Sql injection
The first attack will be a SQLi attack. Please use Chrome browser to best follow the insrtuctions.
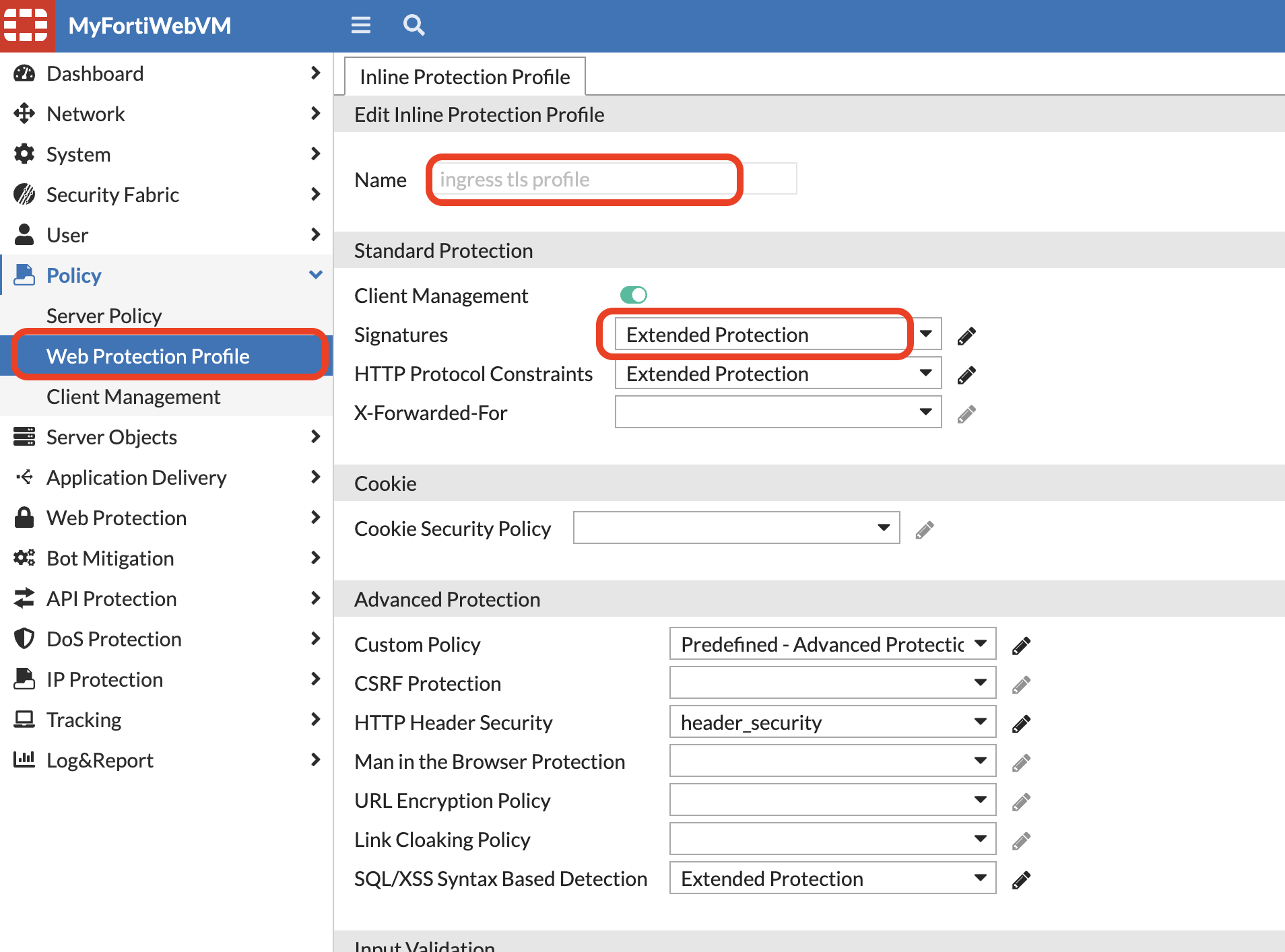
FortiWeb ingress TLS protection profile already has Extended protection enabled for Signature based protection, so we can just continue to do an attack.
- Proceed with the Attack!
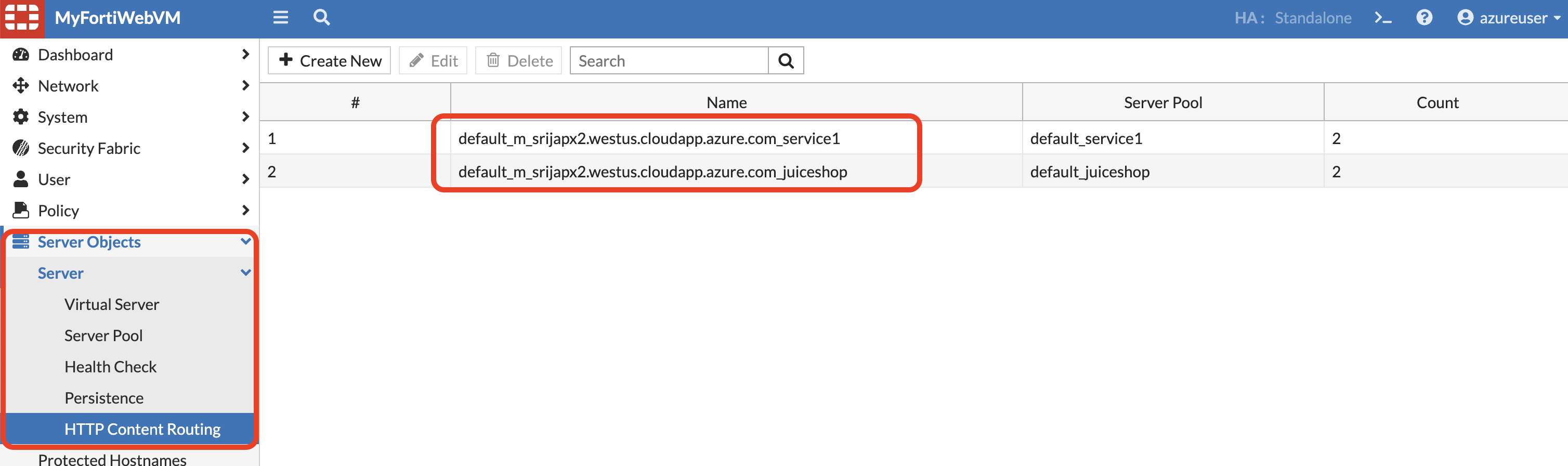
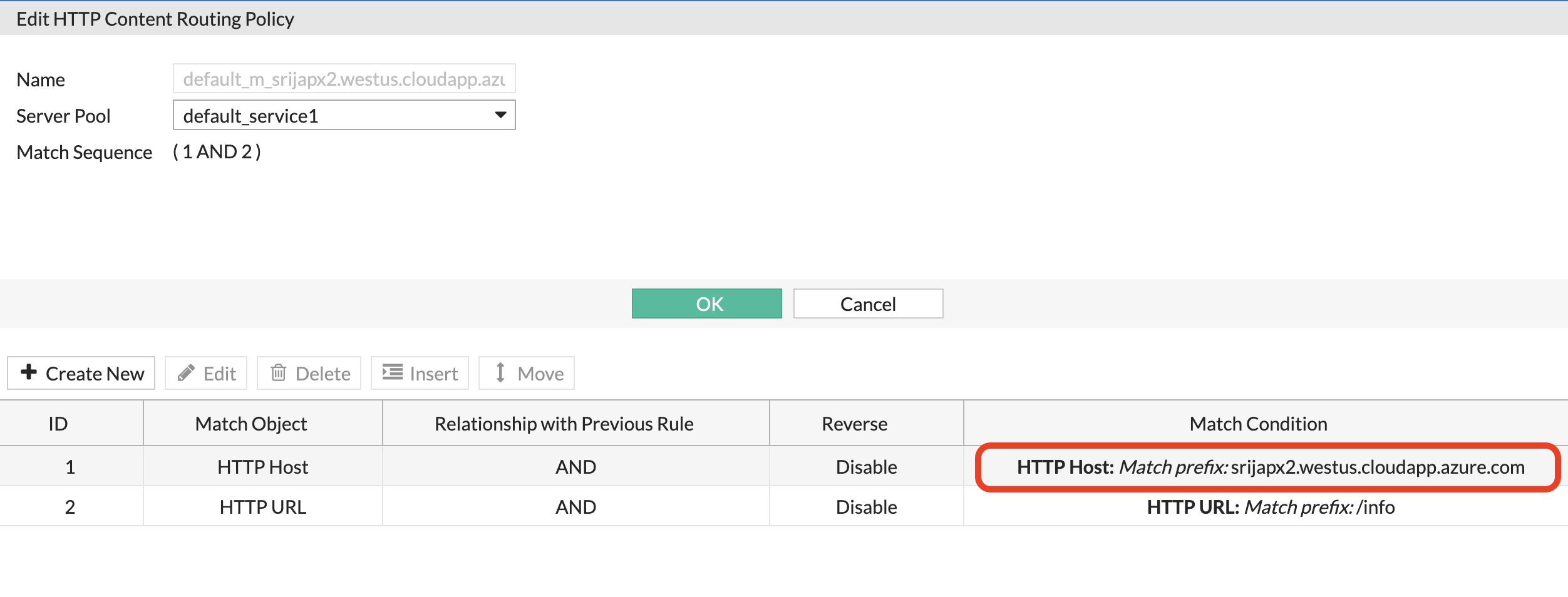
- To get the Juiceshop hostname, on FortiWeb > Server Objects > Server > HTTP Content Routing > click on one of the content routing policy.
Copy the hostname and enter it into your Chrome browser, followed by ‘/’ prefix.
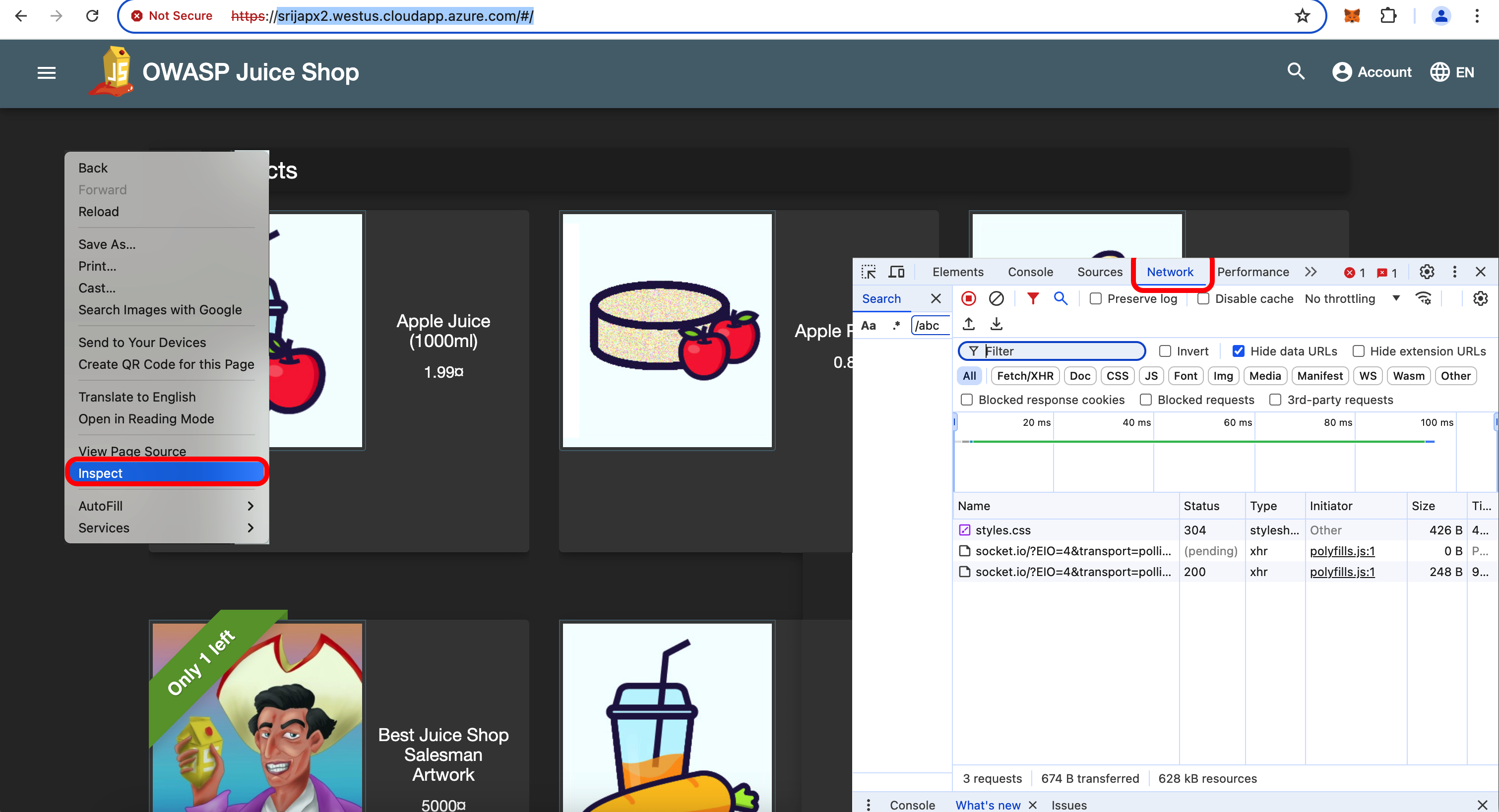
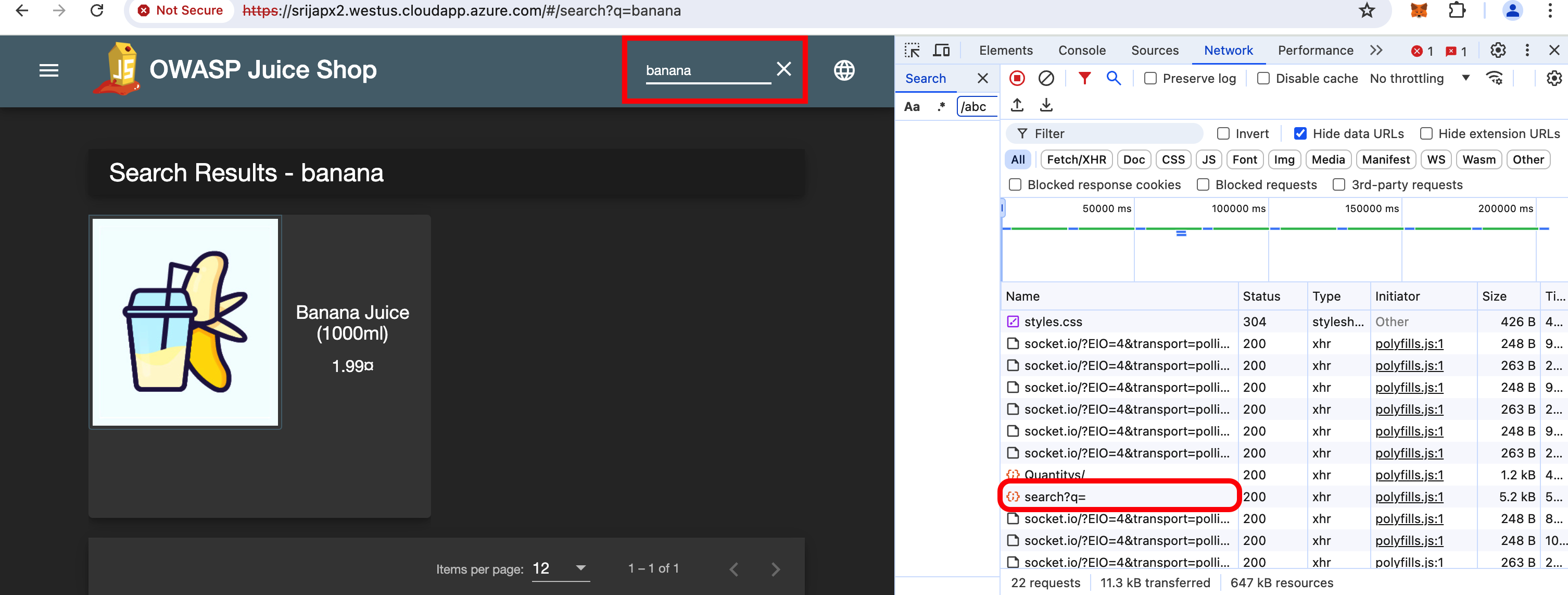
- While viewing the network settings, In the Juiceshop search tab, search for “banana” or “apple” and hit enter.
- You will see a search?q= request in the network tab.
Click on that request to see more information about headers, cookies etc.
Notice the backend Request URL, status code, Request method etc. This request URL is the backend URL to the express API of the juiceshop app and this is how attackers inject malicious input to extract data from DB.
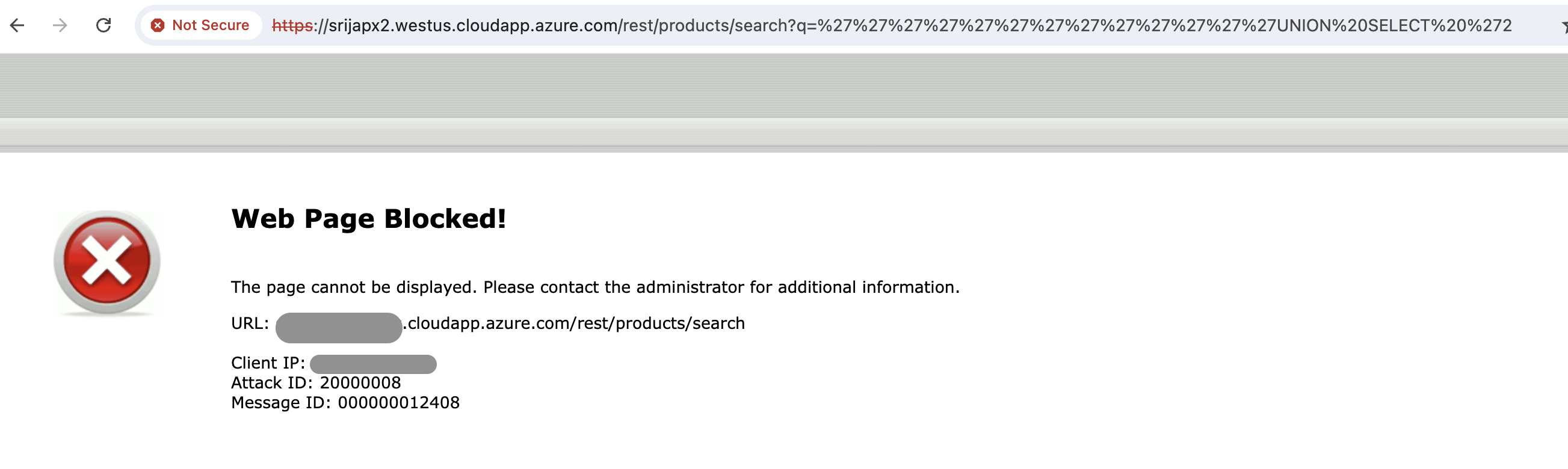
Copy this URL and paste into a browser. do not hit enter yet
- You will see a search?q= request in the network tab.
Repeat the same attack with another payload.
<script>$('input').value="';DELETE FROM USERS;--";$('form').submit()</script>
example:
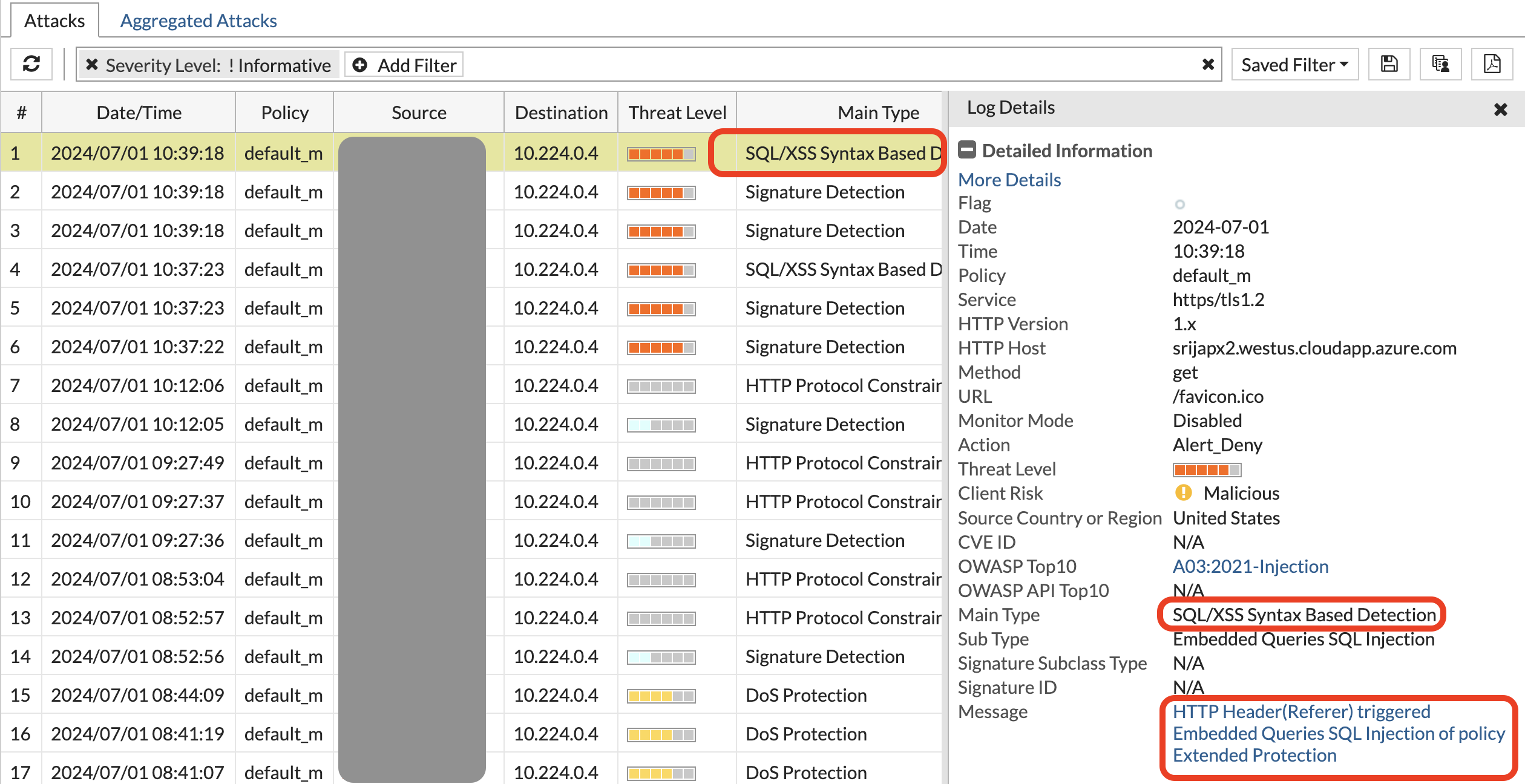
"https://srijapx2.westus.cloudapp.azure.com/rest/products/search?q=<script>$('input').value="';DELETE FROM USERS;--";$('form').submit()</script>"We will see block page again but find out from the attack log what attack this is.
Q & A
- What attack was triggered in step 6?
- How are signatures helping to block these OWASP TOP 10 attacks?