Subsections of fortigate-aws-gwlb-cloudformation
Introduction
Welcome
The purpose of this site is to provide a quick start guide for using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates located in the repo fortigate-aws-gwlb-cloudformation.
Reference the prerequisites and deployment sections on this site to get started.
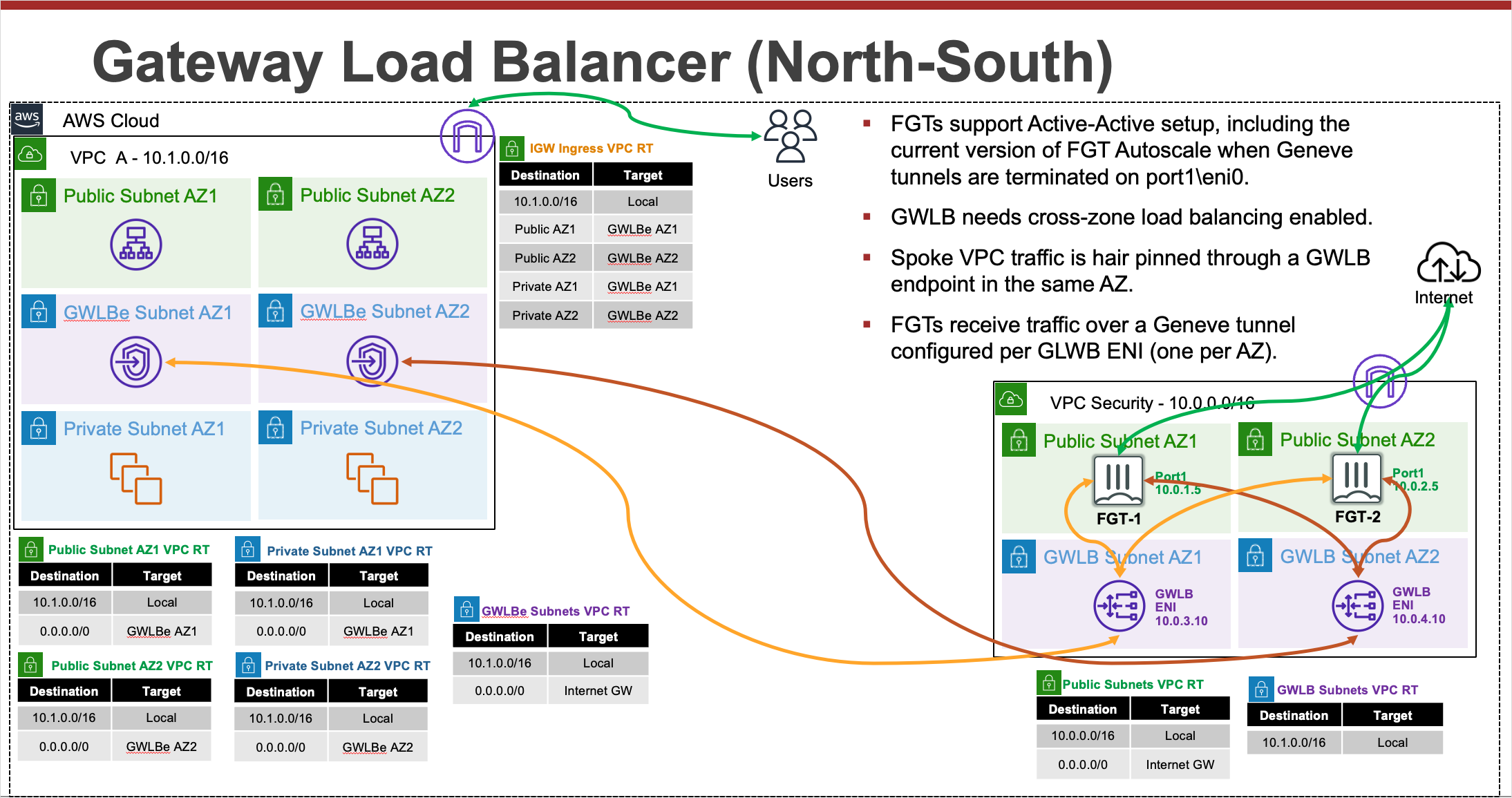
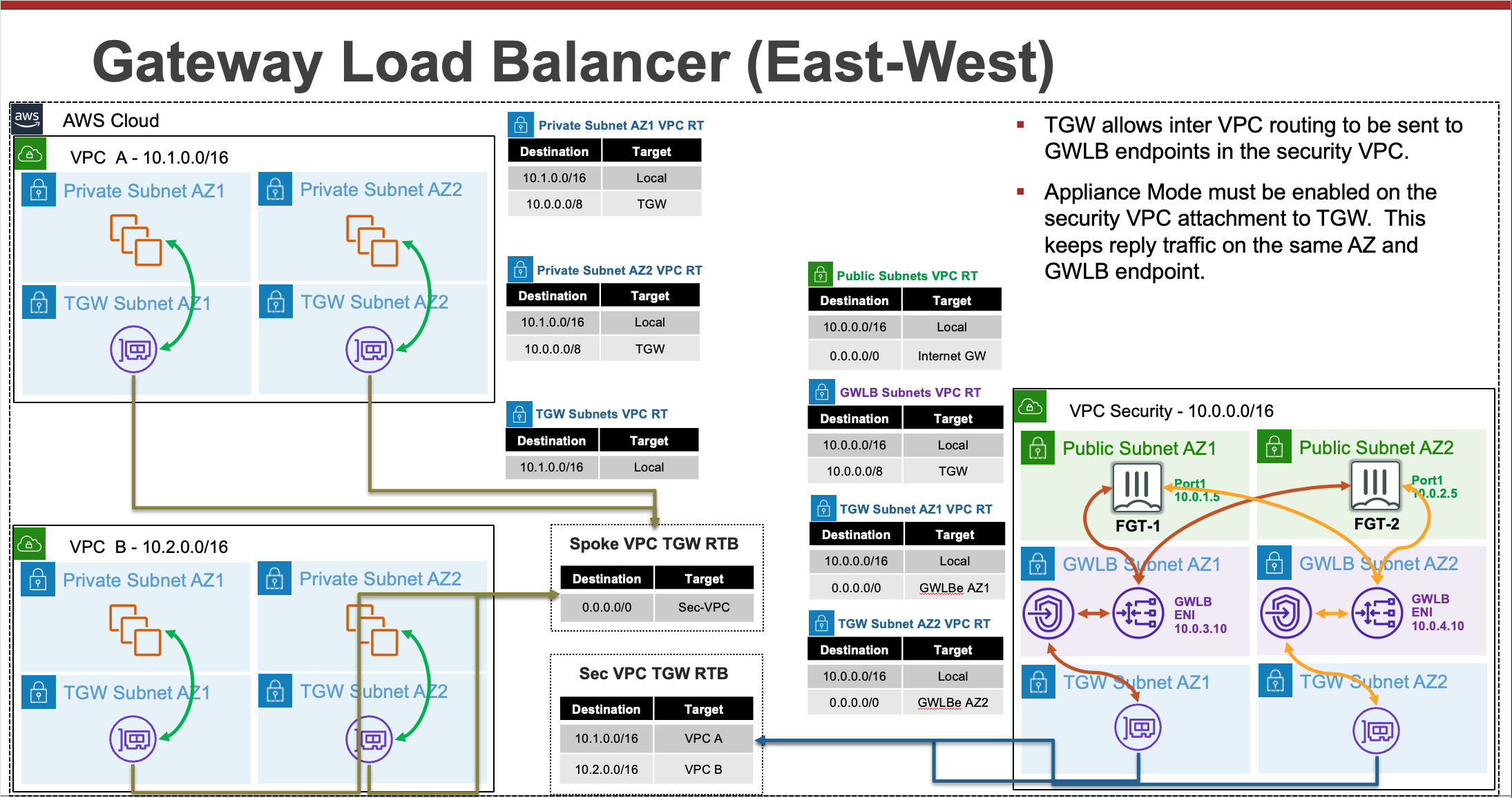
For detailed documentation on FortiGates with GWLB in AWS, walk through of a post deployment failover, and additional use cases, please reference CSE Team GWLB in AWS.
For other documentation needs such as FortiOS administration, please reference docs.fortinet.com.
Prerequisites
Before attempting to create a stack with the templates, a few prerequisites should be checked to ensure a successful deployment:
An AMI subscription must be active for the FortiGate license type being used in the template.
The solution requires 1 EIP per FGT to be created so ensure the AWS region being used has available capacity. Reference AWS Documentation for more information on EC2 service quotas and how to request increases.
If BYOL licensing is to be used, ensure these licenses have been registered on the support site.
If BYOL licensing is to be used, create a new S3 bucket in the same region where the template will be deployed. If the bucket is in a different region than the template deployment, bootstrapping will fail and the FGTs will be inaccessible.
If BYOL licensing is to be used, upload these licenses to the root directory of the same S3 bucket from the step above.
Deployment
Once the prerequisites have been satisfied proceed with the deployment steps below.
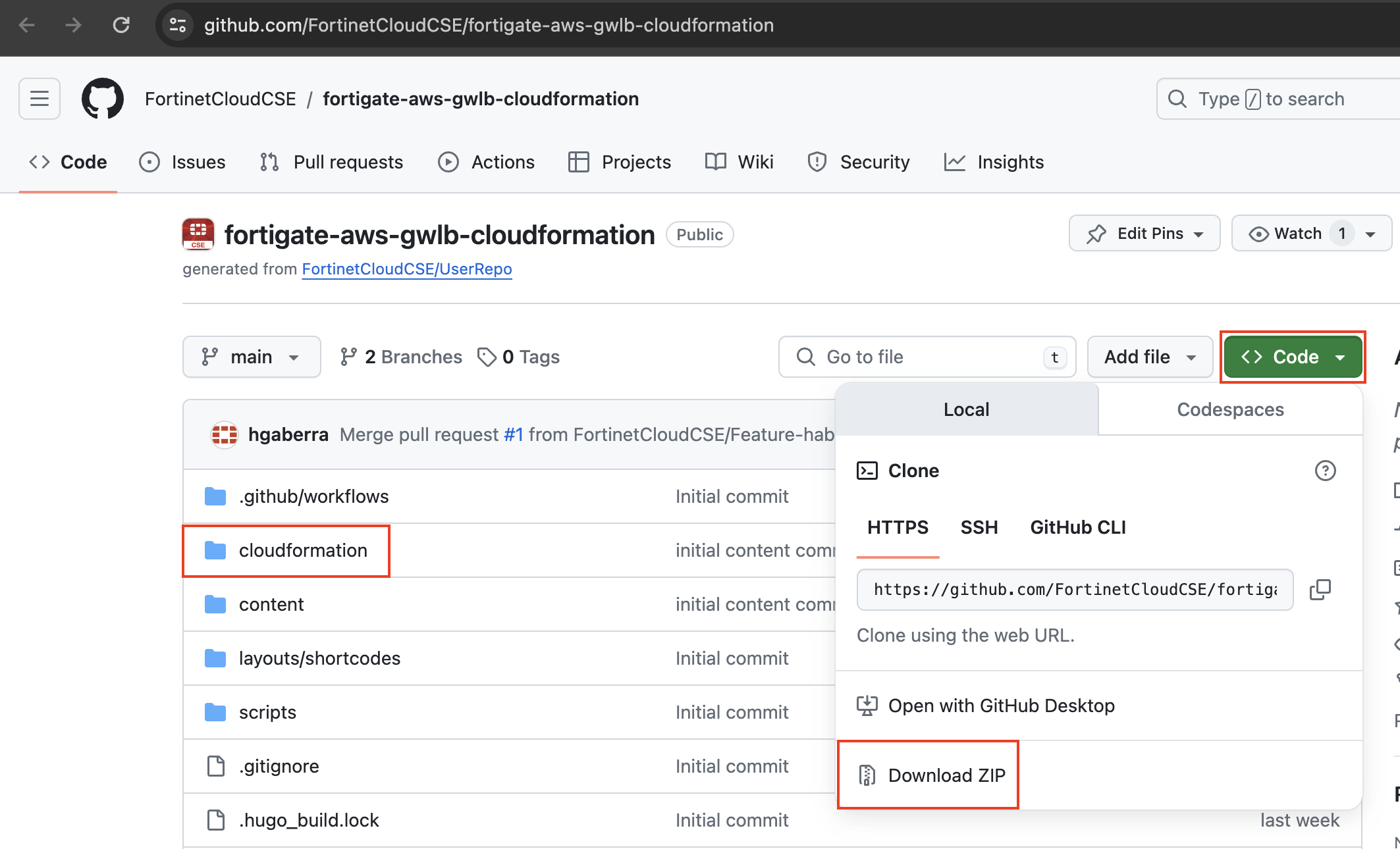
To download the templates, you can either clone the repo with the git command below or download the repo as a ZIP archive. The templates themselves are located in the /cloudformation folder
git clone https://github.com/FortinetCloudCSE/fortigate-aws-gwlb-cloudformation.gitLogin to your AWS account. In the AWS services page under All Services > Management Tools, select CloudFormation.
Select Create Stack then select with new resources.
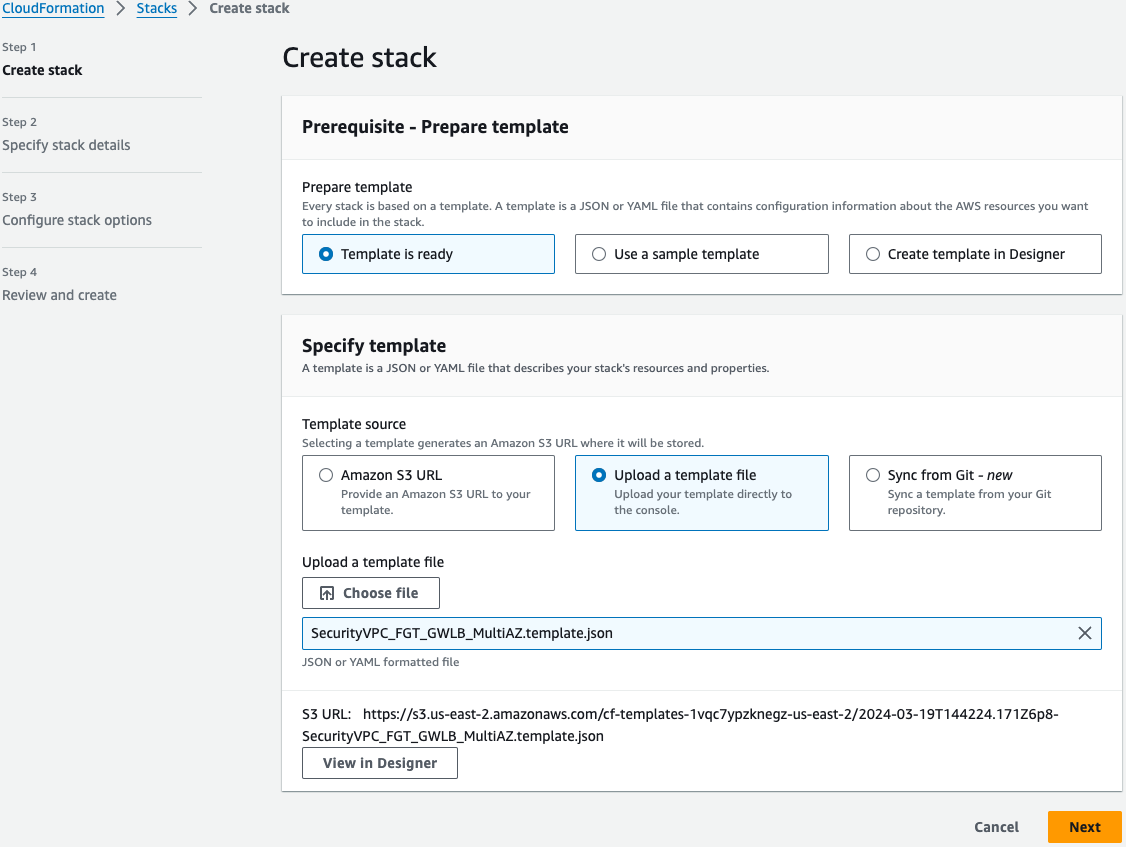
On the Select Template page, under the Specify Template section select Upload a template file to Amazon S3 and browse to your local copy of the chosen deployment template.
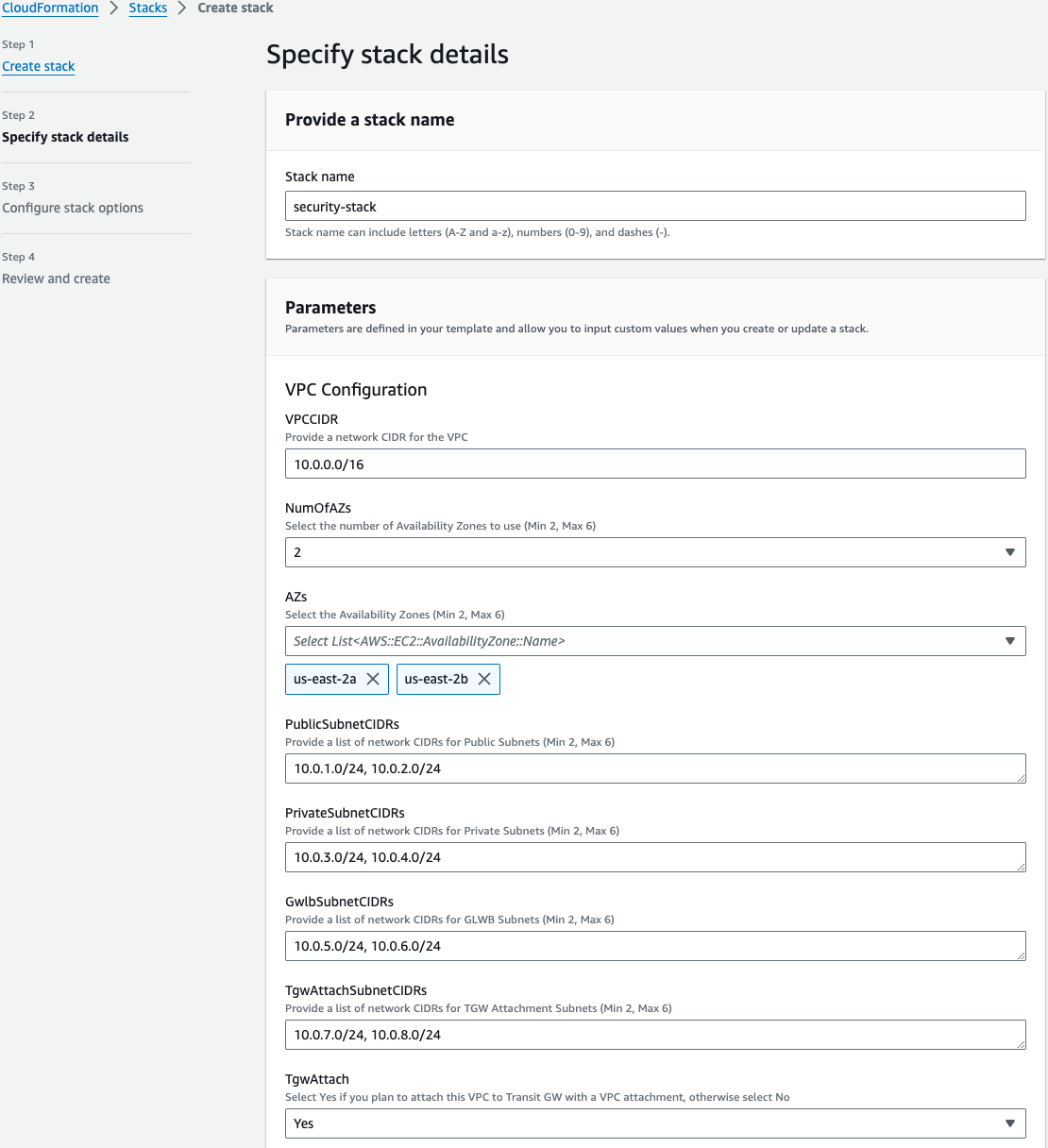
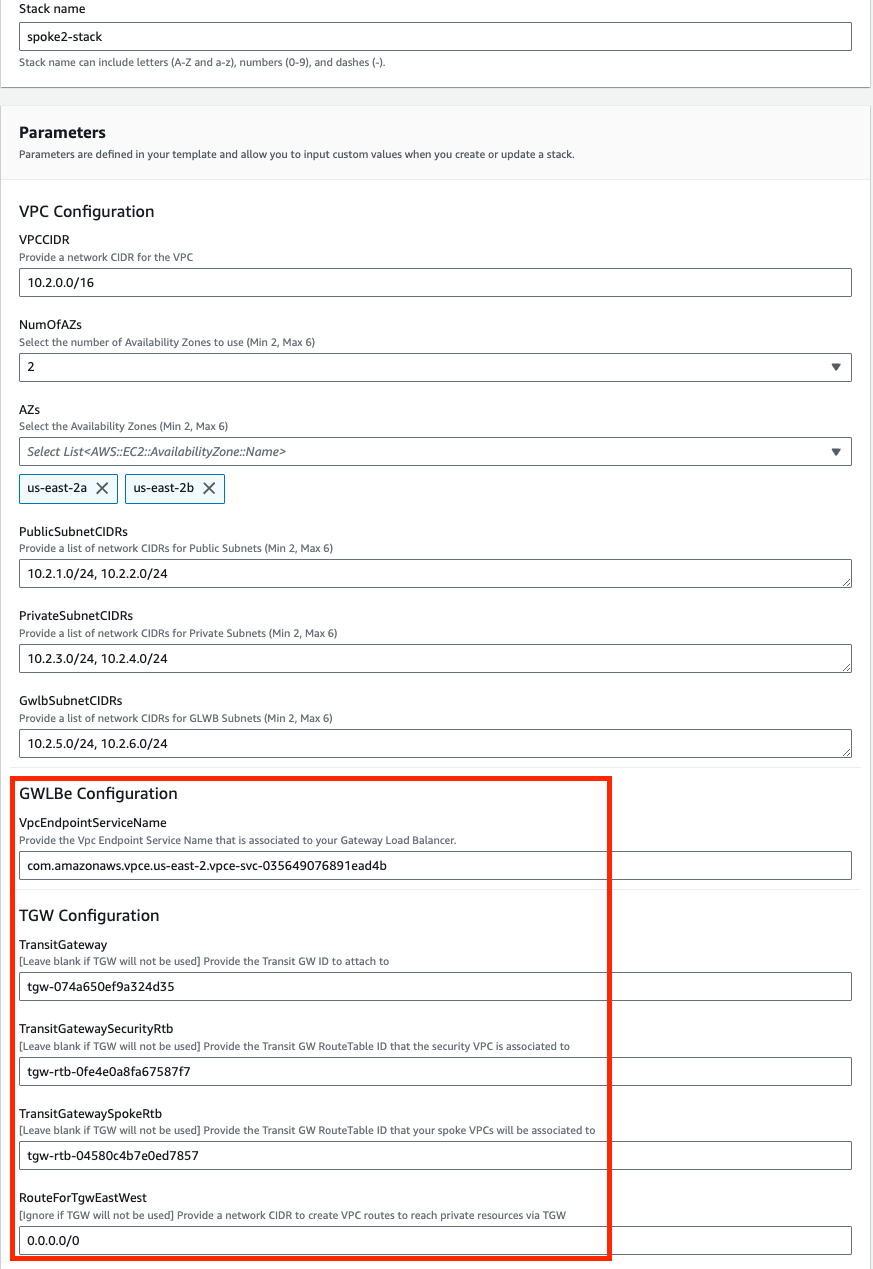
On the Specify Details page, you will be prompted for a stack name and parameters for the deployment. We are using the ‘NewVPC_FGT_GWLB_MultiAZ.template.json’ template which deploys a new VPC, gives options for TGW or CWAN integration, and deploys multiple FGTs as well.
Tip
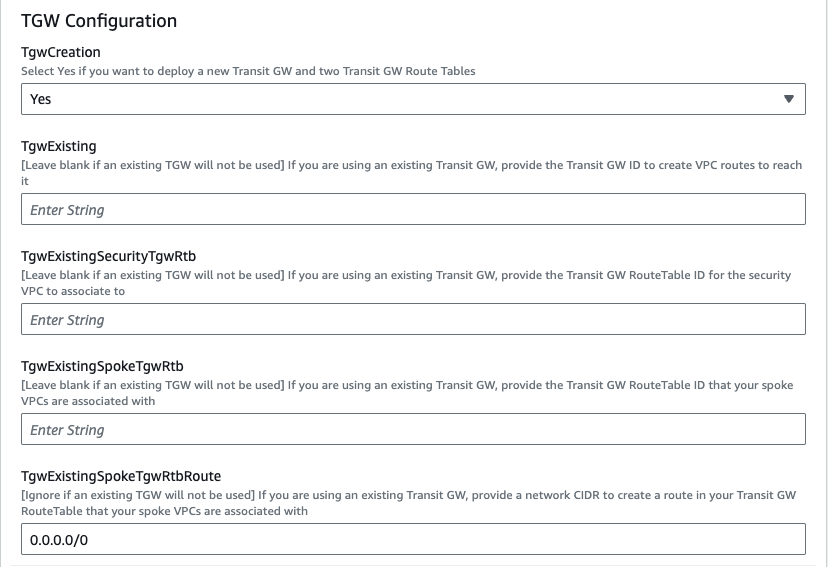
We are choosing to deploy TGW so we have set both ‘Attachment’ and ‘TgwCreation’ to ‘Yes’. We also set ‘CwanCreation’ to ‘NO’. Note you can also attach to an existing TGW by changing ‘TgwCreation’ to ‘No’ and providing the appropriate values for the ‘TgwExisting…’ parameters. The same applies for an existing CWAN using ‘CwanExisting…’ parameters.
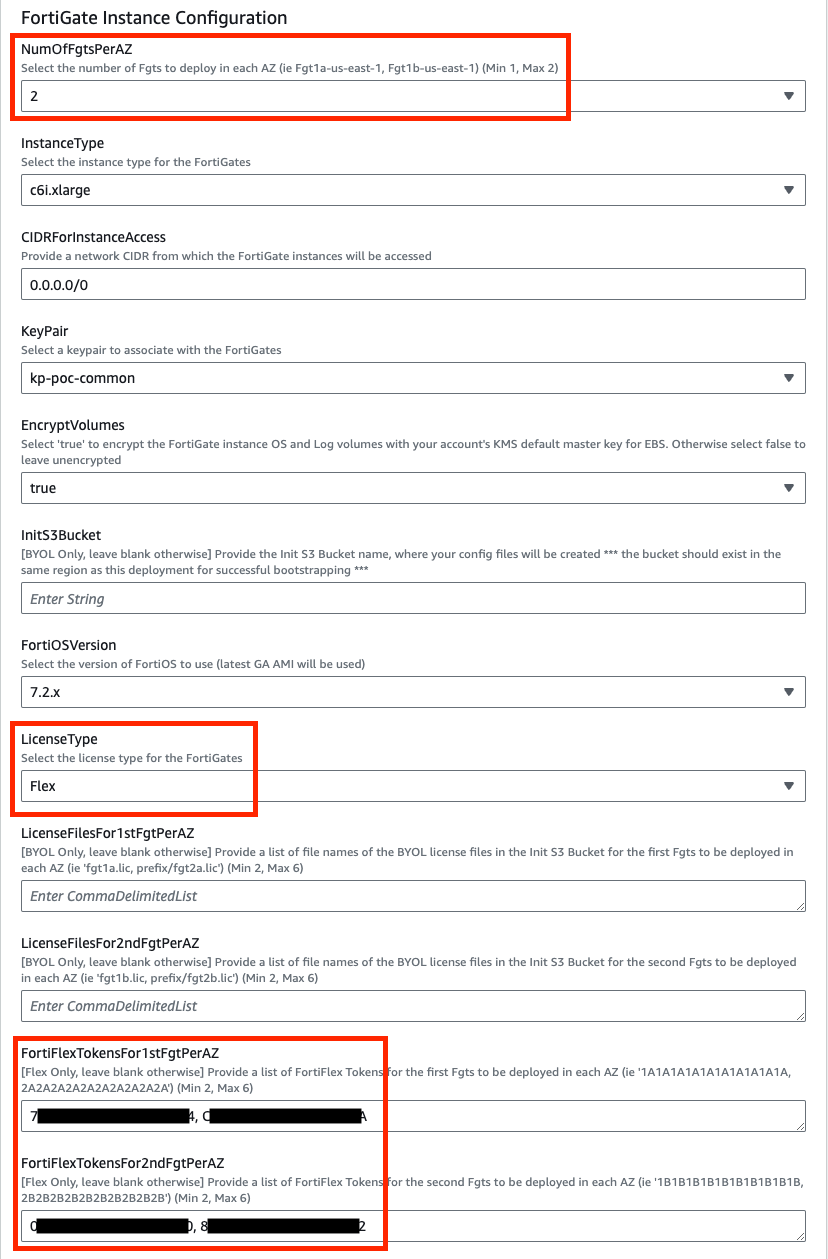
In the FortiGate Instance Configuration parameters section, we have selected the number of FGTs per AZ to 2 and Key Pair to use for the FGTs as well as Flex licensing. Since we are using FLEX licensing, we can leave the InitS3Bucket empty but need to specify the Flex tokens to use. Then select Next.
Tip
Since we are deploying 2 FGTs per AZ, we are specifying the first set of Flex tokens for FGT1a and FGT2a in FortiFlexTokensFor1stFgtPerAZ and then the second set for FGT1b and FGT2b in FortiFlexTokensFor2ndFgtPerAZ.
On the Options page, you can scroll to the bottom and select Next. On the Review page, scroll down to the capabilities section. As the template will create IAM resources, you need to acknowledge this by checking the box next to ‘I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources’ and then click Submit.
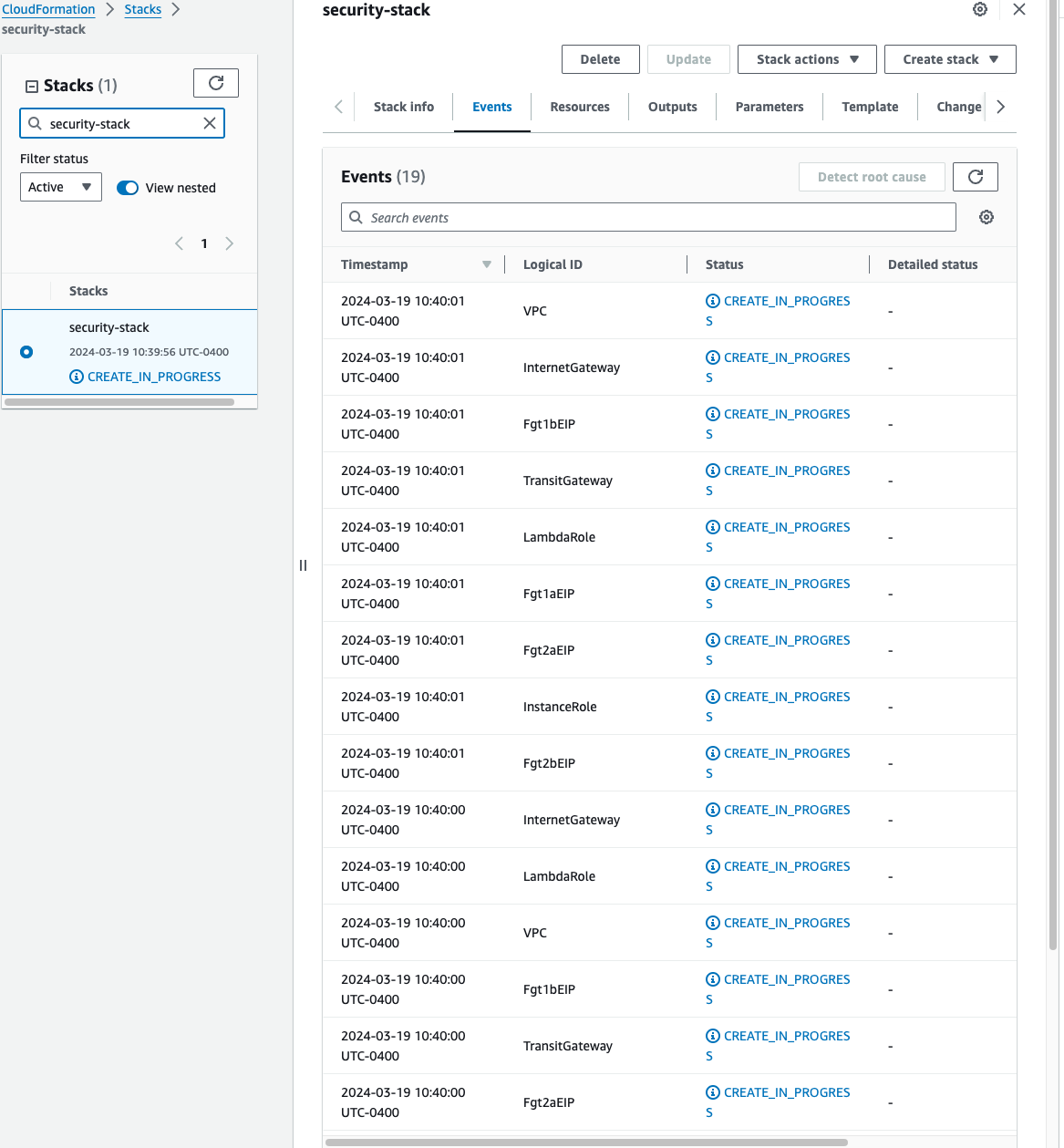
On the main AWS CloudFormation console, you will now see your stack being created. You can monitor the progress by selecting your stack and then select the Events tab.
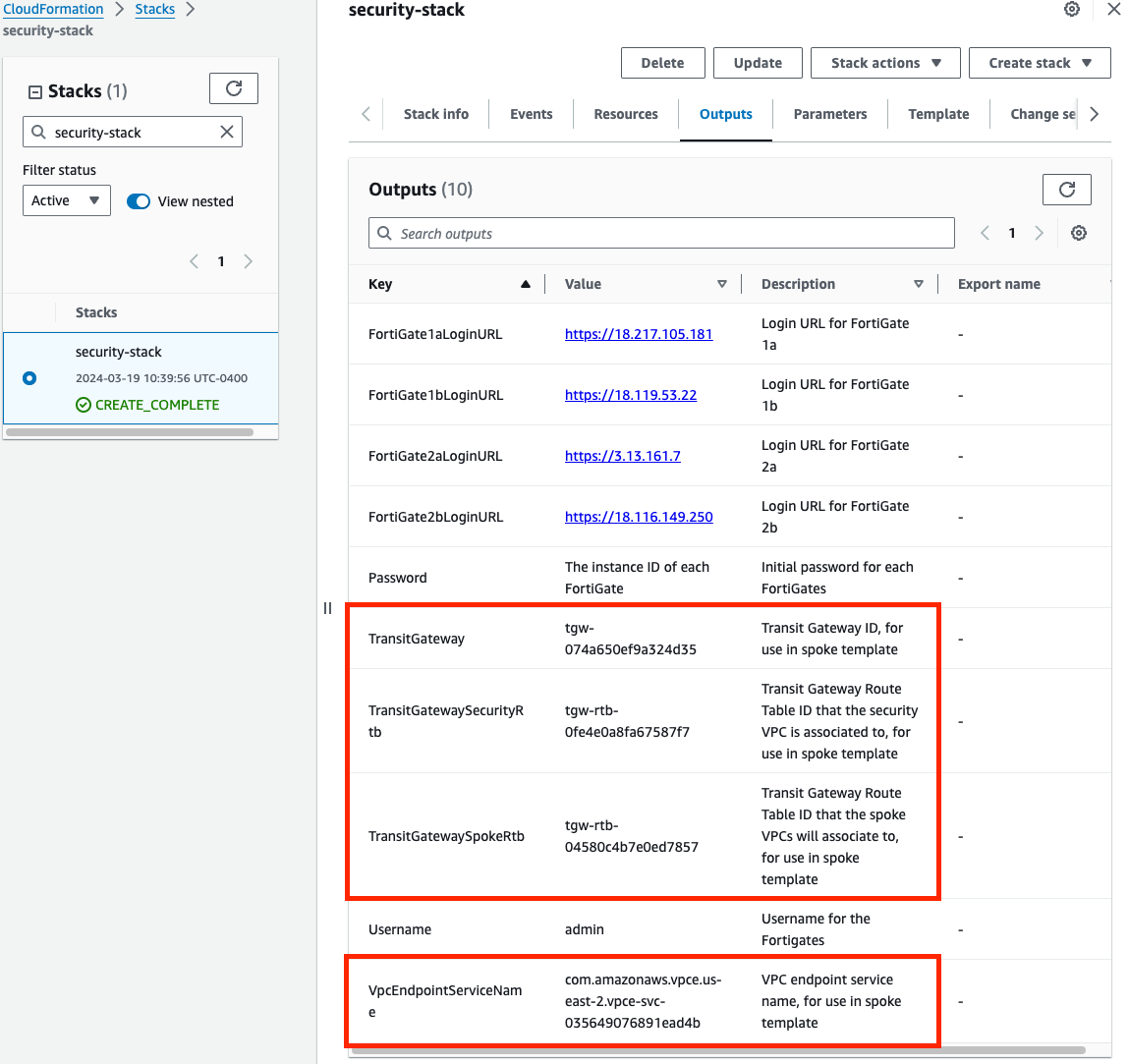
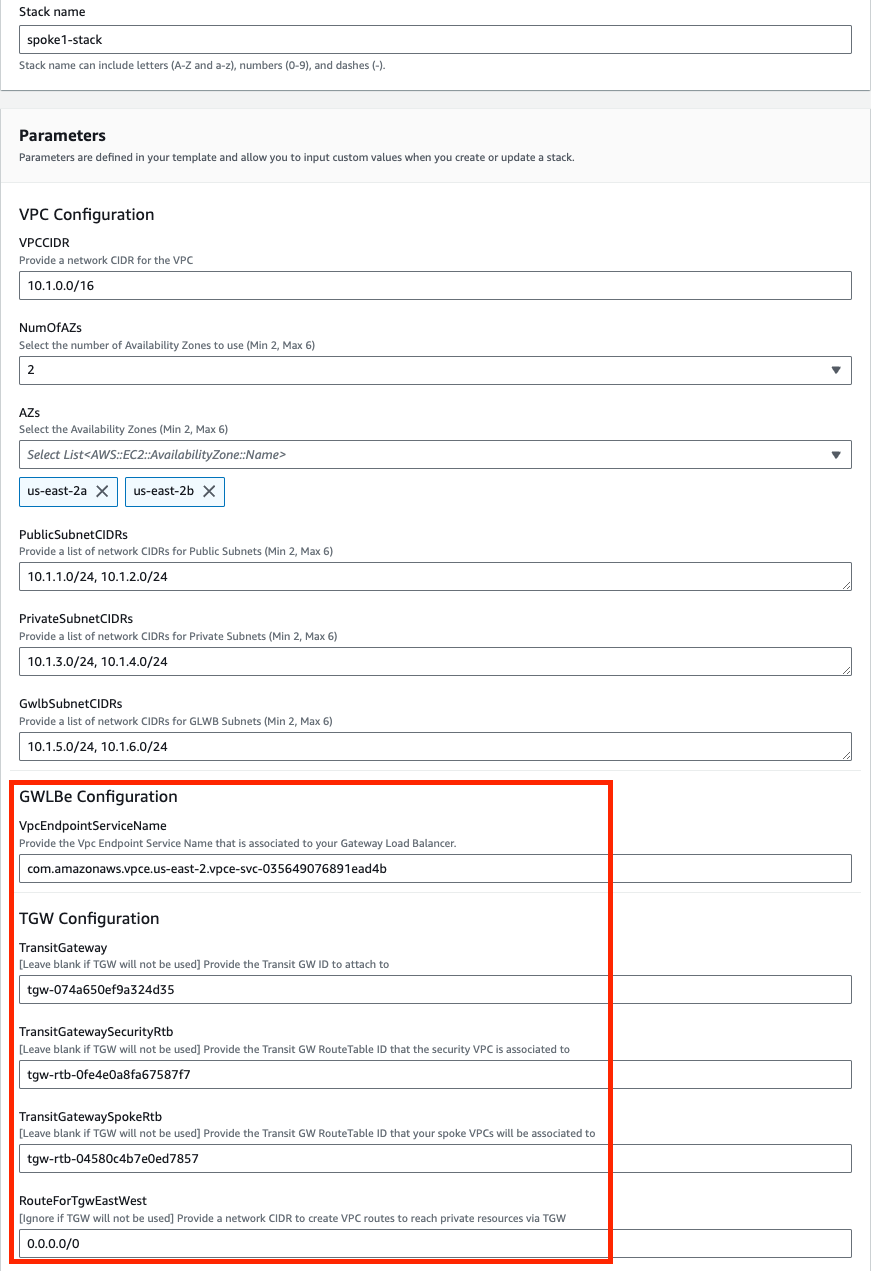
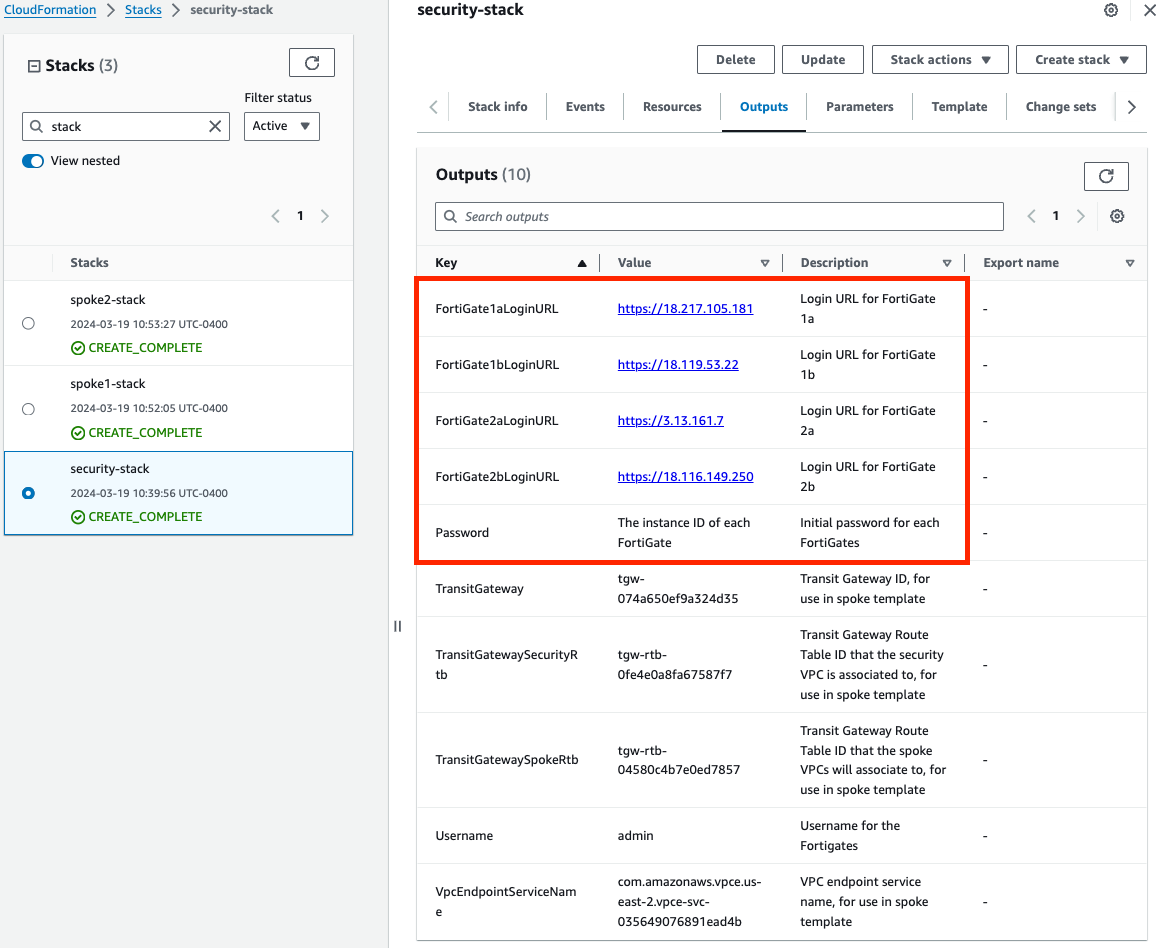
Once the stack creation has completed successfully, select the Outputs tab to get the login information for the FGT instances. If you chose to deploy a new TGW as part of the deployment you will see the IDs of your Transit Gateway and TGW Route Tables. These will be used as inputs for the ‘NewVPC_Spoke_GWLBe_MultiAZ.template.json’ template.
Select the Outputs tab of the security stack to get the login information for the FGT instances.
This concludes the template deployment example.