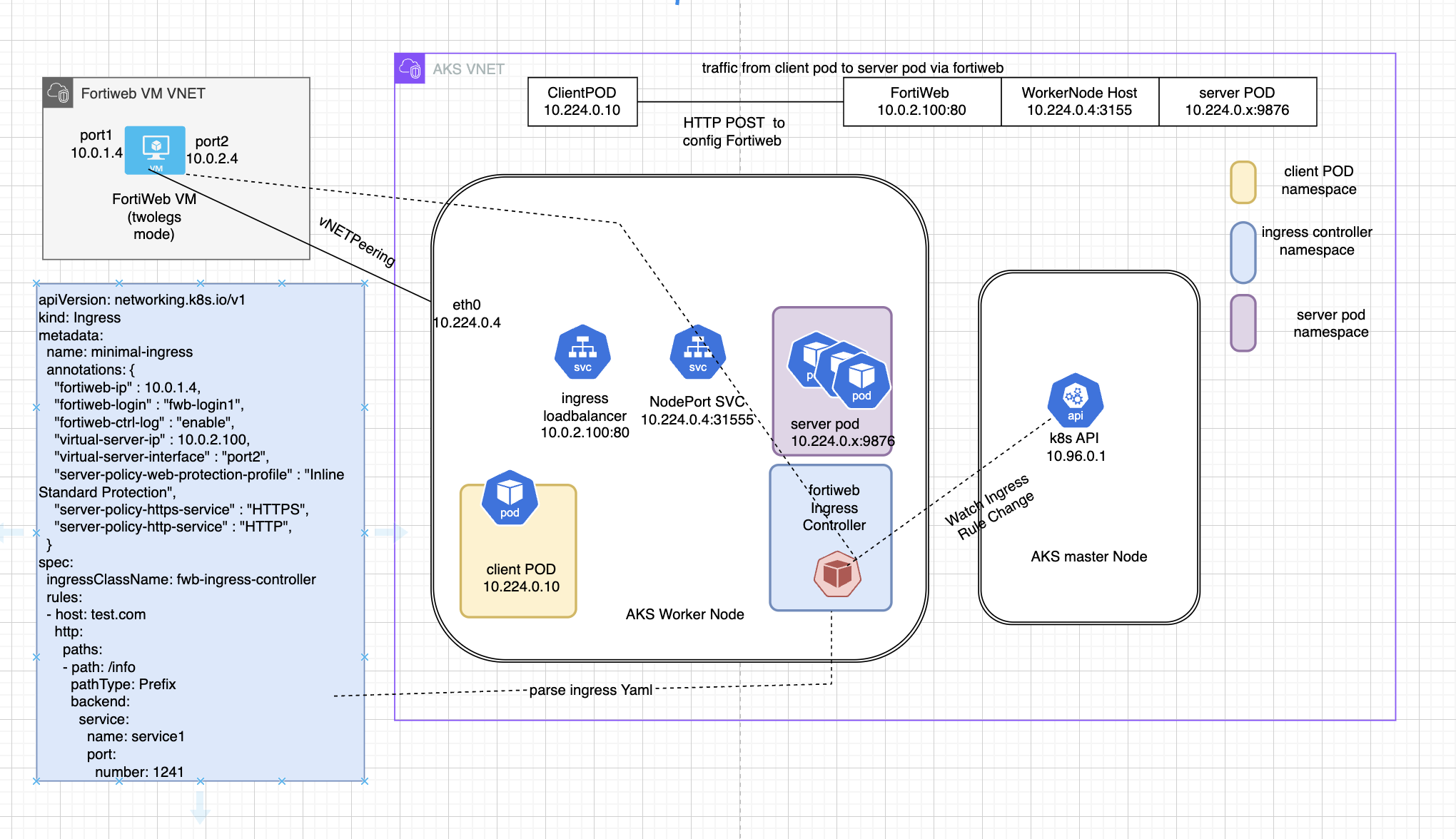
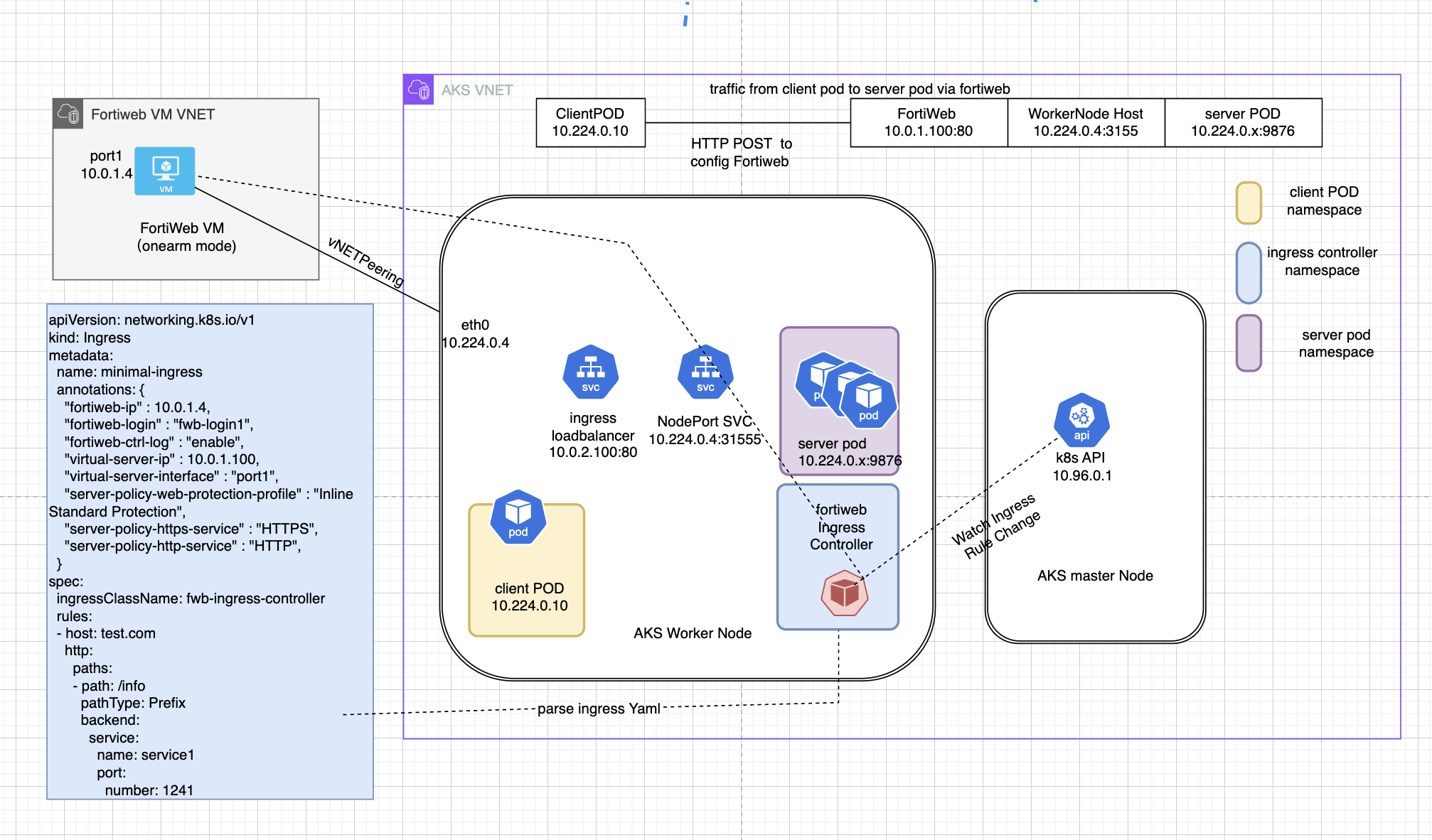
Install and Setup FortiWeb Ingress Controller
Network Diagram
In this chapter, we are going to create a lab setup as illustrated in the network diagram below.
FortiWeb can be configured with two ports: port1 for incoming traffic and port2 for proxy traffic to the backend application. This is called the twoarms mode here.
FortiWeb can also be configured with a single port, where port1 handles both incoming traffic and proxy traffic to the backend application. This is called the one-arm mode.
Note
In this workshop, please use default onearm mode.
1. Prepare Environment Variables
read -p "Enter deploy mode (twoarms/onearm) [onearm]: " fortiwebdeploymode
fortiwebdeploymode=${fortiwebdeploymode:-onearm}
echo $fortiwebdeploymode
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
secondaryIp="10.0.2.100"
else
secondaryIp="10.0.1.100"
fi
owner="tecworkshop"
currentUser=$(az account show --query user.name -o tsv)
resourceGroupName=$(az group list --query "[?contains(name, '$(whoami)') && contains(name, 'workshop')].name" -o tsv)
#resourceGroupName=$(az group list --query "[?tags.UserPrincipalName=='$currentUser'].name" -o tsv)
if [ -z "$resourceGroupName" ]; then
resourceGroupName=$owner-$(whoami)-"fortiweb-"$location-$(date -I)
az group create --name $resourceGroupName --tags UserPrincipalName=$currentUser --location $location
resourceGroupName=$resourceGroupName
fi
location=$(az group show --name $resourceGroupName --query location -o tsv)
echo "Using resource group $resourceGroupName in location $location"
cat << EOF | tee > $HOME/variable.sh
#!/bin/bash -x
vnetName="fortiweb-VNET"
aksVnetName="AKS-VNET"
imageName="fortinet:fortinet_fortiweb-vm_v5:fortinet_fw-vm:latest"
fortiwebUsername="azureuser"
fortiwebPassword='Welcome.123456!'
fortiwebvmdnslabel="$(whoami)fortiwebvm7"
aksClusterName=$(whoami)-aks-cluster
rsakeyname="id_rsa_tecworkshop"
vm_name="$(whoami)fortiwebvm7.${location}.cloudapp.azure.com"
fortiwebvmdnslabelport2="$(whoami)px2"
svcdnsname="$(whoami)px2.${location}.cloudapp.azure.com"
remoteResourceGroup="MC"_${resourceGroupName}_$(whoami)-aks-cluster_${location}
nicName1="NIC1"
nicName2="NIC2"
alias k=kubectl
EOF
echo fortiwebdeploymode=$fortiwebdeploymode >> $HOME/variable.sh
echo secondaryIp=$secondaryIp >> $HOME/variable.sh
echo location=$location >> $HOME/variable.sh
echo owner=$owner >> $HOME/variable.sh
echo resourceGroupName=$resourceGroupName >> $HOME/variable.sh
chmod +x $HOME/variable.sh
line='if [ -f "$HOME/variable.sh" ]; then source $HOME/variable.sh ; fi'
grep -qxF "$line" ~/.bashrc || echo "$line" >> ~/.bashrc
source $HOME/variable.sh
$HOME/variable.sh
if [ -f $HOME/.ssh/known_hosts ]; then
grep -qxF "$vm_name" "$HOME/.ssh/known_hosts" && ssh-keygen -R "$vm_name"
fi2. Create Kubernetes Cluster
We can use either managed K8s like AKS, EKS or self-managed k8s like kubeadm etc., in this workshop, let’s use AKS.
We will create aks VNET and fortiweb VNET in same resourceGroup, in reality, you can also create them in different resourceGroup.
- Create aks VNET and subnet
az network vnet create -g $resourceGroupName --name $aksVnetName --location $location --subnet-name aksSubnet --subnet-prefix 10.224.0.0/24 --address-prefix 10.224.0.0/16- Get aksSubnetId
this aksSubnetId will be need when create AKS.
aksSubnetId=$(az network vnet subnet show \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--vnet-name $aksVnetName \
--name aksSubnet \
--query id -o tsv)
echo $aksSubnetId- Create AKS cluster
this may take a while to complete
[ ! -f ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname ] && ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -q -N "" -f ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname
az aks create \
--name ${aksClusterName} \
--node-count 1 \
--vm-set-type VirtualMachineScaleSets \
--network-plugin azure \
--location $location \
--service-cidr 10.96.0.0/16 \
--dns-service-ip 10.96.0.10 \
--nodepool-name worker \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--kubernetes-version 1.28.9 \
--vnet-subnet-id $aksSubnetId \
--only-show-errors \
--ssh-key-value ~/.ssh/${rsakeyname}.pub
az aks get-credentials -g $resourceGroupName -n ${aksClusterName} --overwrite-existingCheck Creation result with
kubectl get node -o wide- You should see nodes are in “ready” status and “VERSION” is v.1.28.9,
- The node should have an internal ip assigned.
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
aks-worker-12061195-vmss000000 Ready agent 8m51s v1.28.9 10.224.0.4 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS 5.15.0-1064-azure containerd://1.7.15-1Check the Vnet of this aks cluster.
az network vnet list -g $resourceGroupName -o tableyou will find azure created a Vnet for this AKS.
k8s51 [ ~ ]$ az network vnet list -g $resourceGroupName -o table
Name ResourceGroup Location NumSubnets Prefixes DnsServers DDOSProtection VMProtection
-------- --------------------- ---------- ------------ ------------- ------------ ---------------- --------------
AKS-VNET k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus 1 10.224.0.0/16 False3. Prepare to deploy fortiweb VM in dedicated VNET
In this workshop, We are going to deploy fortiweb VM in it’s own VNET, fortiweb will use twoarms or onearm deployment model, below lists the components going to be deployed
- VNET : 10.0.0.0/16
- Subnet1: 10.0.1.0/24
- Subnet2: 10.0.2.0/24 when fortiweb in twoarms mode
- NSG : allow all traffic
- NIC1 with Public IP for SSH access and Management, in Subnet1
- NIC2 for internal traffic, in Subnet2, when fortiweb in twoarms mode
- VM with Extra DISK for log
- Create VNET with Subnet1
az network vnet create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--name $vnetName \
--location $location \
--address-prefix 10.0.0.0/16 \
--subnet-name ExternalSubnet \
--subnet-prefix 10.0.1.0/24- Create Subnet2 in same VNET if use twoarms mode
Warning
This is only for Two arm mode, if one arm mode dont run the below commands
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
az network vnet subnet create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--vnet-name $vnetName \
--name InternalSubnet \
--address-prefix 10.0.2.0/24
fi- Create NSG with Rule
this NSG will be attached to fortiweb VM NICs.
az network nsg create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--location $location \
--name MyNSG
az network nsg rule create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--nsg-name MyNSG \
--name AllowAll \
--protocol '*' \
--direction Inbound \
--priority 1000 \
--source-address-prefix '*' \
--source-port-range '*' \
--destination-address-prefix '*' \
--destination-port-range '*'- Create PublicIP with a DNS name
this publicip serve for mgmt purpose, we can use this ip for SSH and WebGUI to fortiweb VM via IP address or DNS name
the fortiweb factory default configuration only have SSH service and WebGUI service enabled on Port1. so this Public IP will be associated to fortiweb VM Port1.
az network public-ip create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--location $location \
--name FWBPublicIP \
--allocation-method Static \
--sku Standard \
--dns-name $fortiwebvmdnslabel \
--only-show-errors - Create NIC1 and attach PublicIP
az network nic create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--location $location \
--name NIC1 \
--vnet-name $vnetName \
--subnet ExternalSubnet \
--network-security-group MyNSG \
--public-ip-address FWBPublicIP
az network nic update \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--name NIC1 \
--ip-forwarding true- Create NIC2 if Fortiweb use twoarms mode
Warning
This is only for Two arm mode, if one arm mode dont run the below commands
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
az network nic create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--location $location \
--name NIC2 \
--vnet-name $vnetName \
--subnet InternalSubnet \
--network-security-group MyNSG
az network nic update \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--name NIC2 \
--ip-forwarding true
fi 4. Deploy fortiweb VM
- Create VM with storage Disk
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
nics="NIC1 NIC2"
else
nics="NIC1"
fi
az vm create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--name MyfortiwebVM \
--size Standard_F2s \
--image $imageName \
--admin-username $fortiwebUsername \
--admin-password $fortiwebPassword \
--nics $nics \
--location $location \
--public-ip-address-dns-name $fortiwebvmdnslabel \
--data-disk-sizes-gb 30 \
--ssh-key-values @~/.ssh/${rsakeyname}.pub \
--only-show-errorsyou shall see output like this
one-arm mode
{
"fqdns": "k8s52fortiwebvm7.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com",
"id": "/subscriptions/02b50049-c444-416f-a126-3e4c815501ac/resourceGroups/k8s52-k8s101-workshop/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/MyfortiwebVM",
"location": "eastus",
"macAddress": "60-45-BD-D6-B4-8C",
"powerState": "VM running",
"privateIpAddress": "10.0.1.4",
"publicIpAddress": "52.170.217.44",
"resourceGroup": "k8s52-k8s101-workshop",
"zones": ""
}or if in two-arm mode
{
"fqdns": "k8s51fortiwebvm7.eastus.cloudapp.azure.com",
"id": "/subscriptions/02b50049-c444-416f-a126-3e4c815501ac/resourceGroups/k8s51-k8s101-workshop/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/MyfortiwebVM",
"location": "eastus",
"macAddress": "60-45-BD-D8-14-AF,60-45-BD-D8-1D-FE",
"powerState": "VM running",
"privateIpAddress": "10.0.1.4,10.0.2.4",
"publicIpAddress": "13.90.210.29",
"resourceGroup": "k8s51-k8s101-workshop",
"zones": ""
}- Check all the resource you created
az resource list -g $resourceGroupName -o tableyou shall see output like
k8s51 [ ~ ]$ az resource list -g $resourceGroupName -o table
Name ResourceGroup Location Type Status
------------------------------------------------------ --------------------- ---------- ------------------------------------------ --------
AKS-VNET k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks
k8s51-aks-cluster k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.ContainerService/managedClusters
FortiWeb-VNET k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks
MyNSG k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups
FWBPublicIP k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses
NIC1 k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces
NIC2 k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces
MyfortiwebVM k8s51-k8s101-workshop eastus Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines
MyfortiwebVM_disk2_1a5d56afec9745dba51cfed47fd133dc K8S51-K8S101-WORKSHOP eastus Microsoft.Compute/disks
MyfortiwebVM_OsDisk_1_6259c4a932fe4cfd866015e1fb611558 K8S51-K8S101-WORKSHOP eastus Microsoft.Compute/disks- Verify fortiweb VM has been created and you have ssh access to it
type exit to exit from SSH session
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i $HOME/.ssh/$rsakeyname or directly append fortiweb cli command
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i $HOME/.ssh/$rsakeyname "get system status"5. Create VNET Peering
Because AKS and fortiweb are in different VNETs, they are isolated from each other. We are going to use VNET Peering to connect fortiweb VM with AKS workernode. To do that, we need to get both vnetIds to create peering.
**define localPeer name and RemotePeer name **
localPeeringName="fortiwebToAksPeering"
remotePeeringName="AksTofortiwebPeering"- Get the full resource ID of the local VNet
localVnetId=$(az network vnet show --resource-group $resourceGroupName --name $vnetName --query "id" -o tsv)- Get the full resource ID of the remote VNet
remoteVnetId=$(az network vnet show --resource-group $resourceGroupName --name $aksVnetName --query "id" -o tsv)
echo $remoteVnetId- Create peering from local VNet to remote VNet
az network vnet peering create \
--name $localPeeringName \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--vnet-name $vnetName \
--remote-vnet $remoteVnetId \
--allow-vnet-access- Create peering from remote VNet to local VNet
az network vnet peering create \
--name $remotePeeringName \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--vnet-name $aksVnetName \
--remote-vnet $localVnetId \
--allow-vnet-access- Check vnet peering status
az network vnet peering list -g $resourceGroupName --vnet-name AKS-VNET -o table
az network vnet peering list -g $resourceGroupName --vnet-name fortiweb-VNET -o tableYou should see output like
AllowForwardedTraffic AllowGatewayTransit AllowVirtualNetworkAccess DoNotVerifyRemoteGateways Name PeeringState PeeringSyncLevel ProvisioningState ResourceGroup ResourceGuid UseRemoteGateways
----------------------- --------------------- --------------------------- --------------------------- -------------------- -------------- ------------------ ------------------- --------------------- ------------------------------------ -------------------
False False True False AksTofortiwebPeering Connected FullyInSync Succeeded k8s51-k8s101-workshop e867030a-0101-00b2-19a0-fba24c2151dd False
AllowForwardedTraffic AllowGatewayTransit AllowVirtualNetworkAccess DoNotVerifyRemoteGateways Name PeeringState PeeringSyncLevel ProvisioningState ResourceGroup ResourceGuid UseRemoteGateways
----------------------- --------------------- --------------------------- --------------------------- -------------------- -------------- ------------------ ------------------- --------------------- ------------------------------------ -------------------
False False True False fortiwebToAksPeering Connected FullyInSync Succeeded k8s51-k8s101-workshop e867030a-0101-00b2-19a0-fba24c2151dd False6. Verify the connectivity between fortiweb VM and AKS
- get AKS worker node ip
nodeIp=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.status.addresses[?(@.type=="InternalIP")].address}{"\n"}{end}')
echo $nodeIp- Verify the connectivity between fortiweb VM and AKS worker node Use ping from fortiweb VM to AKS node
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname execute ping $nodeIpYou will see output like
MyfortiwebVM # PING 10.224.0.4 (10.224.0.4): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 10.224.0.4: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=2.5 ms
64 bytes from 10.224.0.4: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=1.1 ms
64 bytes from 10.224.0.4: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=1.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.224.0.4: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=1.2 ms
64 bytes from 10.224.0.4: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=15.0 ms7. Config fortiweb VM
FortiWeb requires some basic configuration to work with ingress Controller config list:
- enable HTTPS API access on TCP port 443
- enable traffic log
- config static route
- static route to AKS vnet subnet via Port1
- default route to internet via Port2 when use fortiweb in twoarms mode
- static route to your client IP (your azure shell) via Port1
- This ensures your client session (your azure shell) can SSH into fortiweb via Port1 public ip.
##get your azure shell client ip
myclientip=$(curl -s https://api.ipify.org)
echo $myclientip
cat << EOF | tee > basiconfig.txt
config system global
set admin-sport 443
end
config log traffic-log
set status enable
end
EOF
cat << EOF | tee > interfaceport2config.txt
config system interface
edit "port2"
set type physical
set allowaccess ping ssh snmp http https FWB-manager
set mode dhcp
next
end
EOF
cat << EOF | tee > staticrouteconfigtwoarms.txt
config router static
edit 10
set dst 10.224.0.0/16
set gateway 10.0.1.1
set device port1
next
edit 2000
set dst 0.0.0.0/0
set gateway 10.0.2.1
set device port2
next
edit 1000
set dst $myclientip
set gateway 10.0.1.1
set device port1
next
end
EOF
cat << EOF | tee > staticrouteconfigonearm.txt
config router static
edit 10
set dst 10.224.0.0/16
set gateway 10.0.1.1
set device port1
next
EOF
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname < basiconfig.txt
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname < interfaceport2config.txt
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname < staticrouteconfigtwoarms.txt
else
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname < staticrouteconfigonearm.txt
fi- Verify the fortiweb Configuration
you can ssh into fortiweb to check configuration like static route etc.,
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname show router static8. SSH into fortiweb via internal ip
You may lose connectivity to fortiweb Public IP via SSH if your client ip subnet is not in fortiweb static route config. In this case, you can use fortiweb internal IP for ssh. We can create an ssh client pod to connect to fortiweb via internal IP.
cat << EOF | tee sshclient.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: ssh-jump-host
labels:
app: ssh-jump-host
spec:
containers:
- name: ssh-client
image: alpine
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["-c", "apk add --no-cache openssh && apk add --no-cache curl && tail -f /dev/null"]
stdin: true
tty: true
EOF
kubectl apply -f sshclient.yamlthen
nic1privateip=$(az network nic show --name NIC1 -g $resourceGroupName --query "ipConfigurations[0].privateIPAddress" --output tsv)
echo $nic1privateip
echo username $fortiwebUsername
echo password $fortiwebPassword
kubectl exec -it po/ssh-jump-host -- ssh $fortiwebUsername@$nic1privateip9. Use Helm to deploy fortiweb Ingress controller
- What is Helm
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes that simplifies the deployment and management of applications within Kubernetes clusters. It uses charts, which are pre-configured packages of Kubernetes resources. Helm also uses Helm repositories, which are collections of charts that can be shared and accessed by others, facilitating the distribution and collaboration of Kubernetes applications. If you use the Azure Cloud Shell, the Helm CLI (Helm v3.6.3 or later ) is already installed. For installation instructions on your local platform, see Installing Helm https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/
- prepare namespace and releasename variable
fortiwebingresscontrollernamespace="fortiwebingress"
releasename="fortiweb-ingress-controller/fwb-k8s-ctrl"- Add Helm Repository for fortiweb Ingress Controller
helm repo add fortiweb-ingress-controller https://fortinet.github.io/fortiweb-ingress/- Update Helm Repositories
helm repo update- Create Namespace in Kubernetes
kubectl create namespace $fortiwebingresscontrollernamespace- Install fortiweb Ingress Controller using Helm
helm install first-release $releasename --namespace $fortiwebingresscontrollernamespaceyou shall see output like this
NAME: first-release
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Jun 11 03:19:14 2024
NAMESPACE: fortiwebingress
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None- Check the manifest that deployed by Helm
helm get manifest first-release -n $fortiwebingresscontrollernamespace - Check Resource Deployment Status
kubectl rollout status deployment first-release-fwb-k8s-ctrl -n fortiwebingress- Check fortiweb Ingress controller startup log
kubectl logs -n 50 -l app.kubernetes.io/name=fwb-k8s-ctrl -n $fortiwebingresscontrollernamespaceyou are expected to see output like
Stopping fortiweb ingress controller
Starting fortiweb ingress controller
time="2024-06-11T03:19:34Z" level=info msg="==Starting fortiweb Ingress controller"10. Deploy Backend Application in AKS
We will deploy two service and expose with ClusterIP SVC , service1 and service2
- deploy service1
imageRepo="public.ecr.aws/t8s9q7q9/andy2024public"
cat << EOF | tee > service1.yaml
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sise
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sise
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sise
spec:
containers:
- name: sise
image: $imageRepo:demogeminiclient0.5.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: PORT
value: "9876"
- name: GEMINI_API_KEY
value: ""
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: service1
annotations:
health-check-ctrl: HLTHCK_ICMP
lb-algo: round-robin
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 1241
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9876
selector:
app: sise
sessionAffinity: None
EOF
kubectl apply -f service1.yaml
kubectl rollout status deployment sise- deploy service2
imageRepo="public.ecr.aws/t8s9q7q9/andy2024public"
cat << EOF | tee > service2.yaml
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: goweb
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: goweb
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: goweb
spec:
containers:
- name: goweb
image: $imageRepo:demogeminiclient0.5.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
env:
- name: PORT
value: "9876"
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: service2
annotations:
health-check-ctrl: HLTHCK_ICMP
lb-algo: round-robin
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 1242
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9876
selector:
app: goweb
sessionAffinity: None
EOF
kubectl apply -f service2.yaml
kubectl rollout status deployment goweb- Verify service
kubectl get ep service1
kubectl get ep service2you shall see output like
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
service1 10.224.0.22:9876 14s
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
service2 10.224.0.19:9876 6s11. Create ingress rule with yaml file
FortiWeb ingress controller is the default ingress controller, it will read and parse the ingress rule. the ingress controller will also read annotation from yaml file for some configuration parameters like fortiweb login ip and secrets etc., We will tell fortiweb ingress controller use fortiweb port1 ip for API access, and create VIP on fortiweb Port2, the VIP address is on same subnet with Port2 with last octet set to .100.
Use the script below to get fortiweb Port1 and Port2 IP address , then create yaml file with these IP address
output=$(ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname 'get system interface')
port1ip=$(echo "$output" | grep -A 7 "== \[ port1 \]" | grep "ip:" | awk '{print $2}' | cut -d'/' -f1)
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
port2ip=$(echo "$output" | grep -A 7 "== \[ port2 \]" | grep "ip:" | awk '{print $2}' | cut -d'/' -f1)
echo port2ip=$port2ip
vip=$(echo "$port2ip" | cut -d'.' -f1-3).100
else
vip=$(echo "$port1ip" | cut -d'.' -f1-3).100
fi
echo port1ip=$port1ip
echo vip=$vip- Create secret for fortiweb API access
the fortiweb Ingress controller require username and password to access fortiweb VM, therefore, we need to create a secret for fortiweb Ingress controller, the secret save username/password in base64 encoded strings which is more secure then plain text.
kubectl create secret generic fwb-login1 --from-literal=username=$fortiwebUsername --from-literal=password=$fortiwebPassword- Create ingress yaml file
Ingress Controller will read ingress object, then use the annotations to config fortiweb use API. “fwb-login1” is the secret that keep fortiweb VM username and password “virtual-server-ip” is the VIP to be configured on fortiweb In spec, we also define a rules with host set to port2 public ip dns name. if request url is /generate, the traffic will be redirect to service1 if request url is /info , the traffic will be redirect to service2
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
vipport="port2"
else
vipport="port1"
fi
cat << EOF | tee > 04_minimal-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: m
annotations: {
"fortiweb-ip" : $port1ip,
"fortiweb-login" : "fwb-login1",
"fortiweb-ctrl-log" : "enable",
"virtual-server-ip" : $vip,
"virtual-server-addr-type" : "ipv4",
"virtual-server-interface" :$vipport,
"server-policy-web-protection-profile" : "Inline Standard Protection",
"server-policy-https-service" : "HTTPS",
"server-policy-http-service" : "HTTP",
"server-policy-syn-cookie" : "enable",
"server-policy-http-to-https" : "disable"
}
spec:
ingressClassName: fwb-ingress-controller
rules:
- host: $fortiwebvmdnslabelport2
http:
paths:
- path: /generate
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: service1
port:
number: 1241
- path: /info
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: service2
port:
number: 1242
EOFNow you have 04_minimal-ingress.yaml file created.
you can go ahead to deploy this yaml file directly, but if you want monitor the activities of fortiweb Ingress Controller after apply this yaml file, you can do
kubectl logs -f -l app.kubernetes.io/name=fwb-k8s-ctrl -n fortiwebingress &
kubectl apply -f 04_minimal-ingress.yaml12. fortiweb Configuration
You will see now fortiweb has configured a few thingss.
- VIP config on Port2
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname 'get system vip'- Server-policy policy
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname show server-policy policy - Server Policy Vserver
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname show server-policy vserver - server-policy server pool
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname show server-policy server-pool- server-policy http-content-routing-policy
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i ~/.ssh/$rsakeyname show server-policy http-content-routing-policy13. Verify ingress rule
Verify the ingress rule created on k8s
kubectl get ingressCreate test pod
cat << EOF | tee > clientpod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: clientpod
labels:
app: clientpod
spec:
containers:
- name: clientpod
image: praqma/network-multitool
EOF
kubectl apply -f clientpod.yamlVerify nodePort svc
Since fortiweb VM is outside of cluster, fortiweb will use AKS nodePort to reach backend application. Therefore the backend application has exposed via NodePort Svc , the client pod shall able to reach backend application via nodePort. So does fortiweb VM.
nodePort=$(kubectl get svc service1 -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}')
kubectl exec -it po/clientpod -- curl http://$nodeIp:$nodePort/info and
ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" azureuser@$vm_name -i $HOME/.ssh/$rsakeyname execute curl http://$nodeIp:$nodePort/infoYou will see output like
MyfortiwebVM # % Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0* Trying 10.224.0.10:30890...
* Connected to 10.224.0.10 (10.224.0.10) port 30890
> GET /info HTTP/1.1
> Host: 10.224.0.10:30890
> User-Agent: curl/8.4.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json
< Date: Tue, 25 Jun 2024 01:59:56 GMT
< Content-Length: 20
<
{ [20 bytes data]
100 20 100 20 0 0HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Tue, 25 Jun 2024 01:59:56 GMT
Content-Length: 20
{"version":"0.6.0"}
5333 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 6666
* Connection #0 to host 10.224.0.10 left intact14. Create secondary ip and associate with public ip
This is to create an IP to use as VIP on fortiweb and associate with a public ip for external access, when run fortiweb with twoarms mode the secondary ip is on NIC2 , when in onearm mode, the secondary ip is on NIC1.
if [ "$fortiwebdeploymode" == "twoarms" ]; then
vipnicname="NIC2"
else
vipnicname="NIC1"
fi
az network public-ip create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--name FWBPublicIPPort2 \
--allocation-method Static \
--sku Standard \
--dns-name $fortiwebvmdnslabelport2
# Add a secondary IP configuration to NIC2
az network nic ip-config create \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--nic-name $vipnicname \
--name ipconfigSecondary \
--private-ip-address $secondaryIp \
--public-ip-address FWBPublicIPPort2- Verify the secondary IP address
az network nic show \
--resource-group $resourceGroupName \
--name $vipnicname \
--query "ipConfigurations[]" \
--output tableYou will see output like
in twoarms mode
Name Primary PrivateIPAddress PrivateIPAddressVersion PrivateIPAllocationMethod ProvisioningState ResourceGroup
----------------- --------- ------------------ ------------------------- --------------------------- ------------------- ---------------------
ipconfig1 True 10.0.2.4 IPv4 Dynamic Succeeded k8s51-k8s101-workshop
ipconfigSecondary False 10.0.2.100 IPv4 Static Succeeded k8s51-k8s101-workshopin onearm mode
Name Primary PrivateIPAddress PrivateIPAddressVersion PrivateIPAllocationMethod ProvisioningState ResourceGroup
----------------- --------- ------------------ ------------------------- --------------------------- ------------------- ---------------------
ipconfig1 True 10.0.1.4 IPv4 Dynamic Succeeded k8s51-k8s101-workshop
ipconfigSecondary False 10.0.1.100 IPv4 Static Succeeded k8s51-k8s101-workshopVerify connectivity to fortiweb VIP FortiWeb has VIP configured which it’s an alias of NIC2 interface(in twoarms mode) or NIC1 (in onearm mode). from client pod, you shall able to ping it.
kubectl exec -it po/clientpod -- ping -c 5 $secondaryIpReach ingress rule via fortiweb reverse proxy on VIP
Because fortiweb has configured with reverseProxy on VIP with ingress rule. client pod shall able to access url via fortiweb.
We have add “Host: $svcdnsname” in HTTP request Host header, as this is required in the ingress rule definition. the target application is gemini AI client. so we can send request data with your “prompt”.
kubectl exec -it po/clientpod -- curl -v -H "Host: $svcdnsname" http://$secondaryIp:80/generate -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"prompt": "hi"}' | grep "HTTP/1.1 200 OK"you shall get the response from backend server like this , which indicate you do not have Token for use gemini yet.
Access ingress service via external public ip or dns name
kubectl exec -it po/clientpod -- curl http://$svcdnsname/info 15. Clean up:
Warning
Only run this step if you want to start over the deployment, if not please continue to next section.
- delete all resource
if you want startover again, you can delete all resource then redo the installation
resources=$(az resource list -g $resourceGroupName --query "[].{name:name, type:type}" -o tsv)
az resource list -g $resourceGroupName -o table
echo delete aks cluster
az aks delete --name $aksClusterName -g $resourceGroupName
echo delete fortiweb vm
az vm delete --name MyfortiwebVM -g $resourceGroupName
echo delete nic
az network nic delete --name NIC1 -g $resourceGroupName
az network nic delete --name NIC2 -g $resourceGroupName
echo delete public ip
az network public-ip delete --name FWBPublicIP -g $resourceGroupName
az network public-ip delete --name FWBPublicIPPort2 -g $resourceGroupName
echo delete fortiwebvm disk
disks=$(az disk list -g $resourceGroupName --query "[].name" -o tsv)
for disk in $disks; do
az disk delete --name $disk --resource-group $resourceGroupName
done
echo delete NSG
az network nsg delete --name MyNSG --resource-group $resourceGroupName
echo delete vnet
az network vnet delete --name $vnetName -g $resourceGroupName
az network vnet delete --name $aksVnetName -g $resourceGroupName
az resource list -g $resourceGroupName -o table
rm ~/.kube/config
ssh-keygen -R $vm_name