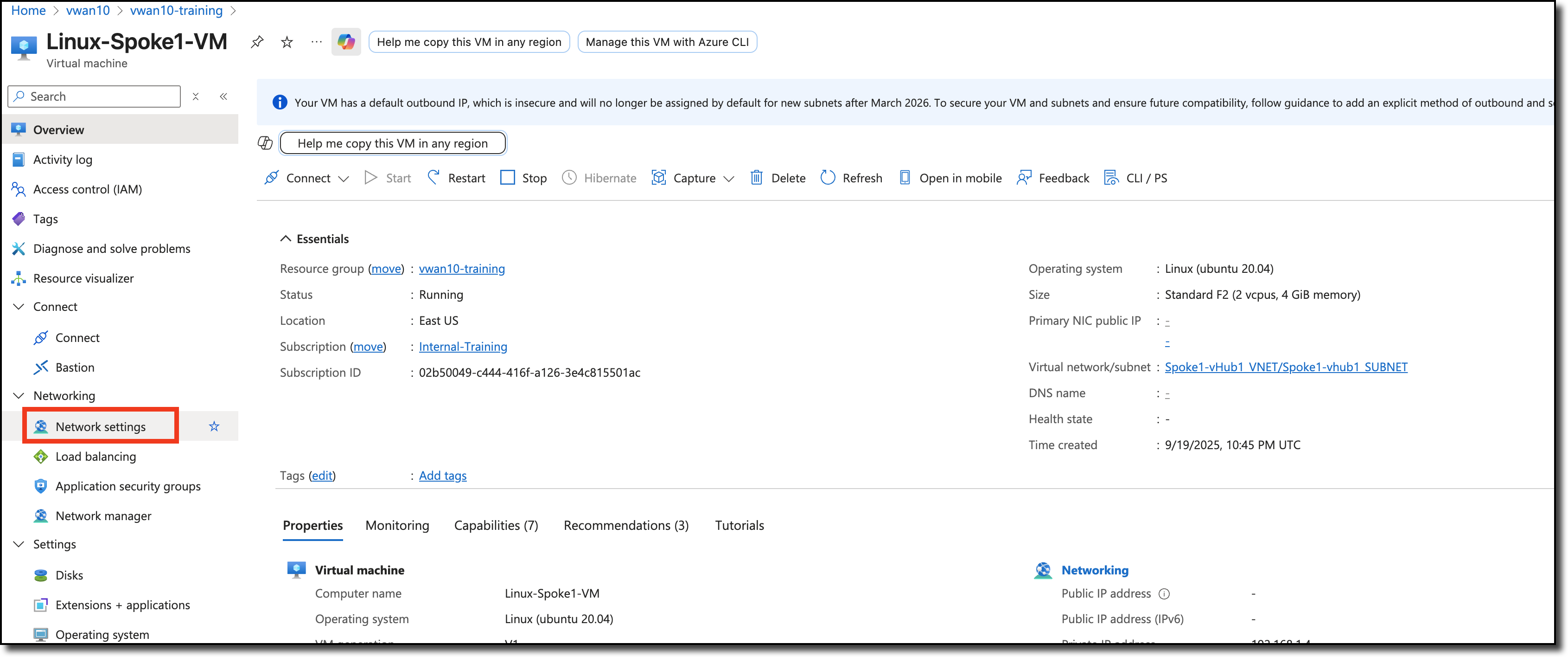
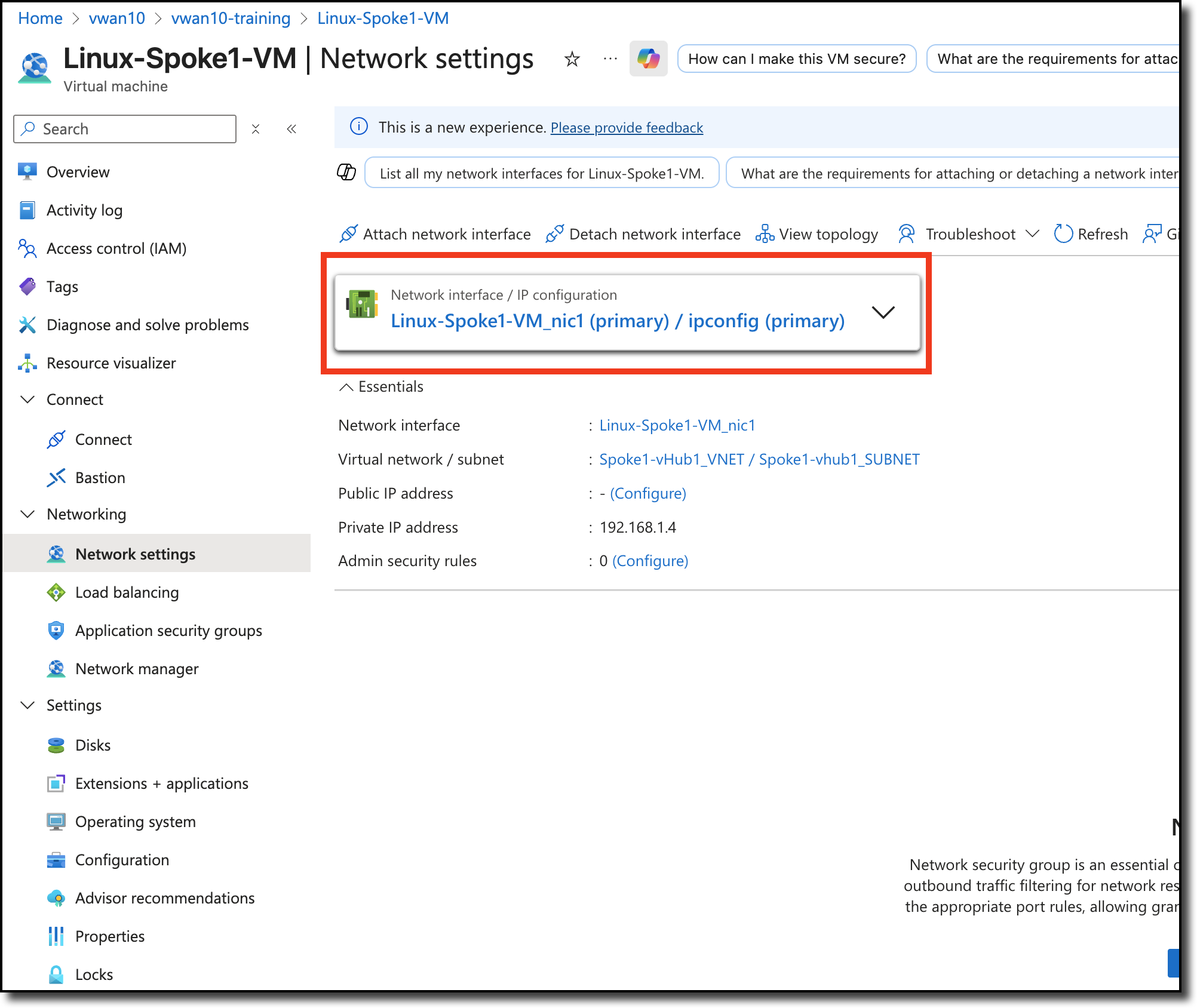
The effective route’s next hop IP is the IP address of internal load balancer that is deployed in the vWAN hub with the FortiGate NVAs.
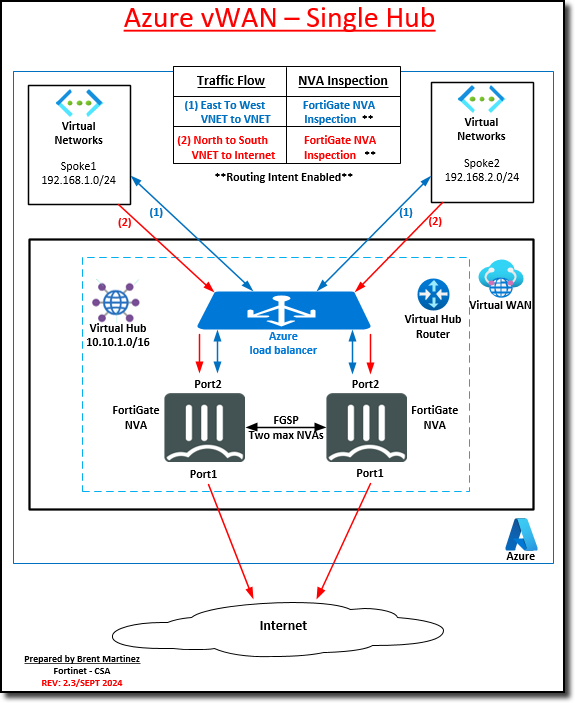
The diagram below is a visual representation of what you have deployed and configured. Congrats!
Continue to Chapter 5 - Network Traffic Management